Abstract
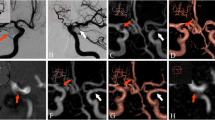
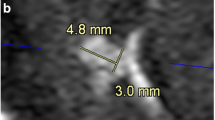
Two MRA techniques were evaluated for the follow-up of coiled intracranial aneurysms. Twenty-nine coiled aneurysms were evaluated for a total of 36 follow-up assessments using 3D time-of flight MRA (TOF MRA), an auto-triggered elliptic–centric-ordered three-dimensional gadolinium-enhanced MR angiogram (ATECO MRA), as well as a selective digital subtraction angiography (DSA), which served as the “gold standard”. Confident visualization was seen in 36 (100%) of ATECO MRAs and in 32 (89%) of the TOF MRAs. Eleven residual aneurysm components (RACs) greater than 2 mm were described on DSA. Of these, nine were seen on ATECO MRA (sensitivity of 81% and specificity of 88%) and four were seen on TOF MRA (sensitivity of 40% and specificity of 90%). The two RACs not seen on ATECO MRA both measured 3 mm. The six RACs not seen on TOF MRA measured 3, 4 and 5 mm. ATECO MRA provides a non-invasive reliable angiogram for the surveillance of coiled aneurysms and is superior to TOF MRA for this purpose.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dion J (2003) Brain aneurysms successfully treated without open surgery. In: RSNA press release and media briefing 19 June 2003. RSNA, New York
Molyneux A, Kerr R, Stratton I, et al (2002) International subarachnoid aneurysm trial (ISAT) of neurosurgical clipping versus endovascular coiling in 2143 patients with ruptured intracranial aneurysms: a randomised trial. Lancet 360:1267–1274
Ausman JI (2001) The death of cerebral aneurysm surgery. Surg Neurol 56:348
Lindsay KW (2003) The impact of the international subarachnoid aneurysm treatment trial (ISAT) on neurosurgical practice. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 145:97–99
Byrne JV, Sohn MJ, Molyneux AJ, Chir B (1999) Five-year experience in using coil embolization for ruptured intracranial aneurysms: outcomes and incidence of late rebleeding. J Neurosurg 90:656–663
Vinuela F, Duckwiler G, Mawad M (1997) Guglielmi detachable coil embolization of acute intracranial aneurysm: perioperative anatomical and clinical outcome in 403 patients. J Neurosurg 86:475–482
Roy D, Milot G, Raymond J (2001) Endovascular treatment of unruptured aneurysms. Stroke 32:1998–2004
Willinsky RA, Taylor SM, terBrugge K, Farb RI, Tomlinson G, Montanera W (2003) Neurologic complications of cerebral angiography: prospective analysis of 2,899 procedures and review of the literature. Radiology 227:522–528
Farb RI, McGregor C, Kim JK, et al (2001) Intracranial arteriovenous malformations: real-time auto-triggered elliptic-centric-ordered 3D gadolinium-enhanced MR angiography—initial assessment. Radiology 220:244–251
Farb R, Scott J, Willinsky R, Montanera W, Wright G, terBrugge K (2003) Intracranial venous system: gadolinium-enhanced three-dimensional MR venography with auto-triggered elliptic centric-ordered sequence—initial experience. Radiology 206:203–209
Farb RI, Kim J, Willinsky RA, et al (2002) Spinal dural arteriovenous fistula localization with a technique of first-pass gadolinium-enhanced MR angiography: initial experience. Radiology 222:843–850
Maki JH, Prince MR, Londy FJ, Chenevert TL (1996) The effects of time varying intravascular signal intensity and k-space acquisition order on three-dimensional MR angiography image quality. J Magn Reson Imaging 6:642–651
Wilman AH, Riederer SJ, King BF, Debbins JP, Rossman PJ, Ehman RL (1997) Fluoroscopically triggered contrast-enhanced three-dimensional MR angiography with elliptical–centric view order: application to the renal arteries. Radiology 205:137–146
Fleiss JL (1981) Statistical methods for rates and proportions, 2nd edn. Wiley, New York
Connor SE, West RJ, Yates DA (2001) The ability of plain radiography to predict intracranial aneurysm occlusion instability during follow-up of endosaccular treatment with Guglielmi detachable coils. Neuroradiology 43:680–686
