Abstract
Objectives
This study evaluated patients with multiple sclerosis using diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) to obtain fractional anisotropy (FA) and mean diffusivity (MD) values.
Methods
We investigated the possible statistically significant variation of MD and FA in different MS patients, compared simultaneously, putting in comparison their normal appearing white matter (NAWM) and white matter affected by disease (plaques), both during activity and in remission, with normal white matter (NWM) of control subjects.
Results
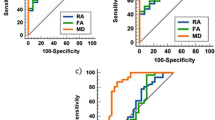
Statistical analysis using Levene’s test for comparison of variances revealed significant (P < 0.05) differences between FA values of the NWM of the controls and those of NAWM and active or inactive lesions, of the patients in the study. However, the differences between MD values of the NWM of the controls and those of NAWM and active or inactive lesions of the patients in the study were judged not significant (P > 0.05).
Conclusion
Imaging of MS using MRI techniques is constantly searching for reproducible quantitative parameter. This study shows how these parameters can be identified in the MD and FA values, and thus suggests the implementation of MRI routine protocols for diagnosing MS with the DTI analysis, since it can provide valuable information otherwise unobtainable.
Key Points
-
Magnetic resonance imaging is widely performed in multiple sclerosis (MS) patients
-
Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) can be implemented using a 3T magnet
-
DTI provides quantitative parameters as mean diffusivity (MD) and fractional anisotropy (FA)
-
MD and, especially, FA can help evaluate the lesion load in MS patients and also assess variation in normal appearing white matter (NAWM) in MS







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schmierer K, Wheeler-Kingshott CA, Boulby PA, Scaravilli F, Altmann DR, Barker GJ, Tofts PS, Miller DH (2007) Diffusion tensor imaging of post mortem multiple sclerosis brain. Neuroimage 35:467–477
Zollinger LV, Kim TH, Hill K, Jeong EK, Rose JW (2011) Using diffusion tensor imaging and immunofluorescent assay to evaluate the pathology of multiple sclerosis. J Magn Reson Imaging 33:557–564
Zhou F, Zee CS, Gong H, Shiroishi M, Li J (2010) Differential changes in deep and cortical gray matters of patients with multiple sclerosis: a quantitative magnetic resonance imaging study. J Comput Assist Tomogr 34:431–436
Rueda F, Hygino LC Jr, Domingues RC, Vasconcelos CC, Papais-Alvarenga RM, Gasparetto EL (2008) Diffusion tensor MR imaging evaluation of the corpus callosum of patients with multiple sclerosis. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 66:449–453
Commowick O, Fillard P, Clatz O, Warfield SK (2008) Detection of DTI white matter abnormalities in multiple sclerosis patients. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv 11:975–982
Trapp BD, Peterson J, Ransohoff RM, Rudick R, Mork S, Bo L (1998) Axonal transection in the lesions of multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med 388:278–285
Allen IV, McKeown SR (1979) A histological, histochemical and biochemical study of the macroscopically normal white matter in multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci 41:81–91
Rovaris M, Agosta F, Pagani E, Filippi M (2009) Diffusion tensor MR imaging. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 19:37–43
Pagani E, Bammer R, Horsfield MA, Rovaris M, Gass A, Ciccarelli O, Filippi M (2007) Diffusion MR imaging in multiple sclerosis: technical aspects and challenges. Am J Neuroradiol 28:411–420
Rovaris M, Filippi M (2007) Diffusion tensor MRI in multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimaging 17:27S–30S
Rovaris M, Gass A, Bammer R, Hickman SJ, Ciccarelli O, Miller DH, Filippi M (2005) Diffusion MRI in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 65:1526–1532
Kurtzke JF (1955) A new scale for evaluating disability in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 5:580–583
Kurtzke JF (1961) On the evaluation of disability in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 11:686–694
Kurtzke JF (1965) Further notes on disability evaluation in multiple sclerosis, with scale modifications. Neurology; 15:654–661
Kurtzke JF (1970) Neurologic impairment in multiple sclerosis and the disability status scale. Acta Neurol Scand 46:493–512
Kurtzke JF (1983) Rating neurologic impairment in multiple sclerosis: an expanded disability status scale (EDSS). Neurology 33:1444–1452
Gallo A, Rovaris M, Riva R, Ghezzi A, Benedetti B, Martinelli V et al (2005) Diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging detects normal-appearing white matter damage unrelated to short-term disease activity in patients at the earliest clinical stage of multiple sclerosis. Arch Neurol 62:803–808
Rovaris M, Bozzali M, Iannucci G, Ghezzi A, Caputo D, Montanari E et al (2002) Assesment of normal appearing white and grat matter in patients with primary progressive multiple sclerosis. Arch Neurol 59:1406–1412
Ceccarelli A, Rocca M, Falini A, Tortorella P, Pagani E, Rodegher M et al (2007) Normal appearing white and grey matter damage in MS—A volumetric and diffusion tensor MRI study at 3,0 Tesla. J Neurol 254:513–518
Castriota-Scanderbeg A, Fasano F, Hagberg G, Nocentini U, Filippi M, Caltagirone C (2003) Coefficient D(av) is more sensitive than fractional anisotropy in monitoring progression of irreversible tissue damage in focal nonactive multiple sclerosis lesions. Am J Neuroradiol 24:663–670
Cercignani M, Inglese M, Pagani E, Comi G, Filippi M (2001) Mean diffusivity and fractional anisotropy histograms of patients with multiple sclerosis. Am J Neuroradiol 22:952–958
Harrison DM, Caffo BS, Shiee N, Farrell JA, Bazin PL, Farrell SK, Ratchford JN, Calabresi PA, Reich DS (2011) Longitudinal changes in diffusion tensor-based quantitative MRI in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 76:179–186
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Testaverde, L., Caporali, L., Venditti, E. et al. Diffusion tensor imaging applications in multiple sclerosis patients using 3T magnetic resonance: a preliminary study. Eur Radiol 22, 990–997 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-011-2342-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-011-2342-9