Abstract
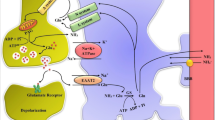
While the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy (HE) remains elusive, there is considerable evidence pointing to a key role of ammonia-induced dysfunction of astrocytes in this condition. Deficits in the ability of astrocytes to take up glutamate from the extracellular space may lead to abnormal glutamatergic neurotransmission. Furthermore, excessive stimulation of neuronal and glial glutamate receptors by elevated extracellular levels of glutamate may lead to excitotoxicity and greater glial dysfunction. Ammonia also causes upregulation of astroglial peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptors (PBRs) which is associated with increased production of neurosteroids. These neurosteroids have potent positive modulatory effects on the neuronal GABAA receptor which, combined with an ammonia-induced astroglial defect in GABA uptake, may result in enhanced GABAergic tone. Brain edema, associated with fulminant hepatic failure, may also result from astroglial abnormalities as the edema appears to be principally caused by swelling of these cells. Increased amounts of glutamine in astrocytes resulting from elevated brain ammonia levels may be a factor in this swelling. Other osmolytes such as glutathione may also be involved. Glial swelling may also result from NH4 +- and K+-mediated membrane depolarization as well as by the actions of PBR agonists and neurosteroids. These findings show that an ammonia-induced gliopathy is a major factor in the pathogenesis of HE.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Aguila-Mansilla, N., Bender, A.S., Petito, C.K. and Norenberg, M.D. (1997). Effect of neurosteroids on glutamate uptake in cultured rat astrocytes. Soc. Neurosci. Abstr. 23:1462.
Aguila-Mansilla, N., Bender, A.S. and Norenberg, M.D. (1998). Effect of ammonia, peripheral benzodiazepine ligands and neurosteroids on GABA uptake in cultured astrocytes. J. Neurochem. 70Suppl 1 S28
Albrecht, J., Hilgier, W., Lazarewicz, J.W., Rafalowska, U. and Wysmyk-Cybula, U. (1988). Astrocytes in acute hepatic encephalopathy: metabolic properties and transport functions. In (M.D. Norenberg, L. Hertz and A. Schousboe, eds.), The Biochemical Pathology of Astrocytes, Alan R. Liss, New York, pp. 465–476.
Albrecht, J., Bender, A.S. and Norenberg, M.D. (1994). Ammonia stimulates the release of taurine from cultured astrocytes. Brain Res. 660:288–292.
Albrecht, J. (1998). Roles of neuroactive amino acids in ammonia neurotoxicity. J. Neurosci. Res. 51:133–138.
Albrecht, J. and Faff, L. (1994). Astrocyte-neuron interactions in hyperammonemia and hepatic encephalopathy. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 368:45–54.
Albrecht, J. and Norenberg, M.D. (1990). L-Methionine-DL-sulfoximine induces massive efflux of glutamine from cortical astrocytes in primary culture. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 182:587–590.
Allert, N., Köller, H. and Siebler, M. (1998). Ammonia-induced depolarization of cultured rat cortical astrocytes. Brain Res. 782:261–270.
Anholt, R.R.H., Pedersen, P.L., DeSouza, E.B. and Snyder, S.H. (1986). The peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptor: localization to the mitochondrial outer membrane. J. Biol. Chem. 261:576–583.
Arouma, O.I., Halliwell, B., Hoey, B.Y., and Butler, J. (1988). The antioxidant action of taurine, hypotaurine and their metabolic precursors. Biochem. J. 256:251–255.
Backus, K.H., Kettenmann, H. and Schachner, M. (1989). Pharmacological characterization of the glutamate receptor in cultured astrocytes. J. Neurosci. Res. 22:274–282.
Basile, A.S., Jones, E.A. and Skolnick, P. (1991). The pathogenesis and treatment of hepatic encephalopathy: evidence for the involvement of benzodiazepine receptor ligands. Pharmacol. Rev. 43:27–71.
Basile, A.S. and Jones, E.A. (1997). Ammonia and GABA-ergic neurotransmission: Interrelated factors in the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 25: 1303–1305.
Bender, A.S., Dombro, R.S. and Norenberg, M.D. (1998a). Glutathione as a factor in ammonia-induced swelling. Soc. Neurosci. Abstr. 24:2013.
