Abstract
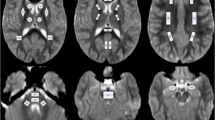
Diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) allows us to image the motion of tissue water. This has been used to demonstrate acute ischaemia. Diffusion imaging is also sensitive to water movement along neuronal tracts. Our objective was to map brain maturation in vivo using maps of apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC). We studied 22 children without neurological disease aged between 2 and 720 days. MRI was performed at 1.5 tesla. Multislice single-shot echoplanar DWI was performed at b 0 and 1000 s/mm2. ADC maps were generated automatically and measurements were performed in the basal ganglia, frontal and temporal white matter and the pons. There was a decrease over time in water diffusion in the areas examined, most marked in the frontal (0.887–1.898×10–3 mm2/s) and temporal (1.077–1.748×10–3 mm2/s)lobes. There was little change, after an initial decrease, in the basal ganglia (0.690–1.336×10–3 mm2/s). There was a difference in water diffusion between the anterior (0.687–1.581×10–3 mm2/s) and posterior (0.533–1.393×10–3 mm2/s) pons. These changes correlate well with those observed in progressive myelination: the increased water content probably reflects incomplete myelination and the decrease with time in water motion reflects the increase in myelinated brain.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Martin E, Kikinis R, Zuerrer M, et al (1988) Developmental stages of human brain: an MR study. J Comput Assist Tomogr 12: 917–922
Martin E, Boesch C, Zuerrer M, et al (1990) MR imaging of brain maturation in normal and developmentally handicapped children. J Comput Assist Tomogr14: 685–692
Le Bihan D, Breton E, Lallemand D, Grenier P, Cabanis E, Laval-Jeantet M (1986) MR imaging of intravoxel incoherent motions: application to diffusion and perfusion in neurologic disorders. Radiology 161: 401–407
Lövblad K, Laubach H, Baird A, et al (1998) Clinical experience with diffusion-weighted MR in patients with acute stroke. AJNR 19: 1061–1066
Bydder GM, Rutherford MA, Cowan FM (2001) Diffusion-weighted imaging in neonates. Child's Nerv Syst 17: 190–194
Beaulieu C, D'Arceuil H, Hedehus M, de Crespigny A, Kastrup A, Moseley ME (1999) Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging: theory and potential applications to child neurology. Semin Pediatr Neurol 6: 87–100
Forbes KP, Pipe JG, Bird CR. (2002) Changes in brain water diffusion during the 1st year of life. Radiology 222: 405–409
Engelbrecht V, Scherer A, Rassek M, Witsack HJ, Modder U(2002) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging in the brain in children: findings in the normal brain and in the brain with white matter diseases. Radiology 222: 410–418
Weber J, Mattle HP, Heid O, Remonda L, Schroth G (2000) Diffusion-weighted imaging in ischaemic stroke: a follow-up study. Neuroradiology 42: 184–191
Gelal FM, Grant PE, Fischbein NJ, Henry RG, Vigneron DB, Barkovich AJ (2001) The role of isotropic diffusion MRI in children under 2 years of age. Eur Radiol 11: 1006–1014
Huppi PS, Maier SE, Peled S, et al (1998) Microstructural development of human newborn cerebral white matter assessed in vivo by diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging. Pediatr Res 44: 584–590
Klingberg T, Vaidya CJ, Gabrieli JD, Moseley ME, Hedehus M (1999) Myelination and organization of the frontal white matter in children: a diffusion tensor MRI study. NeuroReport 10: 2817–2821
Morriss MC, Zimmerman RA, Bilaniuk LT, Hunter JV, Haselgrove JC (1999) Changes in brain water diffusion during childhood. Neuroradiology 41: 929–934
Wimberger DM, Roberts TP, Barkovich AJ, Prayer LM, Moseley ME, Kucharczyk J (1995) Identification of "premyelination" by diffusion-weighted MRI. J Comput Assist Tomogr 19: 28–33
Vorisek I, Sykova E (1997) Evolution of anisotropic diffusion in the developing rat corpus callosum. J Neurophysiol 78: 912–919
Toft PB, Leth H, Peitersen B, Lou HC, Thomsen C (1996) The apparent diffusion coefficient of water in gray and white matter of the infant brain. J Comput Assist Tomogr 20: 1006–1011
Miller SP, Vigneron DB, Henry RG, et al (2002) Serial quantitative diffusion tensor MRI of the premature brain: Development in newborns with and without injury. J Magn Reson Imaging 16: 621–632
Schmithorst VJ, Wilke M, Dardzinski BJ, Holland SK (2002) Correlation of white matter diffusivity and anisotropy with age during childhood and adolescence: a cross-sectional diffusion-tensor MR imaging study. Radiology 222: 212–218
Boujraf S, Luypaert R, Shabana W, De Meirleir L, Sourbron S, Osteaux M (2002) Study of pediatric brain development using magnetic resonance imaging of anisotropic diffusion. Magn Reson Imaging 20: 327–336
Mukherjee P, Miller JH, Shimony JS, et al (2001) Normal brain maturation during childhood: developmental trends characterized with diffusion-tensor MR imaging. Radiology 221: 349–358
Mukherjee P, Miller JH, Shimony JS, et al (2002) Diffusion-tensor MR imaging of gray and white matter development during normal human brain maturation. AJNR 23: 1445–1456
Acknowledgements
This study was financed by Swiss National Science Foundation Grant 3100–066348.01
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lövblad, K.O., Schneider, J., Ruoss, K. et al. Isotropic apparent diffusion coefficient mapping of postnatal cerebral development. Neuroradiology 45, 400–403 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-003-1009-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-003-1009-x