Abstract
Introduction
The purpose of this study was to determine the appropriate order of CT angiography and CT perfusion in a multimodal stroke CT protocol.
Methods
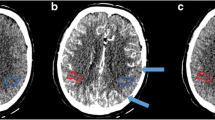
Forty patients with clinical suspicion of an acute cerebral infarct underwent non-enhanced CT (NECT), CT angiography (CTA), and CT perfusion (CTP). Twenty examinations were performed with CTP before CTA (group 1) and 20 in reversed order (group 2). Mean densities were determined at baseline and peak enhancement of CTP, as well as on source images of CTA in defined brain regions. Contrast of extra-/intracranial arteries and veins was rated according to a 5-point scale (1 = excellent, 5 = poor). CT-perfusion maps were assessed by determining the mean transit time (MTT), cerebral blood flow (CBF), and blood volume (CBV) in identical regions.
Results
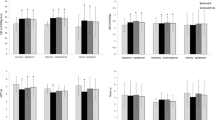
Mean densities between both groups were not significantly different for CTA and CTP at peak enhancement. At CTP baseline, mean densities between groups 1 and 2 were different for all points except for GM and WM. There was no significant difference between both groups for the mean delta (the difference between baseline and peak enhancement), as well as for mean MTT, CBV, and CBF. Subjective evaluation of the CTA quality revealed no difference between both protocols, except for the extracranial venous contrast, which was less severe in group 2.
Conclusion
Reversal of CT stroke protocol had no significant influence on quantitative parameters of CTP. Subjective quality of extracranial venous contrast was rated to be superior when CTA was performed before CTP.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Donnan G, Fisher M, Macleod M, Davis S (2008) Stroke. Lancet 371:1612–1623
The world health report 2004. Annex table 2: Deaths by cause, sex and mortality stratum in who regions, estimates for 2002. Geneva World Health Organization, 2004.
del Zoppo G, Higashida R, Furlan A, Pessin M, Rowley H, Gent M (1998) PROACT: a phase II randomized trial of recombinant pro-urokinase by direct arterial delivery in acute middle cerebral artery stroke. PROACT investigators. Prolyse in acute cerebral thromboembolism. Stroke 29:4–11
Smith W, Sung G, Saver J, Budzik R, Duckwiler G, Liebeskind D, Lutsep H, Rymer M, Higashida R, Starkman S, Gobin Y, Frei D, Grobelny T, Hellinger F, Huddle D, Kidwell C, Koroshetz W, Marks M, Nesbit G, Silverman I, Investigators MM (2008) Mechanical thrombectomy for acute ischemic stroke: final results of the multi MERCI trial. Stroke 39:1205–1212
Smith W, Sung G, Starkman S, Saver J, Kidwell C, Gobin Y, Lutsep H, Nesbit G, Grobelny T, Rymer M, Silverman I, Higashida R, Budzik R, Marks M, Investigators MT (2005) Safety and efficacy of mechanical embolectomy in acute ischemic stroke: results of the merci trial. Stroke 36:1432–1438
Kulcsár Z, Bonvin C, Lovblad K, Gory B, Yilmaz H, Sztajzel R, Rufenacht D (2010) Use of the enterprise intracranial stent for revascularization of large vessel occlusions in acute stroke. Klin Neuroradiol Feb 28 (in press)
Lövblad K, Baird A (2010) Computed tomography in acute ischemic stroke. Neuroradiology 52:175–187
Latchaw RE, Alberts MJ, Lev MH, Connors JJ, Harbaugh RE, Higashida RT, Hobson R, Kidwell CS, Koroshetz WJ, Mathews V, Villablanca P, Warach S, Walters B (2009) American Heart Association Council on Cardiovascular Radiology and Intervention SrC, and the Interdisciplinary Council on Peripheral Vascular Disease: Recommendations for imaging of acute ischemic stroke: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Stroke 40:3646–3678
Klingebiel R, Bohner G, Zimmer C, Rogalla P, Masuhr F, Lehmann R (2002) Using multislice spiral CT in neuroradiologic imaging. Nervenarzt 73:729–735
Mayer T, Hamann G, Baranczyk J, Rosengarten B, Klotz E, Wiesmann M, Missler U, Schulte-Altedorneburg G, Brueckmann H (2000) Dynamic CT perfusion imaging of acute stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:1441–1449
Wintermark M (2005) Brain perfusion-CT in acute stroke patients. Eur Radiol 15(Suppl 4):D28–D31
Konstas A, Goldmakher G, Lee T, Lev M (2009) Theoretic basis and technical implementations of CT perfusion in acute ischemic stroke, part 1: theoretic basis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30:662–668
Soares B, Dankbaar J, Bredno J, Cheng S, Bhogal S, Dillon W, Wintermark M (2009) Automated versus manual post-processing of perfusion-ct data in patients with acute cerebral ischemia: influence on interobserver variability. Neuroradiology 51:445–451
Lee I, You J, Lee J, Whang K, Kim M, Kim Y, Lee M, Group BR (2010) Accuracy of the detection of infratentorial stroke lesions using perfusion CT: an experimenter-blinded study. Neuroradiology 52(12):1095–1100
