Abstract
Introduction
To demonstrate intratumoral susceptibility effects in malignant brain tumors and to assess visualization of susceptibility effects before and after administration of the paramagnetic contrast agent MultiHance (gadobenate dimeglumine; Bracco Imaging), an agent known to have high relaxivity, with respect to susceptibility effects, image quality, and reduction of scan time.
Methods
Included in the study were 19 patients with malignant brain tumors who underwent high-resolution, susceptibility-weighted (SW) MR imaging at 3 T before and after administration of contrast agent. In all patients, Multihance was administered intravenously as a bolus (0.1 mmol/kg body weight). MR images were individually evaluated by two radiologists with previous experience in the evaluation of pre- and postcontrast 3-T SW MR images with respect to susceptibility effects, image quality, and reduction of scan time.
Results
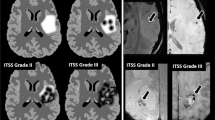
In the 19 patients 21 tumors were diagnosed, of which 18 demonstrated intralesional susceptibility effects both in pre- and postcontrast SW images, and 19 demonstrated contrast enhancement in both SW images and T1-weighted spin-echo MR images. Conspicuity of susceptibility effects and image quality were improved in postcontrast images compared with precontrast images and the scan time was also reduced due to decreased TE values from 9 min (precontrast) to 7 min (postcontrast).
Conclusion
The intravenous administration of MultiHance, an agent with high relaxivity, allowed a reduction of scan time from 9 min to 7 min while preserving excellent susceptibility effects and image quality in SW images obtained at 3 T. Contrast enhancement and intralesional susceptibility effects can be assessed in one sequence.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Reichenbach JR, Essig M, Haacke EM, Lee BC, Przetak C, Kaiser WA, Schad LR (1998) High-resolution venography of the brain using magnetic resonance imaging. MAGMA 6:62–69
Reichenbach JR, Haacke EM (2001) High-resolution BOLD venographic imaging: a window into brain function. NMR Biomed 14:453–467
Reichenbach JR, Jonetz-Mentzel L, Fitzek C, Haacke EM, Kido DK, Lee BC, Kaiser WA (2001) High-resolution blood oxygen-level dependent MR venography (HRBV): a new technique. Neuroradiology 43:364–369
Barth M, Nobauer-Huhmann IM, Reichenbach JR, Mlynarik V, Schoggl A, Matula C, Trattnig S (2003) High-resolution three-dimensional contrast-enhanced blood oxygenation level-dependent magnetic resonance venography of brain tumors at 3 Tesla: first clinical experience and comparison with 1.5 Tesla. Invest Radiol 38:409–414
Nobauer-Huhmann IM, Ba-Ssalamah A, Mlynarik V, Barth M, Schoggl A, Heimberger K, Matula C, Fog A, Kaider A, Trattnig S (2002) Magnetic resonance imaging contrast enhancement of brain tumors at 3 tesla versus 1.5 tesla. Invest Radiol 37:114–119
Noebauer-Huhmann IM, Pinker K, Barth M, Mlynarik V, Ba-Ssalamah A, Saringer WF, Weber M, Benesch T, Witoszynskyj S, Rauscher A, Reichenbach JR, Trattnig S (2006) Contrast-enhanced, high-resolution, susceptibility-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of the brain: dose-dependent optimization at 3 tesla and 1.5 tesla in healthy volunteers. Invest Radiol 41:249–255
Lin W, Mukherjee P, An H, Yu Y, Wang Y, Vo K, Lee B, Kido D, Haacke EM (1999) Improving high-resolution MR bold venographic imaging using a T1 reducing contrast agent. J Magn Reson Imaging 10:118–123
Sehgal V, Delproposto Z, Haacke EM, Tong KA, Wycliffe N, Kido DK, Xu Y, Neelavalli J, Haddar D, Reichenbach JR (2005) Clinical applications of neuroimaging with susceptibility-weighted imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 22:439–450
Sehgal V, Delproposto Z, Haddar D, Haacke EM, Sloan AE, Zamorano LJ, Barger G, Hu J, Xu Y, Prabhakaran KP, Elangovan IR, Neelavalli J, Reichenbach JR (2006) Susceptibility-weighted imaging to visualize blood products and improve tumor contrast in the study of brain masses. J Magn Reson Imaging 24:41–51
Tynninen O, Aronen HJ, Ruhala M, Paetau A, Von Boguslawski K, Salonen O, Jaaskelainen J, Paavonen T (1999) MRI enhancement and microvascular density in gliomas. Correlation with tumor cell proliferation. Invest Radiol 34:427–434
Reichenbach JR, Barth M, Haacke EM, Klarhofer M, Kaiser WA, Moser E (2000) High-resolution MR venography at 3.0 Tesla. J Comput Assist Tomogr 24:949–957
Bagley LJ, Grossman RI, Judy KD, Curtis M, Loevner LA, Polansky M, Detre J (1997) Gliomas: correlation of magnetic susceptibility artifact with histologic grade. Radiology 202:511–516
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pinker, K., Noebauer-Huhmann, I.M., Stavrou, I. et al. High-field, high-resolution, susceptibility-weighted magnetic resonance imaging: improved image quality by addition of contrast agent and higher field strength in patients with brain tumors. Neuroradiology 50, 9–16 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-007-0298-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-007-0298-x