Abstract
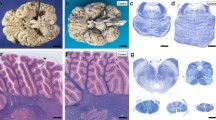
Neuronal ceroid-lipofuscinoses (NCL) are a group of neurodegenerative diseases and autosomal recessive lysosomal storage disorders. We examined the involvement of cell death, oxidative stress, and glutamate excitotoxicity using immunohistochemistry against Bcl-2, Bcl-x, oxidative products to proteins, lipids and DNA, calcium-binding proteins (calbindin-D28K, parvalbumin, calretinin), and glial glutamate transporters (excitatory amino acid transporters 1 and 2), in addition to terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP-nick end labeling (TUNEL) in the brains from three cases of late infantile form of NCL (LINCL) and one case of juvenile form of NCL (JNCL) to investigate the neurodegenerative mechanisms. In the cerebral and cerebellar cortex, all of three LINCL cases demonstrated neurons with TUNEL-immunoreactive nuclei, whereas the JNCL case did not show TUNEL-immunoreactive nuclei. The coexistence of the nuclear TUNEL-immunoreactivity nuclei and cytoplasmic deposition of 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal-modified protein in the frontal cortex and hypoglossal nucleus may suggest a possible interrelationship between DNA fragmentation and lipid oxidation in LINCL. Additionally, glycoxidation of protein and oxidative stress to DNA seemed to be involved in the cerebellar and cerebral degeneration, respectively. Interneurons immunoreactive for calbindin-D28K and parvalbumin were severely reduced in the cerebral cortex, whereas those for calretinin were comparatively well preserved in LINCL, indicating the possibility of altered GABAergic system. The disturbance of expression of glial glutamate transporters seemed to be heterogeneous and mild. These findings suggest the possibility of new treatments for neurodegeneration in LINCL using antioxidative agents and/or GABAergic medications.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beasley CL, Zhang ZJ, Patten I, Reynolds GP (2002) Selective deficits in prefrontal cortical GABAergic neurons in schizophrenia defined by the presence of calcium-binding proteins. Soc Biol Psychiatry 52:708–715
Ben-Manachem E, Kyllerman M, Marklund S (2000) Superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase function in progressive myoclonus epilepsies. Epilepsy Res 40:33–39
Emerit J, Edeas M, Bricarie F (2004) Neurodegenerative diseases and oxidative stress. Biomed Phamacother 58:39–46
Ezaki J, Kominami E (2004) The intracellular location and function of proteins of neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses. Brain Pathol 14:77–85
Goebel HH, Wisniewski KE (2004) Current state of clinical and morphological features in human NCL. Brain Pathol 14:61–69
Haltia M (2003) The neuronal ceroid-lipofuscinoses. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 62:1–13
Hayashi M (2001) Neuropathology of the limbic system and brainstem in West syndrome. Brain Dev 23:516–522
Hayashi M, Arai N, Murakami T, Morimatsu Y, Oda M, Matsuyama H (1998) A study of cell death in Werdnig Hoffmann disease brain. Neurosci Lett 243:117–120
Hayashi M, Itoh M, Araki S, Kumada S, Shioda K, Tamagawa K, Mizutani T, Morimatsu Y, Minagwa M, Oda M (2001) Oxidative stress and glutamate transport in hereditary nucleotide repair disorders. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 60:350–356
Hayashi M, Arai N, Satoh J, Suzuki H, Katayama K, Tamagawa K, Morimatsu Y (2002) Neurodegenerative mechanisms in subacute sclerosing panencephalitis. J Child Neurol 17:725–730
Hayashi M, Araki S, Arai N, Kumada S, Itoh M, Tamagawa K, Oda M, Morimatsu Y (2002) Oxidative stress and disturbed glutamate transport in spinal muscular atrophy. Brain Dev 24:770–775
Hayashi M, Araki S, Kohyama J, Shioda K, Futamatsu R, Tamagawa K (2004) Brainstem and basal ganglia lesions in xeroderma pigmentosum group A. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 63:1048–1057
Hayashi M, Araki S, Kohyama J, Shioda K, Fukatsu R (2005) Oxidative nucleotide damage and superoxide dismutase expression in the brains of xeroderma pigmentosum group A and Cockayne syndrome. Brain Dev 27:34–38
Jenner P (2003) Oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 53:S26–S38
Kikuchi S, Shinpo K, Takeuchi M, Yamagishi S, Makita Z, Sasaki N, Tashiro K (2003) Glycation—a sweet tempter for neuronal death. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 41:306–323