Bender, A.S., Schousboe, A., Reichelt, W. and Norenberg, M.D. (1998b). Ionic mechanisms in glutamate-induced astrocyte swelling: Role of K+ influx. J. Neurosci. Res. 52:307–321.
Bender, A.S. and Hertz, L. (1985). Binding of (3H) R05-4864 in primary cultures of astrocytes. Brain Res. 341:41–9.
Bender, A.S. and Norenberg, M.D. (1993). Effects of ammonia and L-methionine-DL-sulfoximine on K+ and Cl− fluxes in cultured astrocytes. Soc. Neurosci. Abstr. 19:688.
Bender, A.S. and Norenberg, M.D. (1994a). Ammonia enhances inhibitory effects of benzodiazepines and neurosteroids on K+ influx in astrocytes. Soc. Neurosci. Abstr. 20:1502.
Bender, A.S. and Norenberg, M.D. (1994b). Calcium dependence of hypoosmotically induced potassium release in cultured astrocytes. J. Neurosci. 14:4237–4243.
Bender, A.S. and Norenberg, M.D. (1996). Effects of ammonia on L-glutamate uptake in cultured astrocytes. Neurochem. Res. 21:567–573.
Bender, A.S. and Norenberg, M.D. (1998). Effect of benzodiazepines and neurosteroids on ammonia-induced swelling in cultured astrocytes. J. Neurosci. Res. 54:673–680.
Benjamin, A.M., Okamoto, K. and Quastel, J.H. (1978). Effects of ammonium ions on spontaneous action potentials and on contents of sodium, potassium, ammonium and chloride ions in brain in vitro. J. Neurochem. 30:131–143.
Binstock, L. and Lecar, H. (1969). Ammonium ion currents in the squid giant axon. J. Gen. Physiol. 53:342–361.
Blei, A.T. (1991). Cerebral edema and intracranial hypertension in acute liver failure: distinct aspects of the same problem. Hepatology 13:376–379.
Blei, A.T., Olafsson, S., Therrien, G. and Butterworth, R.F. (1994). Ammonia-induced brain edema and intracranial hypertension in rats after portacaval anastomosis. Hepatology 19:1437–1444.
Bosman, D.K., Deutz, N.E., de Graaf, A.A., van Eijk, H.M., Bovee, W.M., Maas, M.A., Jorning, G.G. and Chamuleau, R.A. (1990). Changes in brain metabolism during hyperammonemia failure: results of a comparative 1H-NMR spectroscopy and biochemical investigation. Hepatology 12:281–290.
Boyarsky, G., Ransom, B.R., Schlue, W.R., Davis, M.B. and Boron, W.F. (1993). Intracellular pH regulation in single cultured astrocytes from rat forebrain. Glia 8:241–248.
Bruce, J.H., Neary, J.T., Itzhak, Y. and Norenberg, M.D. (1995). Ammonia inhibits the metabotropic glutamate receptor in cultured astrocytes. Soc. Neurosci. Abstr. 21:1081
Brusilow, S.W. and Traystman, R.J. (1986). Letter to editor. New Engl. J. Med. 314:786
Burg, M.B. (1995). Molecular basis of osmotic regulation. Am. J. Physiol. 268:F9983–F9996.
Busa, W.B. and Nuccitelli, R. (1984). Metabolic regulation via intracellular pH. Amer. J. Physiol. 246:R409
Butterworth, R.F. (1991). Pathophysiology of hepatic encephalopathy; the ammonia hypothesis revisited. In (F. Bengtsson, B. Jeppsson, T. Almdal and H. Vilstrup, eds.) Progress in Hepatic Encephalopathy and Metabolic Nitrogen Exchange, CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp. 9–24.
Butterworth, R.F. (1997). Hepatic encephalopathy and brain edema in acute hepatic failure: Does glutamate play a role?. Hepatology 25:1032–1034.
Chesler, M. and Kaila, K. (1992). Modulation of pH by neuronal activity. Trends Neurosci. 15:396–402.
Cooper, A.J.L. and Plum, F. (1987). Biochemistry and physiology of brain ammonia. Physiol. Rev. 67:440–519.
Córdoba, J. and Blei, A.T. (1996). Brain edema and hepatic encephalopathy. Semin. Liver Dis. 16:271–280.
