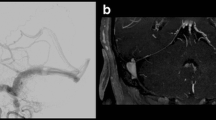
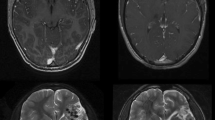
Abstract
Introduction
Risk of further haemorrhage in patients suffering from arteriovenous malformation (AVM) would be eliminated only if complete obliteration of the AVM is obtained. Therefore, these patients frequently need long-term follow-up. Conventional catheter angiography (CCA) with a risk of 0.5 %.to 1.6 % of significant neurological complications has traditionally been used for this purpose. However, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) at 3T may be a safer alternative. The aim of this study was to evaluate if MRI at 3T can accurately evaluate closure of AVM in 2 years after stereotactic radiosurgery.
Methods
Twenty-three patients with both MRI at 3T and a CCA study were examined. The residual AVMs were evaluated by MRI at 3T against CCA in a prospective study.
Results
The time interval between radiosurgery and neuroimaging was on average of 25 months (range, 15–30 months) for MRI study and 33 months (range, 25–46 months) for CCA study. Ten patients showed closure of the AVM on MRI, all of which were confirmed on CCA.
Conclusion
There was a complete agreement between late MRI at 3T scan and CCA in evaluation of AVM patency.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AVMs:
-
Arteriovenous malformations
- CCA:
-
Conventional catheter angiography
- STRS:
-
Stereotactic radiosurgery
- Gd-DTPA:
-
Gadolinium diethylenetriaminepenta-acetic acid
- 3D-TOF:
-
Three-dimensional time-of-flight
- MRDSA:
-
Magnetic resonance digital subtraction angiography
References
Fleetwood IG, Steinberg GK (2002) Arteriovenous malformations. Lancet 9(359(9309)):863–873
Miller CE, Quayyum Z, McNamee P, Al-Shahi Salman R, SIVMS Steering Committee (2009) Economic burden of intracranial vascular malformations in adults: prospective population-based study. Stroke 40(6):1973–1979
Steiner L, Lindquist C, Adler JR Jr, Torner JC, Alves W, Steiner M (1992) Clinical outcome of radiosurgery for cerebral arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 77:1–8
Maesawa S, Flickinger JC, Kondziolka D, Lunsford LD (2000) Repeated radiosurgery for incompletely obliterated arteriovenous malformations. J Neurosurg 92:961–970
Aoki S, Yoshikawa T, Hori M, Nanbu A, Kumagai H, Nishiyama Y, Nukui H, Araki T (2000) MR digital subtraction angiography for the assessment of cranialarteriovenous malformations and fistulas. AJR Am J Roentgenol 175(2):451–453
Willinsky RA, Taylor SM, TerBrugge K, Farb RI, Tomlinson G, Montanera W (2003) Neurologic complications of cerebral angiography: prospective analysis of 2,899 procedures and review of the literature. Radiology 227(2):522–528
Nagaraja S, Lee KJ, Coley SC, Capener D, Walton L, Kemeny AA, Wilkinson ID, Griffiths PD (2006) Stereotactic radiosurgery for brain arteriovenous malformations: quantitative MR assessment of nidal response at 1 year and angiographic factors predicting early obliteration. Neuroradiology 48(11):821–829
Mori H, Aoki S, Okubo T, Hayashi N, Masumoto T, Yoshikawa T, Tago M, Shin M, Kurita H, Abe O, Ohtomo K (2003) Two-dimensional thick-slice MR digital 13 subtraction angiography in the assessment of small to medium-size intracranial arteriovenous malformations. Neuroradiology 45(1):27–33
Hamm KD, Surber G, Schmücking M, Wurm RE, Aschenbach R, Kleinert G, Niesen A, Baum RP (2004) Stereotactic radiation treatment planning and follow-up studies involving fused multimodality imaging. J Neurosurg 101:326–333
Griffiths PD, Hoggard N, Warren DJ, Wilkinson ID, Anderson B, Romanowski CA (2000) Brain arteriovenous malformations: assessment with dynamic MR digital subtraction angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21(10):1892–1899
