Abstract
Background
Zolpidem is a nonbenzodiazepine sedative/hypnotic that acts at GABAA receptors to influence inhibitory neurotransmission throughout the central nervous system. A great deal is known about the behavioral effects of this drug in humans and laboratory animals, but little is known about zolpidem’s specific effects on neurochemistry in vivo.
Objectives
We evaluated how acute administration of zolpidem affected levels of GABA, glutamate, glutamine, and other brain metabolites.
Materials and methods
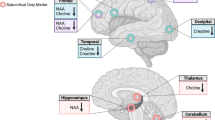
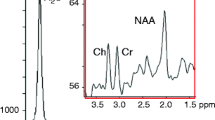
Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1H MRS) at 4 T was employed to measure the effects of zolpidem on brain chemistry in 19 healthy volunteers. Participants underwent scanning following acute oral administration of a therapeutic dose of zolpidem (10 mg) in a within-subject, single-blind, placebo-controlled, single-visit study. In addition to neurochemical measurements from single voxels within the anterior cingulate (ACC) and thalamus, a series of questionnaires were administered periodically throughout the experimental session to assess subjective mood states.
Results
Zolpidem reduced GABA levels in the thalamus, but not the ACC. There were no treatment effects with respect to other metabolite levels. Self-reported ratings of “dizzy,” “nauseous,” “confused,” and “bad effects” were increased relative to placebo, as were ratings on the sedation/intoxication (PCAG) and psychotomimetic/dysphoria (LSD) scales of the Addiction Research Center Inventory. Moreover, there was a significant correlation between the decrease in GABA and “dizzy.”
Conclusions
Zolpidem engendered primarily dysphoric-like effects and the correlation between reduced thalamic GABA and “dizzy” may be a function of zolpidem’s interaction with α1GABAA receptors in the cerebellum, projecting through the vestibular system to the thalamus.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benavides J, Peny B, Dubois A, Perrault G, Morel E, Zivkovic B, Scatton B (1988) In vivo interaction of zolpidem with central benzodiazepine (BZD) binding sites (as labeled by [3H]Ro 15-1788) in the mouse brain. Preferential affinity of zolpidem for the omega 1 (BZD1) subtype. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 245:1033–1041
Brambilla P, Stanley JA, Nicoletti M, Harenski K, Forster Wells K, Mallinger AG, Keshavan MS, Soares JC (2002) 1H MRS brain measures and acute lorazepam administration in healthy human subjects. Neuropsychopharmacology 26:546–551
Brefel-Courbon C, Payoux P, Ory F, Sommet A, Slaoui T, Raboyeau G, Lemesle B, Puel M, Montastruc JL, Demonet JF, Cardebat D (2007) Clinical and imaging evidence of zolpidem effect in hypoxic encephalopathy. Ann Neurol 62:102–105
Brodal P, Bjaalie JG (1992) Organization of the pontine nuclei. Neurosci Res 13:83–118
Brodeur MR, Stirling AL (2001) Delirium associated with zolpidem. Ann Pharmacother 35:1562–1654
Burau T, Schilling AM, Seyfert S, Spies C, Wolf KJ (1997) Cerebral drug effects investigated by 1H MR spectroscopy in volunteers and patients [abstract]. In: Proceedings of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 5:1244
Davanzo P, Oshiro T, Thomas MS, Shah B, Belin T, McCracke J, Ke Y (1997) 1H MR Spectroscopy in human brain with and without lorazepam [abstract]. In: Proceedings of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine 5:1226
Evans SM, Funderburk FR, Griffiths RR (1990) Zolpidem and triazolam in humans: behavioral and subjective effects and abuse liability. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 255:1246–1255
Finelli LA, Landolt HP, Buck A, Roth C, Berthold T, Borbély AA, Achermann P (2000) Functional neuroanatomy of human sleep states after zolpidem and placebo: a H215O-PET study. J Sleep Res 9:161–173
