Abstract
Introduction
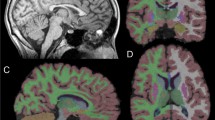
Lysosomal disorders are rare and are caused by genetically transmitted lysosomal enzyme deficiencies. A decreased T2 signal in the thalamus has occasionally been reported.
Aims
Because the finding of bilateral abnormal signal intensity of the thalamus on T2-weighted images has not been systematically reviewed, and its value as a diagnostic tool critically evaluated, we carried out a systematic review of the literature.
Methods
Articles in English with 30 trios of keywords were collected from PubMed. Exclusion criteria were lack of conventional T2-weighted images in the protocol and not being a human study. Finally, 111 articles were included. The thalamus was considered affected only if mentioned in the text or in the figure legends.
Results
Some 117 patients with various lysosomal diseases and five patients with ceruloplasmin deficiency were reported to have a bilateral decrease in T2 signal intensity. At least one article reported a bilateral decrease in signal intensity of the thalami on T2-weighted images in association with GM1 and GM2 gangliosidosis and with Krabbe’s disease, aspartylglucosaminuria, mannosidosis, fucosidosis, and mucolipidosis IV. Furthermore, thalamic alteration was a consistent finding in several types of neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis (NCL) including CLN1 (infantile NCL), CLN2 (classic late infantile NCL), CLN3 (juvenile NCL), CLN5 (Finnish variant late infantile NCL), and CLN7 (Turkish variant late infantile NCL).
Conclusion
A decrease in T2 signal intensity in the thalami seems to be a sign of lysosomal disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agamanolis D (2005) Metabolic and toxic disorders. In: Prayson R, Goldblum J (eds) Neuropathology. Elsevier Churchill Livingstone, Philadelphia, pp 339–372
Pastores GM, Kolodny EH (2006) Lysosomal storage diseases. In: Swaiman KF, Ashwall S, Ferriero DM (eds) Pediatric neurology: principles and practice. Mosby Elsevier, Philadelphia, pp 659–714
Autti T, Raininko R, Vanhanen S-L, Kallio M, Santavuori P (1994) MRI of the normal brain from early childhood to middle age. I Appearances on T2- and proton density-weighted images and occurrence of incidental high-signal foci. Neuroradiology 36:644–648
Autti T, Raininko R, Vanhanen S-L, Kallio M, Santavuori P (1994) MRI of the normal brain from early childhood to middle age. II. Age dependence of signal intensity changes on T2-weighted images. Neuroradiology 36:649–651
Barkovich AJ (ed) (2005) Pediatric neuroimaging. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 76–189
Morita H, Ikeda S, Yamamoto K et al (1995) Hereditary ceruloplasmin deficiency with hemosiderosis: a clinicopathological study of a Japanese family. Ann Neurol 37:646–656
Hatanaka Y, Okano T, Oda K, Yamamoto K, Yoshida K (2003) Aceruloplasminemia with juvenile-onset diabetes mellitus caused by exon skipping in the ceruloplasmin gene. Intern Med 42:599–604
Yonekawa M, Okabe T, Asamoto Y, Ohta M (1998) A case of hereditary ceruloplasmin deficiency with iron deposition in the brain associated with chorea, dementia, diabetes mellitus and retinal pigmentation: administration of fresh-frozen human plasma. Eur Neurol 42:157–162
Al-Essa MA, Bakheet SM, Patay ZJ, Nounou RM, Ozand PT (1999) Cerebral fuorine-18 labeled 2-fluoro-2-deoxyglucose positron emission tomography (FDG PET), MRI, and clinical observations in a patient with infantile G(M1) gangliosidosis. Brain Dev 21:559–562
Chen CY, Zimmerman RA, Lee CC, Chen FH, Yuh YS, Hsiao HS (1998) Neuroimaging findings in late infantile GM1 gangliosidosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:1628–1630
Kobayashi O, Takashima S (1994) Thalamic hyperdensity on CT in infantile GM1-gangliosidosis. Brain Dev 16:472–474
