Abstract
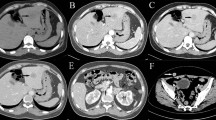
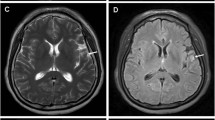
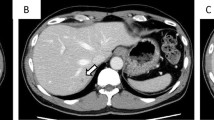
Mesothelioma is a disease mostly involving the pleura, peritoneum, and pericardium. Hematogenously disseminated metastases involving the liver, adrenal glands, kidneys, and contralateral lung have been documented in some patients, but central nervous system (CNS) involvement, especially as leptomeningeal infiltration, is very rare. A 44-yr-old mesothelioma patient admitted to hospital with convulsions and diffuse leptomeningeal infiltration was shown with magnetic resonance imaging. She had a positive history for environmental asbestos exposure. Pleural and axillary lymph node biopsies were consistent with mesothelioma. Diffuse leptomeningeal infiltration is the only constant radiological finding reported as a diagnostic criteria for CNS involvement and histopathological confirmation is usually possible only at autopsy, so clinical and radiological diagnosis is essential after exclusion of other possible causes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kaye, J.A., Wang, A., Joachim, C.L., et al. (1986). Malignant mesothelioma with brain metastases. Am. J. Med. 80, 95–97.
Artvinli, M. and Bariş, Y.I. (1979). Malignant pleural mesothelioma in a small village in the Anatolian region of Turkey. An epidemiologic study. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 63, 17–19.
Kawai, A., Nagasaka, Y., Muraki, M., et al. (1997). Brain metastasis in malignant pleural mesothelioma. Intern. Med. 36, 591–594.
Murray, J.B., Neilly, J.B., Hadley, D., et al. (1990). Diffuse meningeal thickening associated with pleural mesothelioma. Thorax 45, 70–71.
Huncharek, M. and Muscat, J. (1987). Metastases in diffuse pleural mesothelioma: influence of histopathological type. Thorax 42, 897–898.
Falconieri, G., Grandi, G., DiBonito, L., et al. (1991). Intracranial metastases from malignant pleural mesothelioma. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 115, 591–595.
Huncharek, M. and Muscat, J. (1990). Diffuse meningeal thickening associated with pleural mesothelioma. Thorax 45, 571.
Altundag, M.K., Ozisik, Y., Yalcin, S., et al. (2000). Primary low grade B-cell lymphoma of the dura in an immunocompetent patient. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 19, 249–251.
Güllü, I., Yalcin, S., Tekuzman, G., et al. (1993). Tumor markers in effusions: a comparative study of tumor marker levels in sera and effusions, in Use of Biomarkers in Assessing Health and Environmental Impacts of Chemical Pollutants (Travis, C.C., ed), pp 265–271, Plenum, New York.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Öksüzoğlu, B., Yalçin, Ş., Erman, M. et al. Leptomeningeal infiltration of malignant mesothelioma. Med Oncol 19, 167–169 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1385/MO:19:3:167
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/MO:19:3:167