Córdoba, J., Gottstein, J. and Blei, A.T. (1996). Glutamine, myo-inositol, and organic brain osmolytes after portacaval anastomosis in the rat: Implications for ammonia-induced brain edema. Hepatology 24:919–923.
Danbolt, N.C., Storm-Mathisen, J. and Kanner, B.I. (1992). An [Na+ + K+] coupled L-glutamate transporter purified from brain is located in glial cell processes. Neuroscience 51:295–310.
De Knegt, R.J., Schalm, S.W., Van Der Rijt, C.C.D., Fekkes, D., Dalm, E. and Hekking-Weyma, I. (1994). Extracellular brain glutamate during acute liver failure and during acute hyperammonemia simulating acute liver failure: An experimental study based on in vivo brain dialysis. J. Hepatol. 20:19–26.
Dejong, C.H., Kampman, M.T., Deutz, N.E. and Soeters, P.B. (1992). Cerebral cortex ammonia and glutamine metabolism during liver insufficiency-induced hyperammonemia in the rat. J. Neurochem. 59:1071–1079.
DeLorey, T.M. and Olsen, R.W. (1994). GABA and glycine. In (G.J. Siegel, B.W. Agranoff, R.W. Albers and P.B. Molinoff, eds.) Basic Neurochemistry, Raven Press, New York, 5th edition:pp. 389–399.
Dermietzel, R., Hertzberg, E.L., Kessler, J.A. and Spray, D.C. (1991). Gap junctions between cultured astrocytes: Immunocytochemical, molecular, and electrophysiological analysis. J. Neurosci. 11:1421–1432.
Dombro, R.S., Bender, A.S., Hutson, D.G. and Norenberg, M.D. (1995). Intracellular glutamine as a factor in ammonia-induced swelling. Soc. Neurosci. Abstr. 21:1081
Ede, R.J. and Williams, R. (1986). Hepatic encephalopathy and cerebral edema. Semin. Liver Dis. 6:107–118.
Eng, L.F. (1985). Glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP): the major protein of glial intermediate filaments in differentiated astrocytes. J. Neuroimmunol. 8:203–214.
Enkvist, M.O.K. and McCarthy, K.D. (1992). Activation of protein kinase C blocks astroglial gap junction communication and inhibits the spread of calcium waves. J. Neurochem. 59:519–526.
Fischer, G. and Kettenmann, H. (1985). Cultured astrocytes form a syncitium after maturation. Exp. Cell Res. 159:273–279.
Fitzpatrick, S.M., Cooper, A.J. and Hertz, L. (1988). Effects of ammonia and beta-methylene-DL-aspartate on the oxidation of glucose and pyruvate by neurons and astrocytes in primary culture. J. Neurochem. 51:1197–1203.
Ganz, R., Swain, M., Traber, P., Dal Canto, M.C., Butterworth, R.F. and Blei, A.T. (1989). Ammonia-induced swelling of rat cerebral cortical slices: implications for the pathogenesis of brain edema in acute hepatic failure. Metab. Brain Dis. 4:213–223.
Garcia, J.H., Liu, K.F., Yoshida, Y., Chen, S. and Lian, J. (1994). The brain microvessels: factors altering their patency after the occlusion of a middle cerebral artery (Wistar rat). Am. J. Pathol. 145:1–13.
Gegelashvili, G. and Schousboe, A. (1997). High affinity glutamate transporters: regulation of expression and activity. Mol. Pharmacol. 52:6–15.
Giguere, J.F., Hamel, E. and Butterworth, R.F. (1992). Increased densities of binding sites for the “peripheraltype” benzodiazepine receptor ligand [3H]PK 11195 in rat brain following portacaval anastomosis. Brain Res. 585:295–298.
Haghighat, N. and McCandless, D.W. (1997). Effect of ammonium chloride on energy metabolism of astrocytes and C6-glioma cells in vitro. Metab. Brain Dis. 12:287–298.
Hamberger, A., Lindroth, B. and Nystrom, B. (1982). Regulation of glutamate biosynthesis and release in vitro by low levels of ammonium ions. Brain Res. 237:339–350.
Hansson, E. and Rönnbäck, L. (1995). Astrocytes in glutamate neurotransmission. FASEB J. 9:343–350.