Aydin K, Bakir B, Tatli B, Terzibasioglu E, Ozmen M (2005) Proton MR spectroscopy in three children with Tay-Sachs disease. Pediatr Radiol 35:1081–1085
Grosso S, Farnetani MA, Berardi R et al (2003) GM2 gangliosidosis variant B1 neuroradiological findings. J Neurol 250:17–21
Mugikura S, Takahashi S, Higano S, Kurihara N, Kon K, Sakamoto K (1996) MR findings in Tay-Sachs disease. J Comput Assist Tomogr 20:551–555
Yun YM, Lee SN (2005) A case report of Sandhoff disease. Korean J Ophthalmol 19:68–72
Yuksel A, Yalcinkaya C, Islak C, Gunduz E, Seven M (1999) Neuroimaging findings of four patients with Sandhoff disease. Pediatr Neurol 21:562–565
Hittmair K, Wimberger D, Bernert G, Mallek R, Schindler EG (1996) MRI in a case of Sandhoff’s disease. Neuroradiology 38 [Suppl 1]:S78–S80
Caliskan M, Ozmen M, Beck M, Apak S (1993) Thalamic hyperdensity – is it a diagnostic marker for Sandhoff disease. Brain Dev 15:387–388
Koelfen W, Freund M, Jaschke W, Koenig S, Schultze C (1994) GM-2 gangliosidosis (Sandhoff’s disease): two year follow-up by MRI. Neuroradiology 36:152–154
Zafeiriou DI, Anastasiou AL, Michelakaki EM, Augoustidou-Savvopoulou PA, Katzos GS, Kontopoulos EE (1997) Early infantile Krabbe disease: deceptively normal magnetic resonance imaging and serial neurophysiological studies. Brain Dev 19:488–491
Zafeiriou DI, Michelakaki EM, Anastasiou AL, Gombakis NP, Kontopoulos EE (1996) Serial MRI and neurophysiological studies in late-infantile Krabbe disease. Pediatr Neurol 15:240–244
Vanhanen SL, Raininko R, Santavuori P (1994) Early differential diagnosis of infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis, Rett syndrome, and Krabbe disease by CT and MR. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 15:1443–1453
Bernardi B, Fonda C, Franzoni E, Marchiani V, Della Guistina E, Zimmerman RA (1994) MRI and CT in Krabbe’s disease: case report. Neuroradiology 36:477–479
Finelli DA, Tarr RW, Sawyer RN, Horwitz SJ (1994) Deceptively normal MR in early infantile Krabbe disease. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 15:167–171
Barone R, Bruhl K, Stoeter P, Fiumara A, Pavone L, Beck M (1996) Clinical and neuroradiological findings in classic infantile and late-onset globoid-cell leukodystrophy (Krabbe disease). Am J Med Genet 63:209–217
Percy AK, Odrezin GT, Knowles PD, Rouah E, Armstrong DD (1994) Globoid cell leukodystrophy: comparison of neuropathology with magnetic resonance imaging. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 88:26–32
Autti T, Raininko R, Haltia M et al (1997) Aspartylglucosaminuria: radiologic course of the disease with histopathologic correlation. J Child Neurol 12:369–375
Ara JR, Mayayo E, Marzo ME, Guelbenzu S, Chabas A, Pina MA, Calderon C (1999) Neurological impairment in alpha-mannosidosis: a longitudinal clinical and MRI study of a brother and sister. Childs Nerv Syst 15:369–371
Inui K, Akagi M, Nishigaki T, Muramatsu T, Tsukamoto H, Okada S (2000) A case of chronic infantile type of fucosidosis: clinical and magnetic resonance image findings. Brain Dev 22:47–49
Autti T, Raininko R, Launes J, Nuutila A, Santavuori P (1992) Jansky-Bielschowsky variant disease: CT, MRI and SPECT findings. Pediatric Neurol 8:121–126
Vanhanen SL, Raininko R, Autti T, Santavuori P (1996) MRI evaluation of the brain in infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis. Part 2: MRI findings in 21 patients. J Child Neurol 10:444–450
Autti T, Raininko R, Vanhanen SL, Santavuori P (1996) MRI of neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis. I. Cranial MRI of 30 patients with juvenile neuronal ceroidl lipofuscinosis. Neuroradiology 38:476–782
Topçu M, Tan H, Yalnızoğlu D et al (2004) Evaluation of 36 patients from Turkey with neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis: clinical, neurophysiological, neuroradiological and histopathologic studies. Turk J Pediatr 46:1–10
