Abstract
Introduction:
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) may help identify acute stroke patients with a higher potential benefit from thrombolytic therapy. The aim of our study was to assess the correlation between initial cerebral infarct (CI) volume (quantified on diffusion-weighted MRI) and the resulting clinical outcome in acute stroke patients with middle cerebral artery (MCA) (M1–2 segment) occlusion detected on MRI angiography treated by intravenous/intraarterial thrombolysis.
Methods:
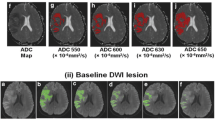
Initial infarct volume (VDWI-I ) was retrospectively compared with neurological deficit evaluated using the NIH stroke scale on admission and 24 h later, and with the 90-day clinical outcome assessed using the modified Rankin scale in a series of 25 consecutive CI patients. The relationship between infarct volume and neurological deficit severity was assessed and, following the establishment of the maximum VDWI-I still associated with a good clinical outcome, the patients were divided into two groups (VDWI-I ≤70 ml and >70 ml).
Results:
VDWI-I ranged from 0.7 to 321 ml. The 24-h clinical outcome improved significantly (P=0.0001) in 87% of patients with a VDWI-I ≤70 ml (group 1) and deteriorated significantly (P=0.0018) in all patients with a VDWI-I >70 ml (group 2). The 90-day mortality was 0% in group 1 and 71.5% in group 2. The 90-day clinical outcome was significantly better in group 1 than in group 2 (P=0.026).
Conclusion:
Clinical outcome could be predicted from initial infarct volume quantified by MRI-DWI in acute CI patients with MCA occlusion treated by intravenous/intraarterial thrombolysis. Patients with a VDWI-I ≤70 ml had a significantly better outcome.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jansen O, Knauth M, Sartor K (1999) Advances in clinical neuroradiology. Akta Neurol 26:1–7
Rotta J (1997) Should thrombolytic therapy be the first-line treatment for acute ischemic stroke? N Engl J Med 337:1309–1310
Schellinger PD, Jansen O, Fiebach JB, Pohlers O, Ryssel H, Heiland S, Steiner T, Hacke W, Sartor K (2000) Feasibility and practicality of MR imaging of stroke in the management of hyperacute cerebral ischemia. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1184–1189
Fiebach JB, Jansen O, Schellinger PD, Knauth M, Hartmann M, Heiland S, Ryssel H, Pohlers O, Hacke W, Sartor K (2001) Comparison of CT with diffusion-weighted MRI in patients with hyperacute stroke. Neuroradiology 43:628–632
Schellinger PD, Fiebach JB, Jansen O, Ringleb PA, Mohr A, Steiner T, Heiland S, Schwab S, Pohlers O, Ryssel H, Orakcioglu B, Sartor K, Hacke W (2001) Stroke magnetic resonance imaging within 6 hours after onset of hyperacute cerebral ischemia. Ann Neurol 49:460–469
Parsons MW, Barber PA, Chalk J, Darby DG, Rose S, Desmond PM, Gerraty RP, Tress BM, Wright PM, Donnan GA, Davis SM (2002) Diffusion and perfusion-weighted MRI response on thrombolysis in stroke. Ann Neurol 51:28–37
Röther J, Schellinger PD, Gass A, Sieber M, Villringer A, Fiebach JB, Fiehler J, Jansen O, Kucinski T, Schoder V, Szabo K, Junge-Hülsing GJ, Hennerici M, Zeumer H, Sartor K, Weiller C, Hacke W (2002) Effect of intravenous thrombolysis on MRI parameters and functional outcome in acute stroke <6 h. Stroke 33:2438–2445
Davalos A, Blanco M, Pedraza S, Leira B, Castellanos M, Pumar JM, Silva Y, Serena J, Castillo J (2004) The Clinical-DWI mismatch: a new diagnostic approach to the brain tissue risk of infarction. Neurology 62:2187–2192
Warach S, Chien D, Li W, Ronthal M, Edelman RR (1992) Fast magnetic resonance diffusion-weighted imaging of acute human stroke. Neurology 42:1717–1723
Baird AE, Warach S (1998) Magnetic resonance imaging of acute stroke. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 18:583–609