Häussinger, D. (1996). The role of cellular hydration in the regulation of cell function. Biochem. J. 313:697–710.
Häussinger, D., Laubenberger, J., Vom Dahl, S., Ernst, T., Bayer, S., Langer, M., Gerok, W. and Hennig, J. (1994). Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy studies on human brain myo-inositol in hypo-osmolarity and hepatic encephalopathy. Gastroenterology 107:1475–1480.
Häussinger, D., Warskulat, U. and Schliess, F. (1997). Osmosignalling and osmolytes in liver and astrocytes. In (V. Felipo and A. Grisolia, eds.) Advances in Cirrhosis, Hyperammonemia, and Hepatic Encephalopathy, Plenum, New York, pp. 195–215.
Hazell, A.S. and Norenberg, M.D. (1997). Manganese decreases glutamate uptake in cultured astrocytes. Neurochem. Res. 22:1443–1447.
Hertz, L., Murthy, C.R.K., Lai, J.C.K., Fitzpatrick, S.M. and Cooper, A.J.L. (1987). Some metabolic effects of ammonia on astrocytes and neurons in primary culture. Neurochem. Pathol. 6:97–129.
Hertz, L., Juurlink, B.H.J. and Szuchet, S. (1994). Cell cultures. In (A. Lajtha, ed.), Handbook of Neurochemistry, Plenum Press, New York, 2nd edition: pp. 603–661.
Hindfelt, B., Plum, F. and Duffy, T.E. (1977). Effect of acute ammonia intoxication on cerebral metabolism in rats with portacaval shunts. J. Clin. Invest. 59:386–396.
Hoffmann, E.K. and Dunham, P.B. (1996). Membrane mechanisms and intracellular signalling in cell volume regulation. Internat. Rev. Cytol. 161:173–262.
Horowitz, M.E., Schafer, D.F., Molnar, P. et al. (1983). Increased blood-brain transfer in a rabbit model of acute liver failure. Gastroenterology 84:1003–1011.
Inoue, E., Hori, S., Narumi, Y., Fujita, M., Kuriyama, K., Kadota, T. and Kuroda, C.H. (1991). Portal-systemic encephalopathy: presence of basal ganglia lesions with high signal intensity on MRI images. Radiology 179:551–555.
Isaacks, R.E., Bender, A.S. and Norenberg, M.D. (1995). Rate of myo-inositol uptake and its content in primary astrocyte cultures after exposure to ammonia. J. Neurochem. 64(Suppl):66
Isaacks, R.E., Bender, A.S., Kim, C.Y., Shi, Y.F. and Norenberg, M.D. (1998). Effect of ammonia and methionine sulfoximine on myo-inositol uptake in cultured astrocytes. Neurochem. Res. (In Press)
Itzhak, Y., Baker, L. and Norenberg, M.D. (1993). Characterization of the peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptor in cultured astrocytes: evidence for multiplicity. Glia 9:211–218.
Itzhak, Y., Roig-Cantisano, A., Dombro, R.S. and Norenberg, M.D. (1995). Acute liver failure and hyperammonemia increase peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptor binding and pregnenolone synthesis in mouse brain. Brain Res. 705:345–348.
Itzhak, Y. and Norenberg, M.D. (1994a). Ammonia-induced upregulation of peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptors in cultured astrocytes labeled with [3H]PK 11195. Neurosci. Lett. 177:35–38.
Itzhak, Y. and Norenberg, M.D. (1994b). Attenuation of ammonia toxicity in mice by PK 11195 and pregnenolone sulfate. Neurosci. Lett. 182:251–254.
Jakubovicz, D.E., Grinstein, S. and Klip, A. (1987). Cell swelling following recovery from acidification in C6 glioma cells: an in vitro model of postischemic brain edema. Brain Res. 435:138–146.
James, J.H., Jeppsson, B., Ziparo, V. and Fischer, J.E. (1979). Hyperammonemia, plasma amino acid imbalance, and blood-brain amino acid transport: a unified theory of portal-systemic encephalopathy. Lancet ii:772–775.
Jessy, J., Mans, A.M., DeJoseph, M.R. and Hawkins, R.A. (1990). Hyperammonaemia causes many of the changes found after portacaval shunting. Biochem. J. 272:311–317.