Eckert B, Küsel T, Leppien A, Michels P, Müller-Jensen A, Fiehler J (2010) Clinical outcome and imaging follow-up in acute stroke patients with normal perfusion ct and normal ct angiography. Neuroradiology Apr 27 (in press)
Bektas H, Wu TC, Kasam M, Harun N, Sitton CW, Grotta JC, Savitz SI (2010) Increased blood–brain barrier permeability on perfusion ct might predict malignant middle cerebral artery infarction. Stroke 41:2539–2544
Hopyan J, Ciarallo A, Dowlatshahi D, Howard P, John V, Yeung R, Zhang L, Kim J, MacFarlane G, Lee TY, Aviv RI (2010) Certainty of stroke diagnosis: incremental benefit with ct perfusion over noncontrast CT and CT angiography. Radiology 255:142–153
de Lucas E, Sánchez E, Gutiérrez A, Mandly A, Ruiz E, Flórez A, Izquierdo J, Arnáiz J, Piedra T, Valle N, Bañales I, Quintana F (2008) Ct protocol for acute stroke: tips and tricks for general radiologists. Radiographics 28:1673–1687
Murphy B, Fox A, Lee D, Sahlas D, Black S, Hogan M, Coutts S, Demchuk A, Goyal M, Aviv R, Symons S, Gulka I, Beletsky V, Pelz D, Chan R, Lee T (2008) White matter thresholds for ischemic penumbra and infarct core in patients with acute stroke: CT perfusion study. Radiology 247:818–825
Wintermark M, Sincic R, Sridhar D, Chien J (2008) Cerebral perfusion CT: technique and clinical applications. J Neuroradiol 35:253–260
Dittrich R, Kloska S, Fischer T, Nam E, Ritter M, Seidensticker P, Heindel W, Nabavi D, Ringelstein E (2008) Accuracy of perfusion-CT in predicting malignant middle cerebral artery brain infarction. J Neurol 255:896–902
Ryu C, Lee D, Kim H, Lee J, Choi C, Kim S, Suh D (2006) Acquisition of MR perfusion images and contrast-enhanced MR angiography in acute ischaemic stroke patients: which procedure should be done first? Br J Radiol 79:962–967
Sourbron S (2010) Technical aspects of MR perfusion. Eur J Radiol 276:304–313
Bokkers RP, van der Worp HB, Mali WP, Hendrikse J (2009) Noninvasive mr imaging of cerebral perfusion in patients with a carotid artery stenosis. Neurology 73:869–875
Bokkers RP, van Osch MJ, van der Worp HB, de Borst GJ, Mali WP, Hendrikse J (2010) Symptomatic carotid artery stenosis: impairment of cerebral autoregulation measured at the brain tissue level with arterial spin-labeling MR imaging. Radiology 256:201–208
Quarles C, Ward B, Schmainda K (2005) Improving the reliability of obtaining tumor hemodynamic parameters in the presence of contrast agent extravasation. Magn Reson Med 53:1307–1316
Schmainda K, Rand S, Joseph A, Lund R, Ward B, Pathak A, Ulmer J, Badruddoja M, Baddrudoja M, Krouwer H (2004) Characterization of a first-pass gradient-echo spin-echo method to predict brain tumor grade and angiogenesis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25:1524–1532
Edelman R, Mattle H, Atkinson D, Hill T, Finn J, Mayman C, Ronthal M, Hoogewoud H, Kleefield J (1990) Cerebral blood flow: assessment with dynamic contrast-enhanced t2*-weighted MR imaging at 1.5 t. Radiology 176:211–220
Camargo EC, Furie KL, Singhal AB, Roccatagliata L, Cunnane ME, Halpern EF, Harris GJ, Smith WS, Gonzalez RG, Koroshetz WJ, Lev MH (2007) Acute brain infarct: detection and delineation with ct angiographic source images versus nonenhanced CT scans. Radiology 244:541–548
Coutts SB, Lev MH, Eliasziw M, Roccatagliata L, Hill MD, Schwamm LH, Pexman JH, Koroshetz WJ, Hudon ME, Buchan AM, Gonzalez RG, Demchuk AM (2004) Aspects on CTA source images versus unenhanced CT: added value in predicting final infarct extent and clinical outcome. Stroke 35:2472–2476
Lin K, Rapalino O, Law M, Babb JS, Siller KA, Pramanik BK (2008) Accuracy of the Alberta Stroke Program early CT score during the first 3 hours of middle cerebral artery stroke: comparison of noncontrast CT, CT angiography source images, and CT perfusion. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29:931–936
Lev MH, Segal AZ, Farkas J, Hossain ST, Putman C, Hunter GJ, Budzik R, Harris GJ, Buonanno FS, Ezzeddine MA, Chang Y, Koroshetz WJ, Gonzalez RG, Schwamm LH (2001) Utility of perfusion-weighted CT imaging in acute middle cerebral artery stroke treated with intra-arterial thrombolysis: prediction of final infarct volume and clinical outcome. Stroke 32:2021–2028
Sharma M, Fox AJ, Symons S, Jairath A, Aviv RI (2010) CT angiographic source images: flow- or volume-weighted? AJNR Am J Neuroradiol Nov 24 (in press)
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dorn, F., Liebig, T., Muenzel, D. et al. Order of CT stroke protocol (CTA before or after CTP): impact on image quality. Neuroradiology 54, 105–112 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-011-0840-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-011-0840-8