Abstract
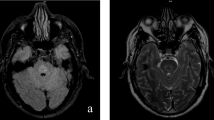
Central pontine myelinolysis (CPM) is one of the serious neurological complications of alcoholism. This study evaluated magnetic resonance images of sequelae of CPM. Approximately 600 alcoholic patients were examined by a 1.0-T magnetic resonance imaging device, and 11 patients were retrospectively found to have a central pontine lesion, a presumed sequela of CPM. The lesions had various shapes and most were cavitary. In 3 of the 11 patients bilateral symmetrical oval lesions were faintly visible in the middle cerebellar peduncles. These middle cerebellar peduncular lesions were diagnosed as having Wallerian degeneration of the pontocerebellar tract secondary to CPM.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams RD, Victor M, Mancall EL (1959) Central pontine myelinolysis. A hitherto undescribed disease occurring in alcoholic and malnourished patients. Arch Neurol Psychiatry 81:154–172
Miller GM, Baker HL Jr, Okazaki H, Whisnant JP (1988) Central pontine myelinolysis and its imitators: MR findings. Radiology 168:795–802
Gocht A, Colmant HJ (1987) Central pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis: a report of 58 cases. Clin Neuropathol 6:262–270
Koci TM, Chiang F, Chow P, Wang A, Chiu LC, Itabashi H, Mehringer CM (1990) Thalamic extrapontine lesions in central pontine myelinolysis. Am J Neuroradiol 11:1229–1233
Bourgouin PM, Chalk C, Richardson J, Duang H, Vezina JL (1995) Subcortical white matter lesions in osmotic demyelination syndrome. Am J Neuroradiol 16:1495–1497
Mangat KS, Sherlala K (2002) Cerebellar peduncle myelinolysis: case report. Neuroradiology 44:768–769
Ohuchi T, Kuru Y, Ri K, Hayashi T, Yasuda R, Honda S, Maki S (1998) Wallerian degeneration of the pontocerebellar tracts and cerebellar atrophy following pontine bleeding. Rinsho Hoshasen 43:449–455
Gallucci M, Amicarelli I, Rossi A, Stratta P, Masciocchi C, Zobel BB, Casacchia M, Passariello R (1989) MR imaging of white matter lesions in uncomplicated chronic alcoholism. J Comput Assist Tomogr 13:395–398
Ho VB, Fitz CR, Yoder CC, Geyer CA (1993) Resolving MR features in osmotic myelinolysis (central pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis). Am J Neuroradiol 14:163–167
Korogi Y, Takahashi M, Shinzato J, Sakamoto Y, Mitsuzaki K, Hirai T, Yoshizumi K (1993) MR findings in two presumed cases of mild central pontine myelinolysis. Am J Neuroradiol 14:651–654
Yuh WTC, Simonson TM, D'Alessandro MP, Smith KS, Hunsicker LG (1995) Temporal changes of MR findings in central pontine myelinolysis. Am J Neuroradiol 16:975–977
McGraw P, Edwards-Brown MK (1998) Reversal of MR findings of central pontine myelinolysis. J Comput Assist Tomogr 22:989–991
Niehaus L, Kulozik A, Lehmann R (2001) Reversible central pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis in a 16-year-old girl. Childs Nerv Syst 17:294–296
Chu K, Kang DW, Ko SB, Kim M (2001) Diffusion-weighted MR findings of central pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis. Acta Neurol Scand 104:385–388
Laubenberger J, Schneider B, Ansorge O, Goetz F, Haussinger D, Volk B, Langer M (1996) Central pontine myelinolysis: clinical presentation and radiologic findings. Eur Radiol 6:177–183
Menger H, Jorg J (1999) Outcome of central pontine and extrapontine myelinolysis (n=44). J Neurol 246:700–705
Norenberg MD (1983) A hypothesis of osmotic endothelial injury. A pathogenetic mechanism in central pontine myelinolysis. Arch Neurol 40:66–69
Lien YH, Shapiro JI, Chan L (1991) Study of brain electrolytes and organic osmolytes during correction of chronic hyponatremia. Implications for the pathogenesis of central pontine myelinolysis. J Clin Invest 88:303–309
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uchino, A., Yuzuriha, T., Murakami, M. et al. Magnetic resonance imaging of sequelae of central pontine myelinolysis in chronic alcohol abusers. Neuroradiology 45, 877–880 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-003-1095-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-003-1095-9