Fritschy JM, Mohler H (1995) GABAA-receptor heterogeneity in the adult rat brain: differential regional and cellular distribution of seven major subunits. J Comp Neurol 359:154–194
Ganzoni E, Santoni JP, Chevillard V, Sébille M, Mathy B (1995) Zolpidem in insomnia: a 3-year post-marketing surveillance study in Switzerland. J Int Med Res 23:61–73
Gillin JC, Buchsbaum MS, Valladares-Neto DC, Hong CC-H, Hazlett E, Langer SZ, Wu J (1996) Effects of zolpidem on local cerebral glucose metabolism during non-REM sleep in normal volunteers: a positron emission tomography study. Neuropsychopharmacology 15:302–313
Goddard AW, Mason GF, Appel M, Rothman DL, Gueorguieva R, Behar KL, Krystal JH (2004) Impaired GABA neuronal response to acute benzodiazepine administration in panic disorder. Am J Psychiatry 161:2186–2193
Hadingham KL, Wingrove P, Le Bourdelles B, Palmer KJ, Ragan CI, Whiting PJ (1993) Cloning of cDNA sequences encoding human alpha 2 and alpha 3 gamma-aminobutyric acidA receptor subunits and characterization of the benzodiazepine pharmacology of recombinant alpha 1-, alpha 2-, alpha 3-, and alpha 5-containing human gamma-aminobutyric acidA receptors. Mol Pharmacol 43:970–975
Haertzen CA (1966) Development of scales based on patterns of drug effects, using the Addiction Research Center Inventory (ARCI). Psychol Rep 18:163–194
Hajak G, Bandelow B (1998) Safety and tolerance of zolpidem in the treatment of disturbed sleep: a post-marketing surveillance of 16944 cases. Int Clin Psychopharmacol 13:157–167
Harazin J, Berigan TR (1999) Zolpidem tartrate and somnambulism. Mil Med 164:669–670
Hoehns JD, Perry PJ (1993) Zolpidem: a nonbenzodiazepine hypnotic for treatment of insomnia. Clin Pharm 12:814–828
Huang CL, Chang CJ, Hung CF, Lin HY (2003) Zolpidem-induced distortion in visual perception. Ann Pharmacother 37:683–686
Jasinski DR (1977) Assessment of the abuse potential of morphine-like drugs (methods used in man). In: Martin WR (ed) Drug addiction I, vol 45/1. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 197–258
Karnath HO, Ferber S, Dichgans J (2000) The neural representation of postural control in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:13931–13936
Kassem MN, Bartha R (2003) Quantitative proton short-echo-time LASER spectroscopy of normal human white matter and hippocampus at 4 Tesla incorporating macromolecule subtraction. Magn Reson Med 49:918–927
Khan ZU, Gutierrez A, Mehta AK, Miralles CP, De Blas AL (1996) The α4 subunit of the GABAA receptors from rat brain and retina. Neuropharmacology 35:1315–1322
Langtry HD, Benfield P (1990) Zolpidem: a review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties and therapeutic potential. Drugs 40:291–313
Liappas IA, Malitas PN, Dimopoulos NP, Gitsa OE, Liappas AI, Nikolau ChK, Christodoulou GN (2003) Zolpidem dependence case series: possible neurobiological mechanisms and clinical management. J Psychopharmacol 17:131–135
Licata SC, Penetar DM, Dunlap S, Lukas SE (2008a) A therapeutic dose of zolpidem has limited abuse-like effects in drug-naïve females: a pilot study. Eur J Pharmacol 598:64–67
Licata SC, Platt DM, Cook JM, Van Linn ML, Rowlett JK (2008b) Contribution of α1 subunit-containing γ-aminobutyric acidA (GABAA) receptors to motor-impairing effects of benzodiazepines in squirrel monkeys. Psychopharmacology (in press)
Markowitz JS, Brewerton TD (1996) Zolpidem-induced psychosis. Ann Clin Psychiatry 8:89–91
Matthew E, Andreason P, Pettigrew K, Carson RE, Herscovitch P, Cohen R, King C, Johanson CE, Greenblatt DJ, Paul SM (1995) Benzodiazepine receptors mediate regional blood flow changes in the living human brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 92:2775–2779
McKernan RM, Rosahl TW, Reynolds DS, Sur C, Wafford KA, Atack JR, Farrar S, Myers J, Cook G, Ferris P, Garrett L, Bristow L, Marshall G, Macaulay A, Brown N, Howell O, Moore KW, Carling RW, Street LJ, Castro JL, Ragan CI, Dawson GR, Whiting PJ (2000) Sedative but not anxiolytic properties of benzodiazepines are mediated by the GABAA receptor alpha 1 subtype. Nat Neurosci 3:587–592
