Abstract
Introduction
Congenital brain arteriovenous fistulas (BAVFs) are rare vascular lesions, and conservative management was associated with a high mortality rate. We report our experience in the treatment of congenital BAVFs using detachable coils and Onyx liquid embolic agent.
Methods
Over the past 5 years, 15 patients with congenital BAVFs were treated endovascularly at our hospital using detachable coils and Onyx-34. All patients were clinically followed-up for 12–48 months. We retrospectively reviewed the medical records, cerebral angiograms, and endovascular reports for each patient.
Results
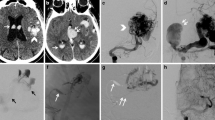
There were 15 patients with a total of 16 BAVFs (six men and nine women, with a mean age of 29.4 years). The clinical presentations were intracranial hemorrhage in six patients, headaches in four patients, and seizure in three patients, with two patients diagnosed incidentally. In all of the cases, transarterial microcatheterization was performed, 13 patients were treated with a combination of detachable coils and Onyx-34, and two with balloon-assisted coils and Onyx-34 embolization. There was no significant morbidity or mortality. All BAVF-related symptoms resolved immediately or gradually on clinical follow-up. Immediate angiographic obliteration was achieved in all patients. The fistulas remained closed in all patients, as ascertained by follow-up angiograms. No new neurological deficits related to the procedure were detected.
Conclusions
In our experience, the endovascular treatment of BAVFs with combination of detachable coils and Onyx is feasible, safe, and effective. This technique affords more control in the Onyx injection and minimizes the risk of distal embolization.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hung PC, Wang HS (2002) Successful endovascular treatment of cerebral arteriovenous fistula. Pediatr Neurol 27:300–302
Weon YC, Yoshida Y, Sachet M, Mahadevan J, Alvarez H, Rodesch G, Lasjaunias P (2005) Supratentorial cerebral arteriovenous fistulas (AVFs) in children: review of 41 cases with 63 non choroidal singlehole. Acta Neurochir 147:17–31
Luo CB, Teng MM, Chang FC, Chang CY (2006) Endovascular treatment of intracranial high-flow arteriovenous fistulas by Guglielmi detachable coils. J Chin Med Assoc 69:80–85
Andreuo A, Ioannidis I, Nasis N (2008) Transarterial balloon-assisted glue embolization of high-flow arteriovenous fistulas. Neuroradiology 50:267–272
Arat A, Inci S (2006) Treatment of a superior sagittal sinus dural arteriovenous fistula with Onyx: technical case report. Neurosurgery 59:169–170
Mounayer C, Hammami N, Piotin M, Spelle L, Benndorf G, Kessler I, Moret J (2007) Nidal embolization of brain arteriovenous malformations using Onyx in 94 patients. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28:518–523
Passacantilli E, Pichierri A, Guidetti G, Santoro A, Delfini R (2006) Surgical treatment of pial cerebellar arteriovenous fistulas with aneurysm of the main feeding artery. Surg Neurol 65:90–94
Giller CA, Batjer HH, Purdy P, Walker B, Mathews D (1994) Interdisciplinary evaluation of cerebral hemodynamics in the treatment of arteriovenous fistulae associated with giant varices. Neurosurgery 35:778–784
Viñuela F, Drake CG, Fox AJ, Pelz DM (1987) Giant intracranial varices secondary to high-flow arteriovenous fistulae. J Neurosurg 66:198–203
Halbach VV, Higashida RT, Hieshima GB, Hardin CW, Dowd CF, Barnwell SL (1989) Transarterial occlusion of solitary intracerebral arteriovenous fistulas. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 10:747–752
Coubes P, Humbertclaude V, Rodesch G, Lasjaunias P, Echenne B, Frerebeau P (1996) Total endovascular occlusion of a giant direct arteriovenous fistula in the posterior fossa in a case of Rendu-Osler-Weber disease. Childs Nerv Syst 12:785–788
van Rooij WJ, Sluzewski M, Beute GN (2007) Brain AVM embolization with Onyx. Am J Neuroradiol 28:172–177
van Rooij WJ, Sluzewski M (2007) Endovascular occlusion of high-flow intracranial arteriovenous shunts: technical note. Neuroradiology 49:1029–1031
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Contract grant sponsor: National Natural Science Foundation of China; contract grant number: 30872676
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, X., Wang, Q., Chen, G. et al. Endovascular treatment of congenital brain arteriovenous fistulas with combination of detachable coils and onyx liquid embolic agent. Neuroradiology 52, 1121–1126 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-010-0681-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-010-0681-x