Abstract
Introduction
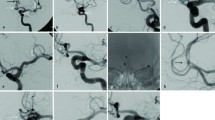
We report imaging and clinical characteristics of patients with aneurysms that repeatedly reopened over time and were coiled three times or more during a follow-up period of 2–11 years.
Methods
At angiographic follow-up of 624 of 827 aneurysms coiled between 1995 and 2005, 74 aneurysms (8.9%) reopened and were additionally coiled. During an extended follow-up, 12 aneurysms (1.5%) in 12 patients repeatedly reopened and were repeatedly coiled. Initial aneurysm sizes ranged from 15 to 30 mm. Four aneurysms contained intraluminal thrombus. Eight aneurysms were associated with subarachnoid hemorrhage and two with a mass effect, and two were incidentally discovered. The locations of aneurysms were basilar artery (eight), carotid artery (two), anterior communicating artery (one) and middle cerebral artery (one).
Results
Altogether, 49 coil treatments were performed in the 12 aneurysms, ranging from three to six coil treatments per aneurysm. Of the 49 coil treatments, 20 (41%) were performed with a supporting device. There were no procedural complications (0%, 97.5% CI 0–5.7%). The mean clinical follow-up period was 70.6 months (median 60, range 25–135 months). All 12 patients are neurologically doing well (GOS 5). Reopening was by compaction in nine aneurysms and by migration of coils into intraluminal thrombus in three aneurysms. In two aneurysms, late regrowth became apparent at 76 and 95 months after the previous coiling.
Conclusion
Aneurysms that reopen over time and need to be coiled for a second time should be imaged at regular intervals to detect repeated reopening or regrowth. The treatment strategy of regular follow-up and additional treatments when necessary is effective and safe.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Molyneux A, Kerr R, Stratton I, Sandercock P, Clarke M, Shrimpton J, Holman R; International Subarachnoid Aneurysm Trial (ISAT) Collaborative Group (2002) International Subarachnoid Aneurysm Trial (ISAT) of neurosurgical clipping versus endovascular coiling in 2143 patients with ruptured intracranial aneurysms: a randomised trial. Lancet 360:1267–1274
Brilstra EH, Rinkel GJ, van der Graaf Y, van Rooij WJ, Algra A (1999) Treatment of intracranial aneurysms by embolization with coils: a systematic review. Stroke 30:470–476
Sluzewski M, van Rooij WJ (2005) Early rebleeding after coiling of ruptured cerebral aneurysms: incidence, morbidity, and risk factors. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:1739–1743
Sluzewski M, van Rooij WJ, Beute GN, Nijssen PC (2005) Late rebleeding of ruptured intracranial aneurysms treated with detachable coils. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2542–2549
Byrne JV, Sohn MJ, Molyneux AJ, Chir B (1999) Five-year experience in using coil embolization for ruptured intracranial aneurysms: outcomes and incidence of late rebleeding. J Neurosurg 90:656–663
Raymond J, Guilbert F, Weill A, Georganos SA, Juravsky L, Lambert A, Lamoureux J, Chagnon M, Roy D (2003) Long-term angiographic recurrences after selective endovascular treatment of aneurysms with detachable coils. Stroke 34:1398–1403
Sluzewski M, van Rooij WJ, Rinkel GJ, Wijnalda D (2003) Endovascular treatment of ruptured intracranial aneurysms with detachable coils: long-term clinical and serial angiographic results. Radiology 227:720–724
Slob MJ, Sluzewski M, van Rooij WJ, Roks G, Rinkel GJ (2004) Additional coiling of previously coiled cerebral aneurysms: clinical and angiographic results. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1373–1376
Sluzewski M, van Rooij WJ, Slob MJ, Bescos JO, Slump CH, Wijnalda D (2004) Relation between aneurysm volume, packing, and compaction in 145 cerebral aneurysms treated with coils. Radiology 231:653–658
van Rooij WJ, Sluzewski M, Slob MJ, Rinkel GJ (2005) Predictive value of angiographic testing for tolerance to therapeutic occlusion of the carotid artery. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:175–178
Sluzewski M, Menovsky T, van Rooij WJ, Wijnalda D (2003) Coiling of very large or giant cerebral aneurysms: long-term clinical and serial angiographic results. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:257–262
Majoie CB, Sprengers ME, van Rooij WJ, Lavini C, Sluzewski M, van Rijn JC, den Heeten GJ (2005) MR angiography at 3T versus digital subtraction angiography in the follow-up of intracranial aneurysms treated with detachable coils. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:1349–1356
Leclerc X, Navez JF, Gauvrit JY, Lejeune JP, Pruvo JP (2002) Aneurysms of the anterior communicating artery treated with Guglielmi detachable coils: follow-up with contrast-enhanced MR angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1121–1127
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van Rooij, W.J., Sprengers, M.E., Sluzewski, M. et al. Intracranial aneurysms that repeatedly reopen over time after coiling: imaging characteristics and treatment outcome. Neuroradiology 49, 343–349 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-006-0200-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-006-0200-2