Abstract
Background:
Paragangliomas are rare, hypervascularized benign tumors. In some cases a clear differentiation of paragangliomas and other entities is impossible.
Patients and Methods:
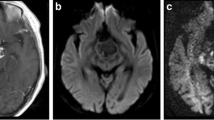
The authors evaluated ten patients with skull base lesions (paraganglioma n = 7, meningioma n = 1, giant cell tumor n = 1, and neurinoma n = 1) in addition to conventional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) with diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI), and calculation of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC).
Results:
Mean ADC values ± standard deviation of the paragangliomas were 1.304 ± 0.257 × 10–3 mm2/s and differed from ADC values of the other jugular fossa tumors with 0.743 ± 0.108 × 10–3 mm2/s and measurement derived from the cerebellum with 0.802 ± 0.075 × 10–3 mm2/s.
Conclusion:
Due to the difference of ADC values, the authors propose that DWI and ADC mapping could be a promising tool in the diagnostic work-up of paragangliomas.
Zusammenfassung
Hintergrund:
Paragangliome sind seltene benigne Tumoren. In wenigen Fällen ist jedoch eine Abgrenzung zu wichtigen Differentialdiagnosen nicht möglich.
Patienten und Methodik:
In die vorliegende Studie wurden zehn Patienten mit Raumforderungen der Schädelbasis eingeschlossen; sieben Glomus-jugulare-Tumoren, ein Meningeom, ein Neurinom und ein Riesenzelltumor. Zusätzlich zur konventionellen MR-Bildgebung wurden eine Diffusionsbildgebung (DWI) und ein apparentes Diffusionskoeffizienten- (ADC-)Mapping durchgeführt.
Ergebnisse:
Die mittleren ADC-Werte ± Standardabweichung lagen für die Glomustumoren bei 1,304 ± 0,257 × 10–3mm2/s, für die Vergleichsgruppe bei 0,743 ± 0,108 × 10–3 mm2/s und 0,802 ± 0,075 × 10–3 mm2/s für das angrenzende Kleinhirn.
Schlussfolgerung:
Aufgrund der deutlichen Unterschiede der ADC-Werte scheinen die DWI und das ADC-Mapping in der Diagnostik von Glomustumoren einen wertvollen Beitrag leisten zu können.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Neumann HP, Pawlu C, Peczkowska M, Bausch B, McWhinney SR, Muresan M, Buchta M, Franke G, Klisch J, Bley TA, Hoegerle S, Boedeker CC, Opocher G, Schipper J, Januszewicz A, Eng C, European-American Paraganglioma Study Group. Distinct clinical features of paraganglioma syndromes associated with SDHB and SDHD gene mutations. JAMA 2004;292:943–51
Löwenheim H, Koerbel A, Ebner FH, Kumagami H, Ernemann U, Tatagiba M. Differentiating imaging findings in primary and secondary tumors of the jugular foramen. Neurosurg Rev 2006;29:1–11, discussion 12–3
Arnold SM, Strecker R, Scheffler K, Spreer J, Schipper J, Neumann HPH, Klisch J. Dynamic contrast enhancement of paragangliomas of the head and neck: evaluation with time-resolved 2D-MR projection angiography. Eur Radiol 2003;13:1608–11
Coley SC, Romanowski CAJ, Hodgson TJ, Griffith PD. Dural arteriovenous fistulae: non-invasive diagnosis with dynamic MR digital subtraction angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2002;23:404–7
Klisch J, Strecker R, Hennig J, Schumacher M. Time resolved projection MRA: clinical application in intracranial vascular malformation. Neuroradiology 2000;42:104–7
Ziyeh S, Schumacher M, Strecker R, Rossler J, Hochmuth A, Klisch J. Head and neck vacular malformations: time-resolved MR projection angiography. Neuroradiology 2003;45:681–6
Strecker R, Scheffler K, Klisch J, Lenhardt S, Winterer J, Laubenberger J, Fischer H, Hennig J. Fast functional MRA using time-resolved projection MR angiography with correlation analysis. Magn Reson Med 2000;43:303–9
Wetzel SG, Bilecen D, Lyrer P. Cerebral dural arteriovenous fistulas: detection by dynamic MRPA. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2000;174:1293–5
Yoshikawa T, Aoki S, Hori M, Nambu A, Kumagai H, Araki T. Time-resolved two-dimensional thick-slice magnetic resonance digital subtraction angiography. Eur Radiol 2000;10:736–44
Barger AV, Block WF, Toropov Y, Grist TM, Mistretta CA. Time-resolved contrast-enhanced imaging with isotropic resolution and broad coverage using an undersampled 3D projection trajectory. Magn Reson Med 2002;48:297–305
Vogl TJ, Mack MG, Juergens M, Bergman C, Grevers G, Jacobsen TF, Lissner J, Felix R. Skull base tumors: gadodiamide injection-enhanced MR-imaging: dropout effect in the early enhancement pattern of paragangliomas versus different tumors. Radiology 1993;188:339–48
Fisch U, Mattox D. Microsurgery of the skull base. Stuttgart–New York: Thieme, 1988:149–53