Frei KP, Patronas NJ, Crutchfield KE. Altarescu G, Schiffmann R (1998) Mucolipidosis type IV: characteristic MRI findings. Neurology 51:565–569
Inglese M, Nusbaum AO, Pastores GM, Gianutsos J, Kolodny EH, Gonen O (2005) MR imaging and proton spectroscopy of neural injury in late-onset GM2 gangliosidosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2037–2042
Gururaj A, Sztriha L, Hertecant, J, Johansen JG, Georgiou T, Campos Y, Drousiotou A, d’Azzo A (2005) Magnetic resonance imaging findings and novel mutations in GM1 gangliosidosis. J Child Neurol 20:57–60
Streifler JY, Gornish M, Hadar H, Gadoth N (1993) Brain imaging in late-onset GM2 gangliosidosis. Neurology 43:2055–2058
Uyama E, Terasaki T, Watanabe S, Naito M, Owada M, Araki S, Ando M (1992) Type 3 GM1 gangliosidosis: characteristic MRI findings correlated with dystonia. Acta Neurol Scand 86:609–615
Fukumizu M, Yoshikawa H, Takashima S, Sakuragawa N, Kurokawa T (1992) Tay-Sachs disease: progression of changes on neuroimaging in four cases. Neuroradiology 34:483–486
Seitz D, Grodd W, Schwab A, Seeger U, Klose U, Nagele T (1998) MR imaging and localized proton MR spectroscopy in late infantile neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19:1373–1377
Choi S, Enzmann DR (1993) Infantile Krabbe disease: complementary CT and MR findings. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 14:1164–1166
Chang YC, Huang CC, Chen CY, Zimmerman RA (2000) MRI in acute neuropathic Gaucher’s disease. Neuroradiology 42:48–50
Moore DF, Ye F, Schiffmann R, Butman JA (2003) Increased signal intensity in the pulvinar on T1-weighted images: a pathognomonic MR imaging sign of Fabry disease. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1096–1101
Politei JM, Capizzano AA (2006) Magnetic resonance image findings in 5 young patients with Fabry disease. Neurologist 12:103–105
Gupta S, Ries M, Kotsopoulos S, Schiffmann R (2005) The relationship of vascular glycolipid storage to clinical manifestations of Fabry disease: a cross-sectional study of a large cohort of clinically affected heterozygous women. Medicine (Baltimore) 84:261–268
Takanashi J, Barkovich AJ, Dillon WP, Sherr EH, Hart KA, Packman S (2003) T1 hyperintensity in the pulvinar: key imaging feature for diagnosis of Fabry disease. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:916–921
Morse RP, Kleta R, Alroy J, Gahl WA (2005) Novel form of intermediate salla disease: clinical and neuroimaging features. J Child Neurol 20:814–816
Parazzini C, Arena S, Marchetti L et al (2003) Infantile sialic acid storage disease: serial ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging features. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:398–400
Linnankivi T, Lonnqvist T, Autti T (2003) A case of Salla disease with involvement of the cerebellar white matter. Neuroradiology 45:107–109
Sonninen P, Autti T, Varho T, Hamalainen M, Raininko R (1999) Brain involvement in Salla disease. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:433–443
Varho T, Jaaskelainen S, Tolonen U, Sonninen P, Vainionpaa L, Aula P, Sillanpaa M (2000) Central and peripheral nervous system dysfunction in the clinical variation of Salla disease. Neurology 55:99–104
Haataja L, Parkkola R, Sonninen P et al (1994) Phenotypic variation and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in Salla disease, a free sialic acid storage disorder. Neuropediatrics 25:238–244
Melis D, Parenti G, Della Casa R et al (2004) Brain damage in glycogen storage disease type I. J Pediatr 144:637–642
Gutschalk A, Harting I, Cantz M, Springer C, Rohrschneider K, Meinck HM (2004) Adult alpha-mannosidosis: clinical progression in the absence of demyelination. Neurology 63:1744–1746