Cottier JP, Bleuzen-Couthon A, Gallas S, et al (2003) Follow-up of intracranial aneurysms treated with detachable coils: comparison of plain radiographs, 3D time-of-flight MRA and digital subtraction angiography. Neuroradiology 45:818–824
Turner CL, Higgins JN, Kirkpatrick PJ (2003) Assessment of transcranial color-coded duplex sonography for the surveillance of intracranial aneurysms treated with Guglielmi detachable coils. Neurosurgery 53:866–871; discussion 871–872
Masaryk AM, Frayne R, Unal O, Rappe AH, Strother CM (2000) Utility of CT angiography and MR angiography for the follow-up of experimental aneurysms treated with stents or Guglielmi detachable coils. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1523–1531
Hartman J, Nguyen T, Larsen D, Teitelbaum GP (1997) MR artifacts, heat production, and ferromagnetism of Guglielmi detachable coils. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 18:497–501
Kahara VJ, Seppanen SK, Ryymin PS, Mattila P, Kuurne T, Laasonen EM (1999) MR angiography with three-dimensional time-of-flight and targeted maximum-intensity-projection reconstructions in the follow-up of intracranial aneurysms embolized with Guglielmi detachable coils. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:1470–1475
Derdeyn CP, Graves VB, Turski PA, Masaryk AM, Strother CM (1997) MR angiography of saccular aneurysms after treatment with Guglielmi detachable coils: preliminary experience. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 18:279–286
Brunereau L, Cottier JP, Sonier CB, et al (1999) Prospective evaluation of time-of-flight MR angiography in the follow-up of intracranial saccular aneurysms treated with Guglielmi detachable coils. J Comput Assist Tomogr 23:216–223
Anzalone N, Righi C, Simionato F, et al (2000) Three-dimensional time-of-flight MR angiography in the evaluation of intracranial aneurysms treated with Guglielmi detachable coils. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:746–752
Weber W, Yousry TA, Felber SR, et al (2001) Noninvasive follow-up of GDC-treated saccular aneurysms by MR angiography. Eur Radiol 11:1792–1797
Nome T, Bakke SJ, Nakstad PH (2002) MR angiography in the follow-up of coiled cerebral aneurysms after treatment with Guglielmi detachable coils. Acta Radiol 43:10–14
Cottier JP, Bleuzen-Couthon A, Gallas S, et al (2003) Intracranial aneurysms treated with Guglielmi detachable coils: is contrast material necessary in the follow-up with 3D time-of-flight MR angiography? AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1797–1803
Leclerc X, Navez JF, Gauvrit JY, Lejeune JP, Pruvo JP (2002) Aneurysms of the anterior communicating artery treated with Guglielmi detachable coils: follow-up with contrast-enhanced MR angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1121–1127
Boulin A, Pierot L (2001) Follow-up of intracranial aneurysms treated with detachable coils: comparison of gadolinium-enhanced 3D time-of-flight MR angiography and digital subtraction angiography. Radiology 219:108–113
Hochmuth A, Spetzger U, Schumacher M (2002) Comparison of three-dimensional rotational angiography with digital subtraction angiography in the assessment of ruptured cerebral aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1199–1205
Hoff DJ, Wallace MC, terBrugge KG, Gentili F (1994) Rotational angiography assessment of cerebral aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 15:1945–1948
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farb, R.I., Nag, S., Scott, J.N. et al. Surveillance of intracranial aneurysms treated with detachable coils: a comparison of MRA techniques. Neuroradiology 47, 507–515 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-005-1375-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-005-1375-7