Abstract
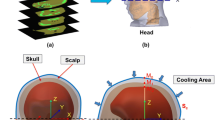
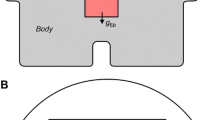
Mild or moderate hypothermia (>30°C) has been proposed for clinical use as a therapeutic option for achieving protection from cerebral ischaemia in brain injury patients. In this research, a theoretical model was developed to examine the brain temperature gradients during selective cooling of the brain surface after head injury. The head was modelled as a hemisphere consisting of several layers, representing the scalp, skull and brain tissue, respectively. The dimensions, physical properties and physiological characteristics for each layer, as well as the arterial blood temperature, were used as the input to the Pennes bioheat transfer equation to simulate the steady-state temperature distribution within the brain. Depending on the head surface temperature, a temperature gradient of up to 13°C exists in the brain tissue. The results have shown that the volumetric-averaged brain tissue temperature Tbt, avg for adults and infants can be 1.7 and 4.3°C, respectively, lower than the temperature of the arterial blood supplied to the brain tissue. The location where the probe should be placed to measure Tbt, avg was also determined by the simulation. The calculation suggests that the temperature sensor should be placed 7.5mm and 5.9 mm beneath the brain tissue surface for adults and infants, respectively, to monitor Tbt, avg continuously.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barone, F. C., Feuerstein, G. Z., andWhite, R. F. (1997): ‘Brain cooling during transient focal ischaemia provides complete neuroprotection’,Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev.,21, pp. 31–44
Blinkov, S. A., andGlezer, I. I. (1968): ‘Human brain in figures and tables: a quantitative handbook’ (Plenum Press, New York, 1968)
Clifton, G. L., Jiang, J. Y., andLyeth, B. G. (1991): ‘Marked protection by moderate hypothermia after experimental traumatic brain injury’,J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab.,11, pp. 114–121
Clark, R. S. B., Kochanek, P. M., Marion, D. W., Schiding, J. K., White, M., Palmer, A. M., andDeKosky, S. T. (1996): ‘Mild posttraumatic hypothermia reduces mortality after severe controlled cortical impart in rats’,J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab.,16, pp. 253–261
Dexter, F., andHinderman, B. J. (1994): ‘Computer simulation of brain cooling during cardiopulmonary bypass’,Ann. Thorac. Surg.,57, pp. 1171–1179
Kolios, M. C., Worthington, A. E., Sherar, M. D., andHunt, J. W. (1998): ‘Experimental evaluation of two simple thermal models using transient temperature analysis’,Phys. Med. Biol.,43, pp. 3325–3340
Kuluz, J. W., Gregory, G. A., Yu, A. C. H., andChang, Y. (1992): ‘Selective brain cooling during and after prolonged global ischemia reduces cortical damage in rats’,Stroke,23, pp. 1792–1797
Jiang, J. Y., Lyeth, B. G., Clifton, G. L., Jenkins, L. W., Hamm, R. J., andHayes, R. L. (1991): ‘Relationship between body and brain temperature in traumatically brain-injured rodents’,J. Neurosurg.,74, pp. 492–496
Lyons, B. E., Samulski, T. V., Cox, R. S., andFessenden, P. (1989): ‘Heat loss and blood flow during hyperthermia in normal canine brain. I: empirical study and analysis’,Int. J. Hypertherm.,5, pp. 225–247
Marion, D. W., Leonov, Y., Ginsberg, M., Katz, L. M., Kochanek, P. M., Lechleuthner, A., Nemoto, E. M., Obrist, W., Safar, P., Sterz, F., Tisherman, S. A., White, R. J., Xiao, F., andZar, H. (1996): ‘Resuscitative hypothermia’,Crit. Care Med.,24, pp. s81-s89
Marion, D. W. (1997): ‘Treatment of traumatic brain injury with moderate hypothermia’,N. Engl. J. Med.,336, pp. 540–546
Mellergard, P., Nordtroem, C.-H., andChristensson, M. (1990): ‘A method for monitoring intracerebral temperature in neurosurgical patients’,Neurosurgery,27, pp. 654–657
Miyazawa, T., andHossmann, K.-A. (1992): ‘Methodological requirements for accurate measurements of brain and body temperature during global forebrain ischaemia of rat’,J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab.,12, pp. 817–822
