Summary
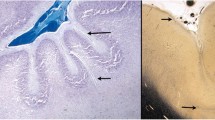
Microgyria (polygria, polymicrogyria) has stimulated continued interest since its first description by Meschede [28]. Based on analysis of case material, available staining techniques, and known principles of human cortical development, subsequent investigators have proposed numerous theories to explain its pathogenesis. We have studied a case which cannot be fully explained by these previously proposed theories. In this case, four-layered microgyria is present bilaterally in middle cerebral artery distribution, but in one hemisphere, in the center of the malformed area, the deep acellular and cellular layers are replaced by radially aligned neurons extending ectopically into prospective white matter. Analysis of the findings in this case provide evidence that the recently described pathogenetic mechanism observed in a rat model of this malformation [15, 16] is applicable to its formation in man.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anton G (1904) Hydrocephalien. Entwicklungsstörungen des Gehirns. In: Flatau E, Jacabsohn L, Minor L (eds) Handbuch der pathologischen Anatomie des Nervensystems. Karger, Basel, pp 416–467
Bankl H, Jellinger K (1967) Zentralnervöse Schäden nach fetaler Kohlenoxydvergiftung. Beitr Pathol Anat 135:350–376
Bertrand I, Gruner J (1955) The status verrucosus of the cerebral cortex. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 14:331–347
Bielschowsky M (1915) Über Microgyrie. J Psychol Neurol 22:1–47
Bielschowsky M (1923) Über die Oberflächengestaltung des Großhirnmantels bei Pachygyrie, Mikogyrie und bei normaler Entwicklung. J Psychol Neurol 30:29–76
Bielschowsky M, Rose M (1929) Über die Pathoarchitektonik der (mikro- und) pachygyren Rinde und ihre Beziehungen zur Morphogenie normaler Rindengebiete. J Psychol Neurol 38:42–46
Binswanger O (1882) Über eine Mißbildung des Gehirns. Virchows Arch A [Pathol Anat] 87:427–476
Bresler (1899) Klinische und pathologisch-anatomische Beiträge zur Mikrogyrie. Arch Psychiat 31:566–573
Chatel M (1976) Developpement de l'isocortex du cerveau humain pendant les périodes embryonnaires et foetales jusqu' à la 24 ème semaine de gestation. J Hirnforsch 17:189–212
Choi BH, Lapham LW (1978) Radial glia in the human fetal cerebrum: a combined Golgi, immunoflourescent and electron microscopic study. Brain Res 148:295–311
Crome L (1952) Microgyria. J Pathol Bact 64:479–495
Crome L, France NE (1959) Microgyria and cytomegalic inclusion disease in infancy. J Clin Pathol 12:427–434
Dekaban A (1965) Large defects in cerebral hemispheres associated with cortical dysgenesis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 24:512–530
deLeon GA (1972) Observations on cerebral and cerebellar microgyria. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 20:278–287
Dvorak K, Feit J (1977) Migration of neuroblasts through partial necrosis of the cerebral cortex in newborn rats —contribution to the problems of morphological development and developmental period of cerebral microgyria. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 38:203–212
Dvorak K, Feit J, Jurankova Z (1978) Experimentally induced focal microgyria and status verrucosus deformis in rats —pathogenesis and interrelation. Histological and autoradiographical study. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 44:121–129
Friede RL (1975) Developmental neuropathology. Springer, New York, pp 107–108, 303–307
Fride RL, Mikolasek J (1978) Postencephalitic porencephaly, hydranencephaly or polymicrogyria. A review. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 43:161–168
Giannelli A (1901) Contributo allo studio della microgyria. Riv Sper Freniat 27:867–893
Groz D (1909) Mikrogyrie und Balkenmangel im menschlichen Gehrin. Arch Psychiat 45:605–620
Heschl R (1878) Über die vordere quere Schläfenwindung des menschlichen Großhirns. In: Festschrift zur 25 Jub. Feier der Landesirrenanstalt in Wien Cited by Nieuwenhuijse (ref. [30])
Heubner (1883) Über cerebrale Kinderlähmung. Wien Med Blätter 6:373–378
Jacob H (1940) Die feinere Oberflächengestaltung der Hirnwindungen, die Hirnwarzenbildung und die Mikropolygyrie. Z Ges Neurol Psychiat 170:64–84
Jelgersma G (1890) Das Gehirn ohne Balken. Neurol Centralbl 9:162–167
Köppen M (1896) Beiträge zum Studium der Hirnrindenerkrankungen. Arch Psychiat 28:931–963
Lapinsky M (1900) Ein Beitrag zur Kenntnis der anatomischen Veränderungen im Cerebralnervensystem bei cerebraler Kinderlähmung. Mschr Psychiat Neurol 8:336–353
Levine DN, Fisher MA, Caviness VS, Jr (1974) Porencephaly with microgyria: a pathologic study. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 29:99–113
Meschede (1864) Über Neubildung grauer Hirnsubstanz in den Wandungen der Seiten-Ventrikel und über eine bisher nicht beschriebene, durch Hyperplasie grauer Cortikalsubstanz bedingle Struktur-Anomalie der Hirnrinde. Allgem Zeitschr Psychiat 21:481–505
Melissinos K (1912) Beitrag zur Kenntnis der pathologischen Anatomie der Mikrogyrie. Arch Psychiat 49:848–872
Nieuwenhuijse P (1913) Zur Kenntnis der Mikrogyrie. Psychiat Neurol Bl (Amst) 17:9–53
Oeconomakis M (1905) Über umschriebene mikrogyrische Verbildungen an der Großhirnoberfläche und ihre Beziehung zur Porencephalie. Arch Psych 39:676–725
Oppenheim H (1895) Über Mikrogyrie und die infantile Form der zerebralen Glossopharyngolabialparalyse. Neurol Centralbl 14:130–133
Otto R (1892) Casuistische Beiträge zur Kenntnis der Mikrogyrie. Arch Psychiat 23:153–166
Poliakov GI (1937) Early and intermediate ontogenesis of the human cerebral cortex. Publ. of Brain Institute-Academy of Medical Sciences, Moscow (in Russian)
Probst M (1901) Über den Bau des vollständig balkenlosen Großhirnes sowie über Mikrogyrie und Heteropie der grauen Substanz. Arch Psychiat 34:709–786
Ranke O (1910) Beitrage zur Kenntnis der normalen und pathologischen Hirnrindenbildung. Beitr Pathol Anat 47:51–125
Richman DP, Stewart RM, Caviness VS, Jr (1974) Cerbral microgyria in a 27-week fetus: an architectonic and topographic analysis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 33:374–384b
Schäffer O (1896) Über die Entstehung der Porencephalic und der Hydranencephalie auf Grund entiwicklungsgeschichtlicher Studien. Virchows Arch A [Pathol Anat] 145:481–537
Sidman RL, Rakic P (1973) Neuromal migration, with special reference to developing human brain: a review. Brain Res 62:1–35
Vander Eecken HM (1959) Anastomoses between the leptomeningeal arteries of the brain, their morphological, pathological and clinical significance. Thomas, Springfield, Ill, pp 69–71, 141–142
Wiliams RS, Ferrante RJ, Caviness VS, Jr (1976) The cellular pathology of microgyria. A Golgi analysis. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 36:269–283
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McBride, M.C., Kemper, T.L. Pathogenesis of four-layered microgyric cortex in man. Acta Neuropathol 57, 93–98 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00685375
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00685375