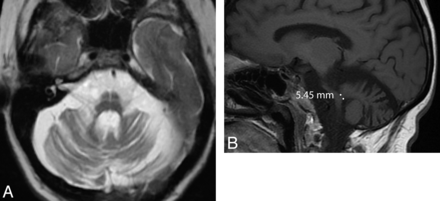
Fig 2.
Axial T2-weighted MR imaging sequence in a patient with MSA with predominant cerebellar ataxia (A) demonstrating the “hot-cross bun” sign, which results from selective loss of myelinated pontine transverse fibers and raphe neurons. One study showed that the sign is 100% specific in differentiating patients with MSA from those with idiopathic Parkinson disease; however, it is only 50% sensitive.6 Marked pontine and cerebellar atrophy is also demonstrated. This olivopontocerebellar volume loss is shown on the sagittal T1-weighted sequences (B), where a middle cerebellar peduncle width <8 mm is demonstrated. All these signs are nonspecific in the wider population—for example, they can be seen in some spinocerebellar ataxia subtypes.