Patlas M, Shapira MY, Nagler A, Sheffer R, Gomori JM (2001) MRI of mannosidosis. Neuroradiology 43:941–943
Dietemann JL, Filippi de la Palavesa MM, Tranchant C, Kastler B (1990) MR findings in mannosidosis. Neuroradiology 32:485–487
Galluzzi P, Rufa A, Balestri P, Cerase A, Federico A (2001) MR brain imaging of fucosidosis type I. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:777–780
Ismail EA, Rudwan M, Shafik MH (1999) Fucosidosis: immunological studies and chronological neuroradiological changes. Acta Paediatr 88:224–227
Terespolsky D, Clarke JT, Blaser SI (1006) Evolution of the neuroimaging changes in fucosidosis type II. J Inherit Metab Dis 19:775–781
Provenzale JM, Barboriak DP, Sims K (1995) Neuroradiologic findings in fucosidosis, a rare lysosomal storage disease. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 16:809–813
Confort-Goyny S, Chabrol B, Vion-Dury J, Mancini J, Cozzone PJ (1993) MRI and localized proton MRS in early infantile form of neuronal ceroid-lipofuscinosis. Pediatr Neurol 9:57–60
Matheus MG, Castillo M, Smith JK, Armao D, Towle D, Muenzer J (2004) Brain MRI findings in patients with mucopolysaccharidosis types I and II and mild clinical presentation. Neuroradiology 46:666–672
Gabrielli O, Polonara G, Regnicolo L, Petroni V, Scarabino T, Coppa GV, Salvolini U (2004) Correlation between cerebral MRI abnormalities and mental retardation in patients with mucopolysaccharidoses. Am J Med Genet 125:224–231
Barone R, Parano E, Trifiletti RR, Fiumara A, Pavone P (2002) White matter changes mimicking a leukodystrophy in a patient with mucopolysaccharidosis: a characterization by MRI. J Neurol Sci 195:171–175
Barone R, Nigro F, Triulzi F, Musumeci S, Fiumara A, Pavone L (1999) Clinical and neuroradiological follow-up in mucopolysaccharidosis type III (Sanfilippo syndrome). Neuropediatrics 30:270–274
Hughes DG, Chadderton RD, Cowie RA, Wraith JE, Jenkins JP (1997) MRI of the brain and craniocervical junction in Morquio’s disease. Neuroradiology 39:381–385
Zafeiriou DI, Savvopoulou Augoustidou PA, Sewell A et al (2001) Serial magnetic resonance imaging findings in mucopolysaccharidosis IIIB (Sanfilippo’s syndrome B). Brain Dev 23:385–389
Petitti N, Holder CA, Williams DW 3rd (1997) Mucopolysaccharidosis III (San Filippo syndrome) type B: cranial imaging in two cases. J Comput Assist Tomogr 21:897–899
Shinomiya N, Nagayama T, Fujioka Y, Aoki T (1996) MRI in the mild type of mucopolysaccharidosis II (Hunter’s syndrome). Neuroradiology 38:483–485
Lee C, Dineen TE, Brack M, Kirsch JE, Runge VM (1994) The mucopolysaccharidoses: characterization by cranial MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 14:1285–1292
Parsons VJ, Hughes DG, Wraith JE (1996) Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain, neck and cervical spine in mild Hunter’s syndrome (mucopolysaccharidoses type II). Clin Radiol 51:719–723
Buyukgebiz B, Eroglu Y, Kovanlikaya I, Sen A, Buyukgebiz A (1995) Maroteaux-Lamy syndrome associated with growth hormone deficiency. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 8:305–307
Murata R, Nakajima S, Tanaka A, Miyagi N, Matsuoka O, Kogame S, Inoue Y (1989) MR imaging of the brain in patients with mucopolysaccharidosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 10:1165–1170
Gabrielli O, Salvolini U, Maricotti M, Mariani MG, Coppa GV, Giorgi PL (1992) Cerebral MRI in two brothers with mucopolysaccharidosis type 1 and different genotypes. Neuroradiology 34:313–315
Shimoda-Matsubayashi S, Kuru Y, Sumie H, Ito T, Hattori N, Okuma Y, Mizuno Y (1990) MRI findings in the mild type of mucopolysaccharidosis II (Hunter’s syndrome). Neuroradiology 32:328–330
Rauch RA, Friloux LA 3rd, Lott I (1989) MR imaging of cavitary lesions in the brain with Hurler/Scheie. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 10 (5 Suppl):S1–S3