Kempski, O., Staub, F., Jansen, M. and Baethmann, A. (1990). Molecular mechanisms of glial cell swelling in acidosis. Adv. Neurol. 52:39–45.
Kettenmann, H., Ransom, B.R. (eds.) (1995). Neuroglia, New York: Oxford.
Kikeri, D., Sun, A., Zeidel, M.L. and Hebert, S.C. (1989). Cell membranes impermeable to NH3. Nature 339:478–480.
Kimelberg, H. (1983). Primary astrocyte cultures — a key to astrocyte function. Cell. Molec. Neurobiol. 3:1–16.
Kimelberg, H.K., Goderie, S.K., Higman, S., Pang, S. and Waniewski, R.A. (1990). Swelling-induced release of glutamate, aspartate, and taurine from astrocyte cultures. J. Neurosci. 10:1583–1591.
Knecht, K., Michalak, A., Rose, C., Rothstein, J.D. and Butterworth, R.F. (1997). Decreased glutamate transporter (GLT-1) expression in frontal cortex of rats with acute liver failure. Neurosci. Lett. 229:201–203.
Knepper, M.A., Packer, R. and Good, D.W. (1989). Ammonium transport in the kidney. Physiol. Rev. 69:179–249.
Kondo, K., Sashimoto, H., Kitanaka, J., Sawada, M., Suzumura, A., Marunouchi, T. and Baba, A. (1995). Expression of glutamate transporters in cultured glial cells. Neurosci. Lett. 188:140–142.
Kosenko, E., Kaminsky, M., Kaminsky, A., Valencia, M., Lee, L., Hermenegildo, C. and Felipo, V. (1997). Superoxide production and antioxidant enzymes in ammonia intoxication in rats. Free Radic. Res. 27:637–644.
Kreis, R., Ross, B.D., Farrow, N.A. and Ackerman, Z. (1992). Metabolic disorders of the brain in chronic hepatic encephalopathy detected with H-1 MR spectroscopy. Radiology 182:19–27.
Krieger, D., Krieger, S., Jansen, O., Gass, P., Theilmann, L. and Lichtnecker, H. (1995). Manganese and chronic hepatic encephalopathy. Lancet 346:270–274.
Kulisevsky, J., Pujol, J., Balanzo, J., Junque, C., Deus, J., Capdevila, A. and Villanueva, C. (1993). Pallidal hyperintensity on magnetic resonance imaging in cirrhotic patients: clinical correlations. Neurology 16:1382–1388.
Kuriyama, K. (1980). Taurine as an neuromodulator. Fed. Proc. 39:2680–2684.
Lambert, J.J., Belelli, D., Hill-Venning, C. and Peters, J.A. (1995). Neurosteroids and GABA-A receptor function. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 16:295–303
Latorre, R. and Miller, C. (1983). Conduction and selectivity in potassium channels. J. Memb. Biol. 71:11–30.
Lavoie, J., Giguere, J.F., Layrargues, G.P. and Butterworth, R.F. (1987). Amino acid changes in autopsied brain tissue from cirrhotic patients with hepatic encephalopathy. J. Neurochem. 49:692–697.
Lavoie, J., Layrargues, G.P. and Butterworth, R.F. (1990). Increased densities of peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptors in brain autopsy samples from cirrhotic patients with hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatology 11:874–878.
Levy, L.M., Lehre, K.P., Rolstad, B. and Danbolt, N.C. (1993). A monoclonal antibody raised against an [Na+ + K+] coupled L-glutamate transporter purified from rat brain confirms glial cell localization. FEBS Lett. 317:79–84.
Marcaida, G., Felipo, V., Hermeneglido, C., Miñana, M.-D. and Grisolía, S. (1992). Acute ammonia toxicity is mediated by the NMDA type of glutamate receptors. FEBS Lett. 296:67–68.
Mena, E.E. and Cotman, C.W. (1985). Pathologic concentrations of ammonium ions block L-glutamate uptake. Exp. Neurol. 89:259–263.
Moroni, F., Lombardi, G., Moneti, G. and Cortesini, C. (1983). The release and the neosynthesis of glutamic acid are increased in experimental models of hepatic encephalopathy. J. Neurochem. 40:850–854.