Lovblad KO, Laubach HJ, Baird AE, Curtin F, Schlaug G, Edelman RR, Warach S (1998) Clinical experience with diffusion-weighted MR in patients with acute stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:1061–1066
Ay H, Buonanno FS, Rodorf G, Schaefer PW, Schwamm LH, Wu O, Gonzalez RG, Yamada K, Sorensen GA, Koroshetz WJ (1999) Normal diffusion-weighted MRI during stroke-like deficits. Neurology 52:1784–1792
Neumann-Haefelin T, Moseley ME, Albers GW (2000) New magnetic resonance imaging methods for cerebrovascular disease: emerging clinical applications. Ann Neurol 47:559–570
Oppenheim C, Logak M, Dormont D, Lehericy S, Manai R, Samson Y, Marsault C, Rancurel G (2000) Diagnosis of acute ischemic stroke with fluid attenuated inversion recovery and diffusion-weighted MR sequences. Neuroradiology 42:602–607
Oppenheim C, Samson Y, Manai R, Laam T, Vandamme X, Crozier S, Srour A, Cornu P, Dormont D, Rancurel G, Marsault C (2000) Prediction of malignant middle cerebral artery infarction by diffusion-weighted imaging. Stroke 31:2175–2181
Jansen O, Brückmann H (2002) Ischemic brain diseases. In: Sartor K (ed) Diagnostic and interventional neuroradiology. Thieme, Stuttgart New York, p 148
Mullins ME, Lev MH, Schellingerhout D, Koroshetz WJ, Gonzales RG (2002) Influence of availability of clinical history on detection of early stroke using unenhanced CT and diffusion-weighted MR imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol 179:223–228
Mullins ME, Schaefer PW, Sorensen AG, Halpern EF, Ay H, He J, Koroshetz WJ, Gonzalez RG (2002) CT and conventional and diffusion weighted MR Imaging in acute stroke: study in 961 patients at presentation to the emergency department. Radiology 224:353–360
Warach S, Li W, Ronthal M, Edelman RR (1992) Acute cerebral ischemia: evaluation with dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging and MR angiography. Radiology 182:41–47
Evans AJ, Richardson DB, Tien R, Mac Fall JR, Hedlund LW, Heinz ER, Boyko O, Sostman HD (1993) Poststenotic signal loss in MR angiography; effects of echo time, flow compensation and fractional echo. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 14:721–729
Schellinger PD, Jansen O, Fiebach JB, Heiland S, Steiner T, Schwab S, Pohlers O, Ryssel H, Sartor K, Hacke W (2000) Monitoring intravenous recombinant tissue plasminogen activator thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke with diffusion and perfusion MRI. Stroke 31:1318–1328
Grant PE, He HJ, Halpern E, Wu O, Schaefer PW, Schwamm LH, Budzik RF, Sorensen AG, Koroshetz WJ, Gonzalez RG (2001) Frequency and clinical context of decreased apparent diffusion coefficient reversal in the human brain. Radiology 221:43–50
Crisostomo RA, Garcia MM, Tong DC (2003) Detection of diffusion-weighted MRI abnormalities in patients with transient ischemic attack. Correlation with clinical characteristics. Stroke 34:932–937
Schaefer PW, Hassankhani A, Pulman C, Sorensen G, Schwamm L, Koroshetz W, Gonzales GR (2004) Characterization and evolution of diffusion MR imaging abnormalities in stroke patients undergoing intra-arterial thrombolysis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:951–957
Kidwell CS, Saver J, Mattiello J, Starkman S, Vinuela F, Duckwiler G, Gobin YP, Jahan R, Vespa P, Kalafut M, Alger JR (2000) Thrombolytic reversal of acute human cerebral ischemic injury shown by diffusion/perfusion magnetic resonance imaging. Ann Neurol 47:462–469
Nighoghossian N, Hermier M, Adeleine P, Derex L, Durgor JF, Philippeau F, Ylmaz H, Honnorat J, Dardel P, Berthezene Y, Froment JC, Trouillas P (2003) Baseline magnetic resonance imaging parameters and stroke outcome in patients treated by intravenous tissue plasminogen activator. Stroke 34:458–463