Lee CC, Chen CY, Chou TY, Chen FH, Lee CC, Zimmerman RA (1996) Cerebral manifestations of Pompe disease in an infant. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 17:321–322
Al-Essa MA, Bakheet SM, Patay ZJ, Powe JE, Ozand PT (1999) Normal fluorine-18-labelled 2-fluoro-2-deoxyglucose positron emission tomography and magnetic resonance imaging of the brain in Wolman disease. J Inherit Metab Dis 22:846–848
Yang YL, Sun F, Zhang Y et al (2006) Clinical and laboratory survey of 65 Chinese patients with Leigh syndrome. Chin Med J 118:373–377
Mannan AA, Sharma MC, Shrivastava P et al (2004) Leigh’s syndrome. Indian J Pediatr 71:1029–1033
Crimi M, Papadimitriou A, Galbiati S et al (2004) A new mitochondrial DNA mutation in ND3 gene causing severe Leigh syndrome with early lethality. Pediatr Res 55:842–846
Filiano JJ, Goldenthal MJ, Mamourian AC, Hall CC, Marin-Garcia J (2002) Mitochondrial DNA depletion in Leigh syndrome. Pediatr Neurol 26:239–242
Cacic M, Wilichowski E, Mejaski-Bosnjak V et al (2001) Cytochrome c oxidase partial deficiency-associated Leigh disease presenting as an extrapyramidal syndrome. J Child Neurol 16:616–619
Nagashima T, Mori M, Katayama K et al (1999) Adult Leigh syndrome with mitochondrial DNA mutation at 8993. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 97:416–422
Chu BC, Terae S, Takahashi C et al (1999) MRI of the brain in the Kearns-Sayre syndrome: report of four cases and a review. Neuroradiology 41:759–764
Nakagawa E, Hirano S, Yamanouchi H, Goto Y, Nonaka I, Takashima S (1994) Progressive brainstem and white matter lesions in Kearns-Sayre syndrome: a case report. Brain Dev 16:416–418
Kim IO, Kim JH, Kim WS, Hwang YS, Yeon KM, Han MC (1996) Mitochondrial myopathy-encephalopathy-lactic acidosis-and strokelike episodes (MELAS) syndrome: CT and MR findings in seven children. AJR Am J Roentgenol 166:641–645
Wray SH, Provenzale JM, Johns DR, Thulborn KR (1995) MR of the brain in mitochondrial myopathy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 16:1167–1173
Nolli M, Barbieri A, Pinna C, Pasetto A, Nicosia F (2005) Wernicke’s encephalopathy in a malnourished surgical patient: clinical features and magnetic resonance imaging. Acta Anaesthesiol 49:1566–1570
Weidauer S, Nichtweiss M, Lanfermann H, Zanella FE (2003) Wernicke encephalopathy: MR findings and clinical presentation. Eur Radiol 13:1001–1009
Oka M, Terae S, Kobayashi R et al (2001) Diffusion-weighted MR findings in a reversible case of acute Wernicke encephalopathy. Acta Neurol Scand 104:178–181
Antunez E, Estruch R, Cardenal C, Nicolas JM, Fernandez-Sola J, Urbano-Marquez A (1998) Usefulness of CT and MR imaging in the diagnosis of acute Wenicke’s encephalopathy. AJR Am J Roentgenol 171:1131–1137
Hahn JS, Berquist W, Alcorn DM, Chamberlain L, Bass D (1998) Wernicke encephalopathy and beriberi during total parenteral nutrition attributable to multivitamin infusion shortage. Pediatrics 101:E10
Huang CC, Chu NS, Yen TC, Wai YY, Lu CS (2003) Dopamine transporter binding in Wilson’s disease. Can J Neurol Sci 30:163–167
Wu JC, Huang CC, Jeng LB, Chu NS (2000) Correlation of neurological manifestations and MR images in a patient with Wilson’s disease after liver transplantation. Acta Neurol Scand 102:134–139
Alanen A, Komu M, Penttinen M, Leino R (1999) Magnetic resonance imaging and proton spectroscopy in Wilson’s disease. Br J Radiol 72:749–756
Takahashi W, Yoshii F, Shinohara Y (1996) Reversible magnetic resonance imaging lesions in Wilson’s disease: clinical-anatomical correlation. J Neuroimaging 6:246–248
Huang CC, Chu NS (1998) Acute dystonia with thalamic and brainstem lesions after initial penicillamine treatment in Wilson’s disease. Eur Neurol 39:32–37
Sener RN (1993) Wilson’s disease: MRI demonstration of cavitations in basal ganglia and thalami. Pediatr Radiol 23:157