Mousseau, D.D. and Butterworth, R.F. (1994). Current theories on the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 206:329–344.
Murthy, C.R. and Hertz, L. (1987). Acute effect of ammonia on branched-chain amino acid oxidation and incorporation into proteins in astrocytes and in neurons in primary cultures. J. Neurochem. 49:735–41.
Myers, R., Manjil, L.G., Cullen, B.M., Price, G.W., Franckowiak, R.S. and Cremer, J.E. (1991). Macrophage and astrocyte populations in relation to (3H)PK 11195 binding following a local ischemic lesion. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 11:314–322.
Nagaraja, T.N. and Brookes, N. (1998). Intracellular acidification induced by passive and active transport of ammonium ions in astrocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 274:C883–C891.
Norenberg, M.D. (1981). The astrocyte in liver disease. In (S. Fedoroff and L. Hertz, eds.), Advances in Cellular Neurobiology, Vol. 2, Academic Press, New York, pp. 303–352.
Norenberg, M.D. (1983). Immunohistochemistry of glutamine synthetase. In (L. Hertz, E. Kvamme, E.G. McGeer and A. Schousboe, eds.) Glutamine, glutamate, and GABA in the Central Nervous System, Alan R. Liss, New York, pp. 95–111.
Norenberg, M.D., Mozes, L.W. and Papendick, R.E. (1985). Effect of ammonia on glutamate, GABA and rubidium uptake by astrocytes. Ann. Neurol. 18:149
Norenberg, M.D., Mozes, L.W., Norenberg, L.-O.B. and Gregorios, J.B. (1986). Effects of ammonia in primary astrocyte cultures: morphological and biochemical considerations. In (T. Grisar, G. Franck, L. Hertz, W.T. Norton, M. Sensenbrenner and D.M. Woodbury, eds.) Dynamic Properties of Glia Cells II: Cellular and Molecular Aspects, Pergamon Press, Oxford, pp. 353–362.
Norenberg, M.D. (1989). The use of cultured astrocytes in the study of hepatic encephalopathy. In (R.F. Butterworth and G. Pomier Layrargues, eds.) Hepatic Encephalopathy. Pathophysiology and Treatment, Humana Press, Clifton, N.J. pp. 215–229.
Norenberg, M.D., Baker, L., Norenberg, L.-O.B., Blicharska, J., Bruce-Gregorios, J.H. and Neary, J.T. (1991). Ammonia-induced astrocyte swelling in primary culture. Neurochem. Res. 16:833–836.
Norenberg, M.D. (1993). Astroglial response to liver failure. In (S. Fedoroff, B.H.J. Juurlink and R. Doucette, eds.) Biology and Pathology of Astrocyte-Neuron Interactions, Plenum Press, New York, pp. 405–416.
Norenberg, M.D. (1995). Hepatic encephalopathy. In (H. Kettenmann and B.R. Ransom, eds.), Neuroglia, Oxford, New York, pp. 950–963.
Norenberg, M.D., Isaacks, R.E., Dombro, R.S. and Bender, A.S. (1995a). Prevention of ammonia-induced toxicity in astrocytes by L-methionine-DL-sulfoximine. In (L. Capocaccia, M. Merli and O. Riggio, eds.) Advances in Hepatic Encephalopathy and Metabolic Nitrogen Exchange, CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp. 176–180.
Norenberg, M.D., Roig-Cantisano, A. and Itzhak, Y. (1995b). Peripheral benzodiazepine receptors and pregnenolone synthesis in models of hepatic encephalopathy and in ammonia-treated astrocytes. J. Neurochem. 64(Suppl):56
Norenberg, M.D., Huo, Z., Neary, J.T. and Roig-Cantisano, A. (1997a). The glial glutamate transporter in hyperammonemia and hepatic encephalopathy: relation to energy metabolism and glutamatergic neurotransmission. Glia 21:124–133.
Norenberg, M.D., Itzhak, Y. and Bender, A.S. (1997b). The peripheral benzodiazepine receptor and neurosteroids in hepatic encephalopathy. In (V. Felipo, ed.) Cirrhosis, Hyperammonemia, and Hepatic Encephalopathy, Plenum Press, pp. 95–111
Norenberg, M.D. (1998). Astrocyte pathophysiology in disorders of the central nervous system. In (H.M. Schipper, ed.) Astrocytes in Brain Aging and Neurodegeneration, R.G. Landes, Georgetown, TX, pp. 41–68.
