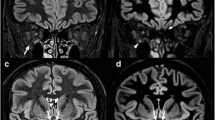
Abstract
MRI of the optic nerves was obtained in 13 patients with acute optic neuritis and 13 with a previous optic neuritis (ON), assessed by clinical features, visual fields and visual evoked potentials. Results of the conventional short tau inversion recovery (STIR) sequence obtained with a short echo time (STE-STIR; 22 ms) were compared with those of a long echo time (LTE-STIR: 80 ms) sequence. The conventional STE-STIR sequence revealed lesions in the optic nerves in 78.5% of acute and 58.8% of previous ON. The LTE-STIR sequence showed abnormalities in 92.8% of acutely symptomatic nerves and 94.1% of nerves with previous ON. The optic nerve lesions appeared significantly longer with the LTE-STIR sequence than with the conventional STE-STIR sequences, in both acute and previous ON.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
McAlpine D (1961) The benign form of multiple sclerosis. A study based on 241 cases seen within three years of onset and followed up until the tenth year or more of disease. Brain 84: 86–203
Poser CM, Paty DW, Scheinberg L, McDonald WI, Davis FA, Johnson KP, Sibley WA, Silberberg DH, Tourtellotte WW (1983) New diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: guidelines for research protocols. Ann Neurol 13: 227–231
Atlas SW, Grossman RI, et al (1988) STIR-MR imaging of the orbit. AJNR 9: 969–974
Larsson HBW, Thomesen C, Frederiksen J, Henriksen O, Olesen J (1988) Chemical shift selective magnetic resonance imaging of the optic nerve in patients with acute optic neuritis. Acta Radiol 29: 629–632
Guy J, Mao J, Bidgood JR, Mancuso A, Quisling RG (1992) Enhancement and demyelination of the intraorbital optic nerve. Fat suppression magnetic resonance imaging. Ophthalmology 99: 713–719
Daniels DL, Kneeland JB, et al (1986) MR imaging of the optic nerve and sheath: correcting the chemical shift misregistration effect. AJNR 7: 249–253
Johnson G, Miller DH, MacManus D, et al (1987) STIR sequences in NMR imaging of the optic nerve. Neuroradiology 29: 238–245
Simon J, Szumowsky J, et al (1988) Fat-suppression MR imaging of the orbit. AJNR 9: 961–968
Miller DH, Newton MR, Poel JC van der, duBoulay GH, Halliday AM, Kendall BE, Johnson G, MacManus DG, Moseley JF, McDonald WI (1988) Magnetic resonance imaging of the optic nerve in optic neuritis. Neuroradiology 38: 175–179
Hendrick RE, Roff U (1992) Image contrast and noise. In: Stark DD, Bradley WG Jr, Magnetic resonance imaging, 2nd edn, Mosby Year Book, St. Louis, pp 109–144
Miller DH, MacManus DG, Bartlett PA, Kapoor R, Morrissey SP, Moseley IF (1993) Detection of optic nerve lesions in optic neuritis using frequency-selective fat-saturation sequences. Neuroradiology 35: 156–158
Finn JP, Kendall BE, et al (1991) Myelination, structural abnormalities and disease of white matter: an assessment using high field MRI. Neuroradiology 33 [Suppl]; 254–256
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Onofrj, M., Tartaro, A., Thomas, A. et al. Long echo time STIR sequence MRI of optic nerves in optic neuritis. Neuroradiology 38, 66–69 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00593226
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00593226