Abstract
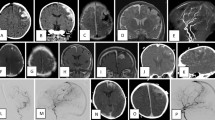
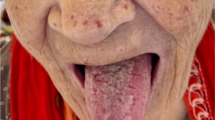
We present four cases of pial arteriovenous fistula (AVF) in children as the presenting manifestation of Rendu-Osler-Weber disease (ROW). The common clinical manifestations of ROW in adults, such as skin telangiectasia and mucosal haemorrhagic complications, seldom occur in children, since telangiectases develop with age. Pial AVF in ROW also conform to the usual age incidence and are therefore present in childhood. Of the four children in this series, three had multiple AVF. Two presented with central nervous system haemorrhage, one with seizures and the other with progressive neurological deficit. There were no clinical or angioarchitectural differences between the AVF associated with ROW and sporadic AVF. The diagnosis was based in all cases on the family history. Transarterial embolisation to obliterate the AVF was carried out in all patients. One patient had early rebleeding after partial embolisation of the AVF, with a fatal outcome. Three patients were cured and one asymptomatic in long-term follow up. No exhaustive search was conducted for multiorgan telangiectases, since there is no indication for treatment of asymptomatic telangiectasia in ROW. No pulmonary fistulae were found. ROW should be suspected in children with multiple pial AVF; they may be the only manifestation of the disease, since epistaxis and telangiectasia are unusual in early life.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aasar S, Friedman C, White J (1991) The natural history of epistaxis in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Laryngoscope 101: 977–980
Bird R, Jacques W (1959) Vascular lesions of hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia. N Engl J Med 260: 557–599
Boynton R, Morgan B (1973) Cerebral arteriovenous fistula with possible hereditary telangiectasia. Am J Dis Child 125: 99–101
John P (1991) Early childhood presentation of neurovascular disease in hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. Pediatr Radiol 22: 140–141
Lasjaunias P, Berenstein A (1987) Surgical neuroangiography, vol 2. Endovascular treatment of craniofacial lesions. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
McCoffrey T, Kern E, Lake C (1977) Management of epistaxis in hemorrhagic hereditary telangiectasia. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 103: 627–630
Sobel D, Norman D (1984) CNS manifestations of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia. AJNR 5: 569–573
Roman G, Fisher M, Perl D, Poser C (1978) Neurological manifestations of hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (Rendu Osler Weber disease): report of 2 cases and review of the literature. Ann Neurol 4: 130–144
Willinksy R, Lasjaunias P, Terbrugge K, Burrows P (1990) Multiple cerebral arteriovenous malformations (AVMs). Neuroradiology 32: 207–210
Aesch B, Lionet E, Toffol B de, Jan M (1991) Multiple cerebral angiomas and Rendu Osler Weber disease: case report. Neurosurgery 29: 599–602
Reddy K, West M, McClarty B (1987) Multiple intracerebral arteriovenous malformations. A case report and literature review. Surg Neurol 27: 495–499
Tress BM, Moseley IF (1977) Cleidocranial dysostosis, hereditary haemorrhagic telangiectasia and epilepsy: a rare association. Neuroradiology 12: 233–236
Berenstein A, Lasjaunias P (1992) Surgical neuroangiography, Vol 4. Endovascular treatment of cerebral lesions. Springer, New York Heidelberg Berlin
Lownie S, Duckwiler G, Fox A, Drake C (1992) Endovascular therapy of non-Galenic cerebral arteriovenous fistulas. In: Viñuela F, Halbach VV, Dion J (eds) Interventional neuroradiology. Endovascular therapy of the central nervous system. Raven Press, New York, pp 87–106
Nelson K, Nimi Y, Lasjaunias P, Berenstein A (1992) Endovascular embolization of congenital intracranial pial arteriovenous fistulas. Neuroimag Clin North Am 2: 309–317
García-Monaco R, Rodesch G, Terbrugge K, Burrows P, Lasjaunias P (1991) Multifocal dural arteriovenous shunts in children. Childs Nerv Syst 7: 425–431
García-Monaco R, De Victor D, Mann C, Hannedouche A, Terbrugge K, Lasjaunias P (1991) Congestive manifestation from cerebrocranial arteriovenous shunts. Endovascular management in 30 children. Childs Nerv Syst 7: 48–52
Iizuka Y, Rodesch G, García-Monaco R, Alvarez H, Burrows P, Hui F, Lasjaunias P (1992) Multiple cerebral arteriovenous shunts in children: report of 13 cases. Childs Nerv Syst 8: 437–444
Lasjaunias P, Hui F, Zerah M, García-Monaco R, Malherbe V, Rodesch G, Tanaka A, Alvarez H (1994) Cerebral arteriovenous malformations in children. Management of 179 cases and review of the literature. Childs Nerv Syst (in press)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
García-Mónaco, R., Taylor, W., Rodesch, G. et al. Pial arteriovenous fistula in children as presenting manifestation of Rendu-Osler-Weber disease. Neuroradiology 37, 60–64 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00588522
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00588522