Norenberg, M.D., Bender, A.S. and Vastag, M. (1998). Effect of ammonia on intracellular pH in cultured astrocytes and endothelial cells. Soc. Neurosci. Abstr. 24:2013.
Norenberg, M.D. and Bender, A.S. (1994). Astrocyte swelling in liver failure: role of glutamine and benzodiazepines. Acta Neurochir. 60(Suppl):24–27.
Oja, S.S., Saransaari, P., Wysmyk, U. and Albrecht, J. (1993). Loss of GABA-B binding sites in the cerebral cortex of rats with acute hepatic encephalopathy. Brain Res. 629:355–357.
Oppong, K.N.W., Bartlett, K., Record, C.O. and Al Mardini, H. (1995). Synaptosomal glutamate transport in thioacetamide-induced hepatic encephalopathy in the rat. Hepatology 22:553–558.
Papadopoulos, V. (1993). Peripheral-type benzodiazepine/diazepam binding inhibitor receptor: Biological role in steroidogenic cell function. Endocr. Rev. 14:222–240.
Park, C.H., Carboni, E., Wood, P.L. and Gee, K.W. (1996). Characterization of peripheral benzodiazepine type sites in a cultured murine BV-2 microglial cell line. Glia 16:65–70.
Parola, A.L., Yamamura, H.I. and Laird, H.E.J. (1993). Peripheral-type benzodiazepine receptors. Life Sci. 52:1329–1342.
Pearce, B. (1993). Amino acid receptors. In (S. Murphy, ed.) Astrocytes: Pharmacology and Function, Academic Press, San Diego, pp. 47–77.
Pileblad, E., Eriksson, P.S. and Hansson, E. (1991). The presence of glutathione in primary neuronal and astroglial cultures from rat cerebral cortex and brain stem. J. Neural. Transm. Gen. Sect. 86:43–49.
Pomier-Layrargues, G., Spahr, L. and Butterworth, R.F. (1995). Increased managanese concentrations in pallidum of cirrhotic patients. Lancet 345:735
Pope, A. (1978). Neuroglia: quantitative aspects. In (E. Schoffeniels, G. Franck, L. Hertz and D.B. Tower, eds.) Dynamic Properties of Glia Cells, Pergamon Press, London, pp. 13–20.
Robinson, M.B., Djali, S. and Buchhalter, J.R. (1993). Inhibition of glutamate uptake with L-trans-pytrolidine-2,4-dicarboxylate potentiates glutamate neurotoxicity in primary hippocampal cultures. J. Neurochem. 61:2099–2103.
Roos, A. and Boron, W.F. (1981). Intracellular pH. Physiol. Rev. 61:296–434.
Rothstein, A. and Mack, E. (1992). Volume-activated calcium uptake: Its role in cell volume regulation of Madin-Darby canine kidney cells. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 262:C339–C347.
Rothstein, J.D., Jin, L., Dykes-Hoberg, M. and Kuncl, R.W. (1993). Chronic inhibition of glutamate uptake produces a model of slow neurotoxicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90:6591–6595.
Rothstein, J.D., Martin, L., Levey, A.I., Dykes-Hoberg, M., Jin, L., Wu, D., Nash, N. and Kuncl, R.W. (1994). Localization of neuronal and glial glutamate transporters. Neuron 13:713–725.
Schlag, B.D., Vondrasek, J.R., Munir, M., Kalandadze, A., Zelenaia, O.A., Rothstein, J.D. and Robinson, M.B. (1998). Regulation of the glial Na+-dependent glutamate transporters by cyclic AMP analogs and neurons. Mol. Pharmacol. 53:355–369.
Schliess, F., Sinning, R., Fischer, R., Schmalenbach, C. and Häussinger, D. (1996). Calcium-dependent activation of Erk-1 and Erk-2 after hypo-osmotic astrocyte swelling. Biochem. J. 320:167–171.
Schmidt, W., Wolf, G., Grungreiff, K., Meier, M. and Reum, T. (1990). Hepatic encephalopathy influences high-affinity uptake of transmitter glutamate and aspartate into the hippocampal formation. Metab. Brain Dis. 5:19–31.