Meng H, May PJ, Dickman JD, Angelaki DE (2007) Vestibular signals in primate thalamus: properties and origins. J Neurosci 27:13590–13602
Merica H, Fortune RD (2004) State transitions between week and sleep, and within the ultradian cycle, with focus on the link to neuronal activity. Sleep Med Rev 8:473–485
Mescher M, Merkle M, Kirsch J, Garwood M, Gruetter R (1998) Simultaneous in vivo spectral editing and water suppression. NMR Biomed 11:266–272
Mintzer MZ, Frey JM, Griffiths RR (1998) Zolpidem is differentiated from triazolam in humans using a three-response drug discrimination procedure. Behav Pharmacol 9:545–559
Morgenthaler TI, Silber MH (2002) Amnestic sleep-related eating disorder associated with zolpidem. Sleep Med 3:323–327
Morlock RJ, Tan M, Mitchell DY (2006) Patient characteristics and patterns of drug use for sleep complaints in the United States: analysis of National Ambulatory Medical Survey Data, 1997–2002. Clin Ther 28:1044–1053
Najjar M (2007) Zolpidem and amnestic sleep related eating disorder. J Clin Sleep Med 15:637–638
Nakamura M, Ishii M, Niwa Y, Yamazaki M, Ito H (2005) Temporal changes in postural sway caused by ultrashort-acting hypnotics: triazolam and zolpidem. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec 67:106–112
Öngür D, Jensen JE, Prescott AP, Stork C, Lundy M, Cohen BM, Renshaw PF (2008) Abnormal glutamatergic neurotransmission and neuronal glial interactions in acute mania. Biol Psychiatry 64:718–726
Pirker S, Schwarzer C, Wieselthaler A, Sieghart W, Sperk G (2000) GABA(A) receptors: immunocytochemical distribution of 13 subunits in the adult rat brain. Neuroscience 101:815–850
Pritchett DB, Seeburg PH (1990) Type I and type II GABAA-benzodiazepine receptors produced in transfected cells. Science 245:1389–1392
Provencher SW (1993) Estimation of metabolite concentrations from localized in vivo proton NMR spectra. Magn Reson Med 30:672–679
Roger M, Attali P, Coquelin JP (1993) Multicenter, double-blind, controlled comparison of zolpidem and triazolam in elderly patients with insomnia. Clin Ther 15:127–136
Rudolph U, Crestani F, Benke D, Brunig I, Benson JA, Fritschy JM, Martin JR, Bleuthmann H, Möhler H (1999) Benzodiazepine actions mediated by specific gamma-aminobutyric acid (A) receptor subtypes. Nature 401:796–800
Rush CR (1998) Behavioral pharmacology of zolpidem relative to benzodiazepines: a review. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 61:253–269
Rush CR, Griffiths RR (1996) Zolpidem, triazolam, and temazepam: behavioral and subject-rated effects in normal volunteers. J Clin Psychopharmacol 16:146–157
Rush CR, Madakasira S, Goldman NH, Woolverton WL, Rowlett JK (1997) Discriminative stimulus effects of zolpidem in pentobarbital-trained subjects: II. Comparison with triazolam and caffeine in humans. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 280:174–188
Rush CR, Armstrong DL, Ali JA, Pazzaglia PJ (1998) Benzodiazepine-receptor ligands in humans: acute performance-impairing, subject-rated and observer-rated effects. J Clin Psychopharmacol 18:154–165
Rush CR, Baker RW, Wright K (1999) Acute behavioral effects and abuse potential of trazodone, zolpidem and triazolam in humans. Psychopharmacology 144:220–233
Salva P, Costa J (1995) Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of zolpidem. Clin Pharmacokinet 29:142–153
Sanger DJ, Perrault G, Morel E, Joly D, Zivkovic B (1987) The behavioral profile of zolpidem, a novel hypnotic drug of imidazopyridine structure. Physiol Behav 41:235–240
Sanna E, Busonero F, Talani G, Carta M, Massa F, Peis M, Maciocco E, Biggio G (2002) Comparison of the effects of zaleplon, zolpidem, and triazolam at various GABA(A) receptor subtypes. Eur J Pharmacol 451:103–110
