Abstract
Introduction
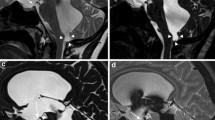
The objective of this study was to evaluate the role of phase-contrast cine magnetic resonance imaging (PC-MRI) in detecting possible communications between intraventricular arachnoid cysts (IV-ACs) and cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) spaces based on MR cisternography (MRC) comparison.
Materials and methods
Twenty-one patients with IV-AC were examined by PC-MRI and MRC. In order to determine the communication of IVAC with its neighbouring CSF spaces, PC-MRI was employed. The communication of IV-ACs with the ventricular system was examined on at least two anatomic planes. Precontrast images and PC-MRI were followed by the intrathecal administration of 0.5–1 ml gadopentetate dimeglumine. Early and delayed MRC were then carried out. Results of PC-MRI were compared with findings of MRC (McNemar’s test).
Results
In seven IV-ACs, no communication was detected by PC-MRI. In 14 IVACs, a pulsatile CSF flow into the IV-ACs was observed. All the IV-ACs, which have been determined as non-communicating (NC) on the PC-MRI, showed NC character on MRC as well. Six cases suggesting a communication on PC-MRI showed no communication on MRC. MRC revealed eight communicating (38%) and 13 NC (62%) IV-ACs among a total of 21 cases. The sensitivity and specificity of PC-MRI imaging in demonstrating the communication between the IV-ACs and the CSF were 100% and 54%, respectively.
Conclusion
PC-MRI is an effective method for evaluating NC IV-ACs. In order to decide about the management of IV-ACs, which are communicating according to the PC-MRI, the results should be confirmed with MRC if suspected jet flow is depicted.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schroeder HWS, Gaab MR, Niendorf WR (1996) Neuroendoscopic approach to arachnoid cysts. J Neurosurg 85:293–298
Miyajima M, Aral H, Okuda O, Hishii M, Nakanishi H, Sato K (2000) Possible origin of suprasellar arachnoid cysts: neuroimaging and neurosurgical observations in nine cases. J Neurosurg 93:62–67
Tali ET, Ercan N, Kaymaz M, Pasaoglu A, Jinkins JR (2004) Intrathecal gadolinium enhanced MR cisternography used to determine potential communication between the cerebrospinal fluid pathways and intracranial arachnoid cysts. Neuroradiology 46:744–754. doi:10.1007/s00234-004-1240-0
Acar O, Kocaogullar Y, Guney O (2003) Arachnoid cyst within the fourth ventricle: a case report. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 105:93–94. doi:10.1016/S0303-8467(02)00111-7
Yildiz H, Erdogan C, Yalcin R, Yazici Z, Hakyemez B, Parlak M, Tuncel E (2005) Evaluation of communication between intracranial arachnoid cysts and cisterns with phase-contrast cine MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:145–151
Hakyemez B, Yildiz H, Parlak M (2003) CSF connection of the intracranial cysts and cyst like lesions: analysis with flow sensitive phase-contrast cine MR imaging. Turk J Diagn Intervent Radiol 9:152–156
Pradilla G, Jallo G (2007) Arachnoid cysts: case series and review of the literature. Neurosurg Focus 22:1–4. doi:10.3171/foc.2007.22.2.7
Okamura K, Watanabe M, Inoue N, Kanoh M, Ohno T, Mitsui Y, Wakabayashi K (1996) Intraventricular arachnoid cyst- on the origin of intraventricular arachnoid cysts. No To Shinkei 48:1015–1021
Zada G, Krieger MD, McNatt SA, Bowen I, McComb G (2007) Pathogenesis and treatment of intracranial arachnoid cysts in pediatric patients younger than 2 years of age. Neurosurg Focus 22:1–5. doi:10.3171/foc.2007.22.2.1
Wester K (1996) Arachnoid cysts in adults: Experience with internal shunts to the subdural compartment. Surg Neurol 45:15–24. doi:10.1016/0090-3019(95)00383-5
Hoffmann KT, Hosten N, Meter BU, Röricht S, Sprung C, Oellinger J, Gutberlet M, Felix R (2000) CSF flow studies of intracranial cysts and cyst-like lesions achieved using reversed fast imaging with steady-state precession MR sequences. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:493–502
Sasaki M, Honda S, Yuasa T, Iwamura A, Shibata E, Ohba H (2008) Narrow CSF space at high convexity and high midline areas in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus detected by axial and coronal MRI. Neuroradiology 50:117–122. doi:10.1007/s00234-007-0318-x
Nilsson S, Örtoft K, Mölstad S (2008) The accuracy of general practitioners’ clinical assessment of chest pain patients. Eur J Gen Pract 14:1–6
Kadowaki C, Hara M, Numoto M, Takeuchi K, Saito I (1995) Cine magnetic resonance imaging of aqueductal stenosis. Childs Nerv Syst 11:107–111. doi:10.1007/BF00303815
Nitz WR, Bradley WG, Watanabe AS, Lee RR, Burgoyne B, O’Sullivan RM, Herbst MD (1992) Flow dynamics of cerebrospinal fluid: assessment with phase-contrast velocity MR imaging performed with retrospective cardiac gating. Radiology 183:395–405
Eguchi T, Taoka T, Nikaido Y, Shiomi K, Fujimoto T, Otsuka H, Takeuchi H (1996) Cine-magnetic resonance imaging evaluation of communication between middle cranial fossa arachnoid cysts and cisterns. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo) 36:353–357. doi:10.2176/nmc.36.353
Bargallo N, Olondo L, Garcia AI, Capurro S, Caral L, Rumia J (2005) Functional analysis of third ventriculostomy patency by quantification of CSF stroke volume by using cine phase-contrast MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:2514–2521
Sankari SSE, Lehmann P, Jouet GC, Fichten A, Godefroy O, Meyer ME, Baledent O (2009) Phase-contrast MR imaging support for the diagnosis of aqueductal stenosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30:209–214. doi:10.3174/A1308
Arbelaez A, Medina E, Rodríguez M, Londono AC, Castillo M (2007) Intrathecal Administration of gadopentetate dimeglumine for MR cisternography of nasoethmoidal CSF fistula. AJR Am J Roentgenol 188:560–564. doi:10.2214/AJR.05.1280
Goel G, Ravishankar S, Jayakumar PN, Vasudev MK, Shivshankar JJ, Rose D, Anandh B (2007) Intrathecal gadolinium-enhanced magnetic resonance cisternography in cerebrospinal fluid rhinorrhea: road ahead? J Neurotrauma 24:1570–1575. doi:10.1089/neu.2007.0326
Dillon WP (2008) Intrathecal gadolinium: its time has come? AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29:1–4. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A0884
Acknowledgement
We gratefully acknowledge Gokhan Ocakoglu, for his suggestions and for reviewing of the statistical analysis.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Algın, O., Hakyemez, B., Gokalp, G. et al. Phase-contrast cine MRI versus MR cisternography on the evaluation of the communication between intraventricular arachnoid cysts and neighbouring cerebrospinal fluid spaces. Neuroradiology 51, 305–312 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-009-0499-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-009-0499-6