Sumi M, Sakihama N, Sumi T, Morikawa M, Uetani M, Kabasawa H, Shigeno K, Hayashi K, Takahashi H, Nakamura T. Discrimination of metastatic cervical lymph nodes with diffusion-weighted MR imaging in patients with head and neck cancer. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2003; 24:1627–34
Habermann CR, Gossrau P, Graessner J, Arndt C, Cramer MC, Reitmeier F, Jaehne M, Adam G. Diffusion-weighted echo-planar MRI: a valuable tool for differentiating primary parotid tumors? Rofo 2005;177:940–5
Abdel Razek AA, Soliman NY, Elkhamary S, Alsharaway MK, Tawfik A. Role of diffusion-weighted MR imaging in cervical lymphadenopathy. Eur Radiol 2006;16:1468–77
Aschenbach R, Eger C, Esser D, Klisch J, Basche S. Diffusion-weighted imaging and ADC-mapping of paragangliomas of the jugular fossa at 1.5T. Proceedings of the 43rd Annual Meeting of ASNR 2005, Toronto, May 23, 2005:52.presentation 104
Tzika AA, Zarifi MK, Goumnerova L, Astrakas LG, Zurakowski D, Young- Poussaint T, Anthony DC, Scott RM, Black PM. Neuroimaging in pediatric brain tumors: Gd-DTPA-enhanced, hemodynamic, and diffusion MR imaging compared with MR spectroscopic imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2002;23:322–33
Castillo M, Smith JK, Kwock L, Wilber K. Apparent diffusion coefficient in the evaluation of high-grade cerebral gliomas. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2001;22:60–4
Sinha S, Bastin ME, Whittle IR, Wardlaw JM. Diffusion tensor imaging of high-grade cerebral gliomas. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2002;23:520–7
Kono K, Inoue Y, Nakayama K, Shakudo M, Morino M, Ohata K, Wakasa K, Yamada R. The role of diffusion weighted imaging in patients with brain tumors. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2001;22:1081–8
DeLano MC, Cooper TG, Siebert JE, Potchen MJ, Kuppusamy K. High b-value diffusion weighted MR imaging of adult brain: image contrast and apperent diffusion coefficient map features. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2000;21:1830–6
Mack MG, Rieger J, Baghi M, Bisdas S, Vogl TJ. Cervical lymph nodes. Eur J Radiol 2008;66:493–500
Chen S, Ikawa F, Kurisu K, Arita K, Takaba J, Kanou Y. Quantitative MR evaluation of intracranial epidermoid tumors by fast fluid-attenuated inversion recovery imaging and echo-planar diffusion-weighted imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2001;22:1089–96
Wang J, Takashima S, Takayama F, Kawakami S, Saito A, Matsushita T, Momose M, Ishiyama T. Head and neck lesions: characterization with diffusion- weighted echo-planar MR imaging. Radiology 2001;220:621–30
Simon JE, Czechowsky DK, Hill MD, Harris AD, Buchan AM, Frayne R. Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery preparation: not an improvement over conventional diffusion-weighted imaging at 3T in acute ischemic stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2004;25:1653–8
Ziyeh S, Strecker R, Berlis A, Weber J, Klisch J, Mader I. Dynamic 3D MR angiography of intra and extra cranial vascular malformations at 3T. A technical note. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2005;26:630–4
Srinivasan A, Dvorak R, Perni K, Rohrer S, Mukherji SK. Differentiation of benign and malignant pathology in the head and neck using 3T apparent diffusion coefficient values: early experience. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 2008;29:40–4
Nakayama T, Yoshimitsu K, Irie H, Aibe H, Tajima T, Shinozaki K, Nishie A, Asayama Y, Kakihara D, Matsuura S, Honda H. Usefulnes of the calculated apparent diffusion coefficient value in the differential diagnosis of retroperitoneal masses. J Magn Reson Imaging 2004;20:735–42
Vandecaveye V, De Keyzer F, Nuyts S, Deraedt K, Dirix P, Hamaekers P, Vander Poorten V, Delaere P, Hermans R. Detection of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma with diffusion weighted MRI after (chemo)therapy: correlation between radiologic and histopathologic findings. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2007;67:960–71
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
*Published in part at the 43rd Annual Meeting of the American Society of Neuroradiology, May 23, 2005, Toronto, Canada.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aschenbach, R., Basche, S., Vogl, T.J. et al. Diffusion-Weighted Imaging and ADC Mapping of Head-and-Neck Paragangliomas. Clin Neuroradiol 19, 215–219 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-009-9004-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-009-9004-1