Schulte RF, Boesiger P (2006) ProFit: two-dimensional prior knowledge fitting of the J-resolved spectra. NMR Biomed 19:255–263
Sharma A, Dewan VK (2005) A case report of zolpidem-induced somnambulism. Prim Care Companion J Clin Psychiatry 7:74
Smith SA, Levante TO, Meier BH, Ernst RR (1994) Computer simulations in magnetic resonance. An object oriented programming approach. J Magn Reson A 106:75–105
Stoops WW, Rush CR (2003) Differential effects in humans after repeated administrations of zolpidem and triazolam. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse 29:281–299
Sur C, Farrar SJ, Kerby J, Whiting PJ, Atack JR, McKernan RM (1999) Preferential coassembly of α4 and δ subunits of the γ-aminobutyric acidA receptor in rat thalamus. Mol Pharmacol 56:110–115
Théberge J, Menon RS, Williamson PC, Drost DJ (2005) Implementation issues of multivoxel STEAM-localized 1H spectroscopy. Magn Reson Med 53:713–718
Tighilet B, Lacour M (2001) Gamma amino butyric acid (GABA) immunoreactivity in the vestibular nuclei of normal and unilateral vestibular neurectomized cats. Eur J Neurosci 13:2255–2267
Toner LC, Tsambiras BM, Catalano G, Catalano MC, Cooper DS (1999) Central nervous system side effects associated with zolpidem treatment. Clin Neuropharmacol 23:54–58
Troy SM, Lucki I, Unruh MA, Cevallos WH, Leister CA, Martin PT, Furlan PM, Mangano R (2000) Comparison of the effects of zaleplon, zolpidem, and triazolam on memory, learning, and psychomotor performance. J Clin Psychopharmacol 20:328–337
Tsai MJ, Tsai YH, Huang YB (2007) Compulsive activity and anterograde amnesia after zolpidem use. Clin Toxicol 45:179–181
Tsai MJ, Huang YB, Wu PC (2003) A novel clinical pattern of visual hallucination after zolpidem use. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol 41:869–872
Veselis RA, Reinsel RA, Beattie BJ, Mawlawi OR, Feshchenko VA, DiResta GR, Larson SM, Blasberg RG (1997) Midazolam changes cerebral blood flow in discrete brain regions: an H2(15)O positron emission tomography study. Anesthesiology 87:1106–1117
Victorri-Vigneau C, Dailly E, Veyrac G, Jolliet P (2007) Evidence of zolpidem abuse and dependence: results of the French Centre for Evaluation and Information on Pharmacodependence (CEIP) network survey. Br J Clin Pharmacol 64:198–209
Volkow ND, Wang GJ, Hitzemann R, Fowler JS, Pappas N, Lowrimore P, Burr G, Pascani K, Overall J, Wolf AP (1995) Depression of thalamic metabolism by lorazepam is associated with sleepiness. Neuropsychopharmacology 12:123–132
Wang GJ, Volkow ND, Overall J, Hitzemann RJ, Pappas N, Pascani K, Fowler JS (1996) Reproducibility of regional brain metabolic responses to lorazepam. J Nucl Med 37:1609–1613
Wisden W, Laurie DJ, Monyer H, Seeburg PH (1992) The distribution of 13 GABAA receptor subunit mRNAs in the rat brain. I. Telencephalon, diencephalon, mesencephalon. J Neurosci 12:1040–1062
Yang W, Dollear M, Muthukrishnan SR (2005) One rare side effect of zolpidem—sleepwalking: a case report. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 86:1265–1266
Acknowledgements
The authors thank R. Ross MacLean for his expert assistance. The authors also thank Dr. George Trksak for the helpful discussion regarding statistical analyses. This study was funded by the National Institutes on Drug Abuse grants K01 DA023659 (Dr. Licata), K05 DA000343 (Dr. Lukas), and K24 DA151116 (Dr. Renshaw). The authors have no financial relationships with the National Institutes on Drug Abuse. The experiments described herein complied with the current laws of the United States of America.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Licata, S.C., Jensen, J.E., Penetar, D.M. et al. A therapeutic dose of zolpidem reduces thalamic GABA in healthy volunteers: a proton MRS study at 4 T. Psychopharmacology 203, 819–829 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-008-1431-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-008-1431-1