Kumada S, Hayashi M, Mizuguchi M, Nakano I, Morimatsu Y, Oda M (2000) Cerebellar degeneration in hereditary dentatorubral-pallidoluysian atrophy and Machado–Joseph disease. Acta Neuropathol 99:48–54
Kurata K, Hayashi M, Satoh J, Kojima H, Nagata J, Tamagawa K, Shinohara T, Morimatsu Y, Kominami E (1999) Pathological study on sibling autopsy cases of the late infantile form of neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis. Brain Dev 21:63–67
Lake BD, Hall NA (1993) Immunolocalization studies of subunit c in late infantile and juvenile Batten disease. J Inherit Metab Dis 16:263–266
Lane SC, Jolly RD, Schmechel DE, Alroy J, Boustany RM (1996) Apoptosis as the mechanism of neurodegeneration in Batten’s disease. J Neurochem 67:677–683
Liu W, Kato M, Akhand AA, Hayakawa A, Suzuki H, Miyata T, Kurokawa K, Hotta Y, Ishikawa N, Nakashima I (2000) 4-hydroxynonenal induces a cellar redox status-related activation of the caspase cascade for apoptotic cell death. J Cell Sci 113:635–641
Mathern GW, Mendoza BS, Lozada BS, Pretorius JK, Dehnes Y, Danbolt NC, Nelson N, Leite JP, Chimelli L, Born DE, Sakamoto AC, Assirati JA, Fried I, Peacock WJ, Ojemann GA, Adelson PD (1999) Hippocampal GABA and glutamate transporter immunoreactivity in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurology 52:453–472
Mikkonen M, Alafuzoff I, Tapiola T, Soininen H, Miettinen R (1999) Subfield- and layer-specific changes in parvalbumin, calretinin and calbindin-D28 immunoreactivity in the entorhinal cortex in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroscience 92:515–532
Mitchison HM, Lim MJ, Cooper JD (2004) Selectivity and types of cell death in the neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses. Brain Pathol 14:86–96
Mole SE (2004) The genetic spectrum of human neuronal ceroid-lipofuscinoses. Brain Pathol 14:70–76
Nunomura A, Perry G, Aliev G, Hirai K, Takeda A, Balraj EK, Jones PK, Ghanbari H, Wataya T, Shimohama S, Chiba S, Atwood CS, Petersen RB, Smith MA (2001) Oxidative damage is the earliest event in Alzheimer disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 60:759–767
Proper EA, Hoogland G, Kappen SM, Jansen GH, Rensen MG, Schrama LH, van Veelen CW, van Rijen PC, van Nieuwenhuizen O, Gispen WH, de Graan PN (2002) Distribution of glutamate transporters in the hippocampus of patients with pharmaco-resistant temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain 125:32–43
Puranam KL, Guo WX, Qian WH, Nikbakht K, Boustany RM (1999) CLN3 defines a novel antiapoptotic pathway operative in neurodegeneration and mediated by ceramide. Mol Genet Metab 66:294–308
Sharp JD, Wheeler RB, Lake BD, Savukoski M, Jarvela IE, Peltonen L, Gardiner RM, Williams RE (1997) Loci for classical and a variant late infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses map to chromosomes 11p15 and 15q21–23. Hum Mol Genet 6:591–595
Sleat DE, Donnelly RJ, Lackland H, Liu CG, Sohar I, Pullarkat RK, Lobel P (1997) Association of mutations in a lysosomal protein with classical late-infantile neuronal ceroid-lipofuscinosis. Science 277:1802–1805
Takedo A, Yasuda T, Miyata T, Mizuno K, Li M, Yoneyama S, Horie K, Maeda K, Sobue G (1996) Immunohistochemical study of advanced glycation end products in aging and Alzheimer’s disease brain. Neurosci Lett 221:17–20
The International Batten Disease Consortium (1995) Isolation of a novel gene underlying Batten disease, CLN3. Cell 82:949–957
Toyokuni S (1999) Reactive oxygen species-induced molecular damage and its application in pathology. Pathol Int 49:91–102
Tyynelä J, Cooper JD, Khan MN, Shemilts SJ, Haltia M (2004) Hippocampal pathology in the human neuronal ceroid-lipofuscinoses: distinct patterns of storage deposition, neurodegeneration and glial activation. Brain Pathol 14:349–357
Walkley SU (1998) Cellular pathology of the lysosomal strage disorders. Brain Pathol 8:175–193
Zarkovic K (2003) 4-hydroxynonenal and neurodegenerative diseases. Mol Aspects Med 24:293–303
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hachiya, Y., Hayashi, M., Kumada, S. et al. Mechanisms of neurodegeneration in neuronal ceroid-lipofuscinoses. Acta Neuropathol 111, 168–177 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-005-0024-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-005-0024-x