Nelson, D. A., andNunneley, S. A. (1998): ‘Brain temperature and limits on transcranial cooling in humans: quantitative modeling results’,Eur. J. Appl. Physiol.,78, pp. 353–359
Ogura, K., Takayasu, M., andDacey, R. G. (1991): ‘Effects of hypothermia and hyperthermia on the reactivity of rat intracerebral arteriolesin vitro’,J. Neurosurg.,75, pp. 433–439
Olsen, R. W., Hayes, L. J., Wissler, E. H., Nikaidoh, H., andEberhart, R. C. (1985): ‘Influence of hypothermia and circulatory arrest on cerebral temperature distributions’,ASME. J. Biomech. Eng.,107, pp. 354–360
Pennes, H. H. (1948): ‘Analysis of tissue and arterial blood temperatures in the resting human forearm’,J. Appl. Physiol.,1, pp. 93–122
Rumana, C. S., Gopinath, S. P., Uzura, M., Valadka, A. B., andRobertson, C. S. (1998): ‘Brain temperature exceeds systemic temperature in head-injured patients’,Crit. Care. Med.,26, pp. 562–567
Samulski, T. V., Cox, R. S., Lyons, B. E., andFessenden, P. (1989): ‘Heat loss and blood flow during hyperthermia in normal canine brain. II: mathematical model’,Int. J. Hypertherm.,5, pp. 249–263
Schwab, S., Spranger, M., Aschoff, A., Steiner, T., andHacke, W. (1997): ‘Brain temperature monitoring and modulation in patients with severe MCA infarction’,Neurology,48, pp. 762–767
Sirimanne, E. S., Blumberg, R. M., Bossana, D., Gunning, M., Edwards, A. D., Gluckman, P. D., andWilliams, C. E. (1996): ‘The effect of prolonged modification of cerebral temperature on outcome after hypoxic-ischaemic brain injury in the infant rat’,Pediat. Res.,39, pp. 591–597
Stone, J. G., Young, W. L., Smith, C. R., Solomon, R. A., Wald, A., Ostapkovich, N., andShrebnick, D. B. (1995): ‘Do standard monitoring sites reflect true brain temperature when profound hypothermia is rapidly induced and reversed?’,Anesthesiology,82, pp. 344–351
Stone, J. G., Goodman, R. R., Baker, K. Z., Baker, C. J., andSolomon, R. A. (1997): ‘Direct intraoperative measurement of human brain temperature’,Neurosurgery,41, pp. 20–24
Thoresen, M., andWyatt, J. (1997): ‘Keeping a cool head, posthypoxic hypothermia—an old idea revisited’,Acta Pediatr.,86, pp. 1029–1033
Verlooy, J., Heytens, L., Veeckmans, G., andSelosse, P. (1995): ‘Intracerebral temperature monitoring in severely head injured patients’,Acta Neurochir (Wien),184, pp. 76–78
Wass, C. T., Lanier, W. L., Hofer, R. E., Scheithauer, B. W., andAndrews, A. G. (1995): ‘Temperature changes of ≥1 °C alter functional neurologic outcome and histopathology in a canine model of complete cerebral ischemia’,Anesthesiology,83, pp. 325–335
Wass, C. T., Waggoner, J. R., Cable, D. G., Schroeder, D. R., andLanier, W. L. (1998): ‘Selective convective brain cooling during normothermic cardiopulmonary bypass in dogs’,J. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg.,115, pp. 1350–1357
Weinbaum, S., Xu, L. X., Zhu, L., andEkpene, A. (1997): ‘A new fundamental bioheat equation for muscle tissue. Part I: blood perfusion term’,ASME J. Biomech. Eng.,121, pp. 1–12
Xu, X., Tikuisis, P., andGiesbrecht, G. (1999): ‘A mathematical model for human brain cooling during cold-water near-drowning’,J. Appl. Physiol.,86, pp. 265–272
Zhu, L., andXu, L. X. (1999): ‘Evaluation of the effectiveness of transurethral radio frequency hyperthermia in the canine prostate: temperature distribution analysis’,ASME J. Biomech. Eng.,121, pp. 584–590
Zhu, L. (2000): ‘Theoretical evaluation of contributions of both radial heat conduction and countercurrent heat exchange in selective brain cooling in humans’,Ann. Biomed. Eng.,28, pp. 269–277
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, L., Diao, C. Theoretical simulation of temperature distribution in the brain during mild hypothermia treatment for brain injury. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 39, 681–687 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02345442
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02345442