Schousboe, A., Drejer, J. and Hertz, L. (1988). Uptake and release of glutamate and glutamine in neurons and astrocytes in primary culture. In (E. Kvamme, ed.) Glutamine and Glutamate in Mammals, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, pp. 21–39.
Sherman, W.R. (1989). Inositol homeostasis, lithium and diabetes. In (R.H. Michell, A.H. Drummond and C.P. Downes, eds.) Inositol Lipids in Cell Signalling, Academic Press, London, pp. 39–79.
Smith, S.J. (1992). Do astrocytes process neural information? In (A.C.H. Yu, L. Hertz, M.D. Norenberg, E. Sykova and S. Waxman, eds.) Neuronal-Astrocytic Interactions: Implications for Normal and Pathological CNS Function, Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp. 119–136.
Sobel, R.A., DeArmond, S.J., Forno, L.S. and Eng, L.F. (1981). Glial fibrillary acidic protein in hepatic encephalopathy. An immunohistochemical study. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 40:625–632.
Strange, K. (1993). Maintenance of cell volume in the central nervous system. Pediatr. Nephrol. 7:689–697.
Sugimoto, H., Koehler, R.C., Wilson, D.A., Brusilow, S.W. and Traystman, R.J. (1997). Methionine sulfoximine, a glutamine synthetase inhibitor, attenuates increased extracellular potassium activity during acute hyperammonemia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 17:44–49.
Swanson, R.A., Miller, J.W., Rothstein, J.D., Farrell, K., Stein, B.A. and Longuemare, M.C. (1997). Neuronal regulation of glutamate transporter subtype expression in astrocytes. J. Neurosci. 17:932–940.
Szerb, J.C. and Butterworth, R.F. (1992). Effect of ammonium ions on synaptic transmission in the mammalian central nervous system. Prog. Neurobiol. 39:135–153.
Takahashi, H., Koehler, R.C., Brusilow, S.W. and Traystman, R.J. (1991). Inhibition of brain glutamine accumulation prevents cerebral edema in hyperammonemic rats. Am. J. Physiol. 261:H825–H829.
Taylor-Robinson, S.D., Sargentoni, J., Marcus, C.D., Morgan, M.Y. and Bryant, D.J. (1994). Regional variations in cerebral proton spectroscopy in patients with chronic hepatic encephalopathy. Metab. Brain Dis. 9:347–359.
Teichberg, V.I. (1991). Glial glutamate receptors: likely actors in brain signalling. FASEB J. 5:3086–3091.
Tossman, U., Delin, A., Eriksson, L.S. and Ungerstedt, U. (1987). Brain cortical amino acids measured by intracerebral dialysis in portacaval shunted rats. Neurochem. Res. 12:265–269.
Turner, M.M., Ransom, R.W., Yang, J.S. and Olsen, R.W. (1989). Steroid anaesthetics and naturally occurring analogs modulate the gamma-aminobutyric acid receptor complex at a site distinct from barbiturates. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 248:960–966
Walz, W. (1997). Role of astrocytes in the spreading depression signal between ischemic core and penumbra. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 21:135–142.
Waniewski, R.A. (1992). Physiological levels of ammonia regulate glutamine synthesis from extracellular glutamate in astrocyte cultures. J. Neurochem. 58:167–174.
Willard-Mack, C.L., Koehler, R.C., Hirata, T., Cork, L.C., Takahashi, H., Traystman, R.J. and Brusilow, S.W. (1996). Inhibition of glutamine synthetase reduces ammonia-induced astrocyte swelling in rat. Neuroscience 71:589–599.
Yudkoff, M., Pleasure, D., Cregar, L., Lin, Z.P., Nissim, I. and Stern, J. (1990). Glutathione turnover in cultured astrocytes: studies with [15N]glutamate. J. Neurochem. 55:137–145.
Zhou, B. and Norenberg, M.D. (1997). Ammonia downregulates GLAST mRNA glutamate transporter in cultured astrocytes. Soc. Neurosci. Abstr. 23:1461
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Norenberg, M.D. Astroglial Dysfunction in Hepatic Encephalopathy. Metab Brain Dis 13, 319–335 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020688925901
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1020688925901