Derex L, Nighoghossian N, Hermier M, Adeleine P, Berthezène, Philippeau F, Honnorat J, Froment J-C, Trouillas P (2004) Influence of pretreatment MRI parameters on clinical outcome, recanalization and infarct size in 49 stroke patients treated by intravenous tissue plasminogen activator. J Neurol Sci 225:3–9
Albers GW (1999) Expanding the window for thrombolytic therapy in acute stroke. The potential role of acute MRI for patient selection. Stroke 30:2230–2237
Barber PA, Davis SM, Darby DG, Desmond PM, Gerraty RP, Yang Q, Jolley D, Donnan GA, Tress BM (1999) Absent middle cerebral artery flow predict the presence and evolution of the ischemic penumbra. Neurology 52:1125–1132
Dugar N, Hoggard N, Wilkinson ID, Griffiths PD (2001) MR Imaging in acute stroke. Imaging Decis 5:2–19
Samson Y, Crozier S, Deltour S, Obadia M, Manai R, Oppenheim C, Marro B, Dormont D, Marsault C, Rancurel G (2002) L’IRM en urgence avant la thrombolyse (abstract). Rev Neurol Paris 158:1S20
Fiebach JB, Schellinger PD, Sartor K, Heiland S, Warach S, Hacke W (2003) Stroke MRI. Steinkopff Verlag, Darmstadt, pp 54–61
Schellinger PD, Fiebach JB, Hacke W (2003) Imaging-based decision making in thrombolytic therapy for ischemic stroke. Stroke 34:575–583
Hacke W, Kaste M, Bogousslavsky J, Brainin M, Chamorro A, Lees K, Leys D, Kwiecinski H, Toni P, Langhorne P, Diener C, Hennerici M, Ferro J, Sivenius J, Gunnar N, Bath P, Olsen TS, Gugging M, European Stroke Initiative Executive Committee and the EUSI Writing Committee (2003) European Stroke Initiative Recommendations for Stroke Management – update 2003. Cerebrovasc Dis 16:311–337
Highasida RT, Furlan AJ (2003) Trial design and reporting standards for intra-arterial cerebral thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 34:109–137
Selim M, Fink JN, Kumar S, Caplan LR, Horkan C, Chen Y, Linfante I, Schlaug G (2002) Predictors of hemorrhagic transformation after intravenous recombinant tissue plasminogen activator. Stroke 33:2047–2052
Barber PA, Darby DG, Desmond PM, Yang Q, Gerraty RP, Jolley D, Donnan GA, Tress BM, Davis SM (1998) Prediction of stroke outcome with echoplanar perfusion- and diffusion-weighted MRI. Neurology 51:418–426
Neumann-Haefelin T, Witsack HJ, Wenserski F, Siebler M, Seitz RJ, Modder U, Freund HJ (1999) Diffusion and perfusion-weighted MRI: the DWI/PWI mismatch region in acute stroke. Stroke 30:1591–1597
Grandin CB, Duprez TP, Smith AM, Mataigne F, Peeters A, Oppenheim C, Cosnard G (2001) Usefulness magnetic resonance-derived quantitative measurements of cerebral blood flow and volume in prediction of infarct growth in hyperacute stroke. Stroke 32:1147–1153
Sorensen AG, Copen WA, Ostergaard L, Buomanno FS, Gonzales RG, Rordorf G, Rosen BR, Schwamm LH, Weisskoff RM, Koroshetz WJ (1999) Hyperacute stroke: simultaneous measurement of relative cerebral blood volume, relative cerebral blood flow, and mean tissue transit time. Radiology 210:519–527
Heiss WD, Sobesky J, Hesselmann V (2004) Identifying thresholds for penumbra and irreversible tissue damage. Stroke 35:2671–2674
Acknowledgements
We thank Ms. Lucie Kopuletá and Ms. Michaela Kotzmundová, Department of Radiology, Division of MRI, University Hospital, Olomouc, Czech Republic, for their technical help in MRI data processing. This work was supported by the IGA Ministry of Health, Czech Republic (grant number NR/8579-3/2005).
Study protocol was in compliance with the Declaration of Helsinki (1964) and was approved by the Ethical Committee of the University Hospital, Olomouc, Czech Republic.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Šaňák, D., Nosál′, V., Horák, D. et al. Impact of diffusion-weighted MRI-measured initial cerebral infarction volume on clinical outcome in acute stroke patients with middle cerebral artery occlusion treated by thrombolysis. Neuroradiology 48, 632–639 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-006-0105-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-006-0105-0