Lee KE, Choi CG, Choi JW, Choi BS, Lee DH, Kim SJ, Kwon do H (2009) Detection of residual brain arteriovenous malformations after radiosurgery: diagnostic accuracy of contrast-enhanced three-dimensional time of flight MR angiography at 3.0 Tesla. Korean J Radiol 10(4):333–339
Eddleman CS, Jeong HJ, Hurley MC, Zuehlsdorff S, Dabus G, Getch CG, Batjer HH, Bendok BR, Carroll TJ (2009) 4D radial acquisition contrast-enhanced MR angiography and intracranial arteriovenous malformations: quickly approaching digital subtraction angiography. Stroke 40(8):2749–2753
Warren DJ, Hoggard N, Walton L, Radatz MW, Kemeny AA, Forster DM, Wilkinson ID, Griffiths PD (2007) Cerebral arteriovenous malformations: comparison of novel magnetic resonance angiographic techniques and conventional catheter angiography. Neurosurgery 61(1 Suppl):187–196
Muthupillai R, Douglas E, Huber S, Lambert B, Pereyra M, Wilson GJ, Flamm SD (2010) Direct comparison of sensitivity encoding (SENSE) accelerated and conventional 3D contrast enhanced magnetic resonance angiography (CE-MRA) of m14 renal arteries: effect of increasing spatial resolution. J Magn Reson Imaging 31(1):149–159
Koktzoglou I, Sheehan JJ, Dunkle EE, Breuer FA, Edelman RR (2010) Highly accelerated contrast-enhanced MR angiography: improved reconstruction accuracy and reduced noise amplification with complex subtraction. Magn Reson Med 64(6):1843–1848
Weiger M, Pruessmann KP, Kassner A et al (2000) Contrast-enhanced 3D MRA using SENSE. J Magn Reson Imaging 12:671–677
Heidenreich JO, Schilling AM, Unterharnscheidt F et al (2007) Assessment of 3D-TOF-MRA at 3.0 Tesla in the characterization of the angioarchitecture of cerebral arteriovenous malformations: a preliminary study. Acta Radiol 48(6):678–686
Gibbs GF, Huston J 3rd, Bernstein MA, Riederer SJ, Brown RD Jr (2004) Improved image quality of intracranial aneurysms: 3.0-T versus 1.5-T time-of-flight MR angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 25(1):84–87
Röttgen R, Haltaufderheide K, Schröder RJ (2005) The effect of the field strength on standardized MRI of the brain to demonstrate cranial nerves and vessels: a comparison of 1.5 and 3.0Tesla. Rofo 177(4):530–535
Perez-Rodriguez J, Lai S, Ehst BD, Fine DM, Bluemke DA (2009) Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: incidence, associations, and effect of risk factor assessment—report of 33 cases. Radiology 250:371–377
International RadioSurgery Association (2009) Radiosurgery practice guideline initiative stereotactic radiosurgery for patients with intracranial arteriovenous malformations (AVM), Radiosurgery Practice Guideline Report #2-03 Issued March 2009. Accessed at 1/1/2011 via http://www.irsa.org/AVM%20Guideline.pdf
Pollock BE, Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC, Patel AK, Bissonette DJ, Lunsford LD (1996) Magnetic resonance imaging: an accurate method to evaluate arteriovenous malformations after stereotactic radiosurgery. J Neurosurg 85(6):1044–1049
LS Chin, WF Regine (eds) (2008) Principles and practice of stereotactic radiosurgery. San Diego, CA, Springer, p. 111
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khandanpour, N., Griffiths, P., Warren, D. et al. Prospective comparison of late 3T MRI with conventional angiography in evaluating the patency of cerebral arteriovenous malformations treated with stereotactic radiosurgery. Neuroradiology 55, 683–687 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-013-1153-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-013-1153-x