Saatci I, Topcu M, Baltaoglu FF, Kose G, Yalaz K, Renda Y, Besim A (1997) Cranial MR findings in Wilson’s disease. Acta Radiol 38:250–258
Huang CC, Chu NS (1996) Wilson’s disease: resolution of MRI lesions following long-term oral zinc therapy. Acta Neurol Scand 93:215–218
Binesh N, Huda A, Thomas MA et al (2006) Hepatic encephalopathy: a neurochemical, and neurophysiological study. J Appl Clin Med Phys 7:86–96
Miyaoka T, Yasukawa R, Mihara T et al (2005) Fluid-attenuated inversion-recovery MR imaging in schizophrenia-associated with idiopathic unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia (Gilbert’s syndrome). Eur Psychiatry 20:327–331
Yilmaz Y, Ekinci G (2002) Thalamic involvement in a patient with kernikterus. Eur Radiol 12:1837–1839
Ozdoba C, Pfenninger J, Schroth G (1997) Initial and follow-up MRI in a case of early diagnosed Reye’s syndrome. Neuroradiology 39:495–498
Hoon AH Jr, Reinhardt EM, Kelley RI, Breiter SN, Morton DH, Naidu SB, Johnston MV (1997) Brain magnetic resonance imaging in suspected extrapyramidal cerebral palsy: observations in distinguishing genetic-metabolic from acquired causes. J Pediatr 131:240–245
Schonberger S, Schweiger B, Schwahn B, Schwarz M, Wendel U (2004) Dysmyelination in the brain of adolescents and young adults with maple syrup urine disease. Mol Genet Metab 82:69–75
Majoie CB, Mourmans JM, Akkerman EM, Duran M, Poll-The BT (2004) Neonatal citrullemia: comparison of conventional MR, diffusion-weighted, and diffusion tensor findings. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:32–35
Takei Y, Akahane C, Ikeda S (2003) Osmotic demyelination syndrome: reversible MRI findings in bilateral cortical lesions. Intern Med 42:867–870
Bourgouin P, Chalk C, Richardson J, Duong H, Vezina J (1995) Subcortical white matter lesions in osmotic demyelination syndrome. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 16:1495–1497
Weber U, Huppe T, Niehaus L (2000) CT and MRI in severe hypophosphataemia with central nervous system involvement. Neuroradiology 42:112–114
Porto L, Lanferman H, Moller-Hartmann W, Jacobi G, Zanella F (1999) Acute necrotising encephalopathy of childhood after exanthema subitum outside Japan or Taiwan. Neuroradiology 41:732–734
Neilson DE, Eiben RM, Waniewski S et al (2003) Autosomal dominant acute necrotizing encephalopathy. Neurology 61:226–230
Hartfield DS, Loewy JA, Yager JY (1999) Transient thalamic changes on MRI in a child with hypernatremia. Pediatr Neurol 20:60–62
Kobari M, Nogawa S, Sugimoto Y, Fukuuchi Y (1997) Familial idiopathic brain calcification with autosomal dominant inheritance. Neurology 48:645–649
Nishio H, Kodama S, Matsuo T, Ichihashi M, Ito H, Fujiwara Y (1988) Cockayne syndrome: magnetic resonance images of the brain in a severe form with early onset. J Inherit Metab Dis 11:88–102
Rabi II, Zacharias JR, Millman S, Kusch P (1938) A new method of measuring nuclear magnetic moment. Phys Rev 53:318
Solomon I (1955) Relaxation processes in a system of two spins. Phys Rev 99:559–565
Bloembergen N, Purcell EM, Pound RV (1948) Relaxation effects in nuclear magnetic resonance absorption. Phys Rev 73:679–712
Cavanagh J, Fairbrother WJ, Palmer AG III, Skelton NJ (1996) Protein NMR spectroscopy: principles and practice. Academic Press, London, p 587
Holmberg V, Lauronen L, Autti T, Santavuori P, Savukoski M, Uvebrant P, Hofman I, Peltonen L, Jarvela I (2000) Phenotype-genotype correlation in eight patients with Finnish variant late infantile NCL (CLN5). Neurology 55:579–581
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Autti, T., Joensuu, R. & Åberg, L. Decreased T2 signal in the thalami may be a sign of lysosomal storage disease. Neuroradiology 49, 571–578 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-007-0220-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-007-0220-6