Abstract
Introduction
This study aimed to evaluate the feasibility of non-contrast-enhanced 4D magnetic resonance angiography (NCE 4D MRA) with signal targeting with alternative radiofrequency (STAR) spin labeling and variable flip angle (VFA) sampling in the assessment of dural arteriovenous fistula (DAVF) in the transverse sinus.
Methods
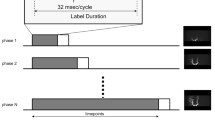
Nine patients underwent NCE 4D MRA for the evaluation of DAVF in the transverse sinus at 3 T. One patient was examined twice, once before and once after the interventional treatment. All patients also underwent digital subtraction angiography (DSA) and/or contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography (CEMRA). For the acquisition of NCE 4D MRA, a STAR spin tagging method was used, and a VFA sampling was applied in the data readout module instead of a constant flip angle. Two readers evaluated the NCE 4D MRA data for the diagnosis of DAVF and its type with consensus. The results were compared with those from DSA and/or CEMRA.
Results
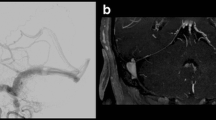
All patients underwent NCE 4D MRA without any difficulty. Among seven patients with patent DAVFs, all cases showed an early visualization of the transverse sinus on NCE 4D MRA. Except for one case, the type of DAVF of NCE 4D MRA was agreed with that of reference standard study. Cortical venous reflux (CVR) was demonstrated in two cases out of three patients with CVR.
Conclusion
NCE 4D MRA with STAR tagging and VFA sampling is technically and clinically feasible and represents a promising technique for assessment of DAVF in the transverse sinus. Further technical developments should aim at improvements of spatial and temporal coverage.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sadowski EA, Bennett LK, Chan MR, Wentland AL, Garrett AL, Garrett RW, Djamali A (2007) Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis: risk factors and incidence estimation. Radiology 243(1):148–157. doi:10.1148/radiol.2431062144
Bi X, Weale P, Schmitt P, Zuehlsdorff S, Jerecic R (2010) Non-contrast-enhanced four-dimensional (4D) intracranial MR angiography: a feasibility study. Magn Reson Med 63(3):835–841. doi:10.1002/mrm.22220
Yan L, Wang S, Zhuo Y, Wolf RL, Stiefel MF, An J, Ye Y, Zhang Q, Melhem ER, Wang DJ (2010) Unenhanced dynamic MR angiography: high spatial and temporal resolution by using true FISP-based spin tagging with alternating radiofrequency. Radiology 256(1):270–279. doi:10.1148/radiol.10091543
Edelman RR, Siewert B, Darby DG, Thangaraj V, Nobre AC, Mesulam MM, Warach S (1994) Qualitative mapping of cerebral blood flow and functional localization with echo-planar MR imaging and signal targeting with alternating radio frequency. Radiology 192(2):513–520
Kim SG, Tsekos NV (1997) Perfusion imaging by a flow-sensitive alternating inversion recovery (FAIR) technique: application to functional brain imaging. Magn Reson Med 37(3):425–435
Deibler AR, Pollock JM, Kraft RA, Tan H, Burdette JH, Maldjian JA (2008) Arterial spin-labeling in routine clinical practice, part 1: technique and artifacts. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29(7):1228–1234. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A1030
Xu J, Shi D, Chen C, Li Y, Wang M, Han X, Jin L, Bi X (2011) Noncontrast-enhanced four-dimensional MR angiography for the evaluation of cerebral arteriovenous malformation: a preliminary trial. J Magn Reson Imaging 34(5):1199–1205. doi:10.1002/jmri.22699
Yu S, Yan L, Yao Y, Wang S, Yang M, Wang B, Zhuo Y, Ai L, Miao X, Zhao J, Wang DJ (2012) Noncontrast dynamic MRA in intracranial arteriovenous malformation (AVM): comparison with time of flight (TOF) and digital subtraction angiography (DSA). Magn Reson Imaging 30(6):869–877. doi:10.1016/j.mri.2012.02.027
Lanzman RS, Kropil P, Schmitt P, Bi X, Gliem M, Miese FR, Hanggi D, Kamp M, Scherer A, Turowski B, Blondin D (2011) Nonenhanced ECG-gated time-resolved 4D steady-state free precession (SSFP) MR angiography (MRA) for assessment of cerebral collateral flow: comparison with digital subtraction angiography (DSA). Eur Radiol 21(6):1329–1338. doi:10.1007/s00330-010-2051-9
Lanzman RS, Kropil P, Schmitt P, Wittsack HJ, Orzechowski D, Kuhlemann J, Buchbender C, Miese FR, Antoch G, Blondin D (2012) Nonenhanced ECG-gated time-resolved 4D steady-state free precession (SSFP) MR angiography (MRA) of cerebral arteries: comparison at 1.5 T and 3 T. Eur J Radiol 81(4):e531–e535. doi:10.1016/j.ejrad.2011.06.044
Gomez J, Amin AG, Gregg L, Gailloud P (2012) Classification schemes of cranial dural arteriovenous fistulas. Neurosurg Clin N Am 23(1):55–62. doi:10.1016/j.nec.2011.09.003
Schmitt P, Speier P, Bi X, Weale P and Mueller E (2011) Non-contrast-enhanced 4D intracranial MR angiography: optimizations using a variable flip angle approach. [abstr]. In: Proceedings of the Eighteenth Meeting of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. Berkeley, Calif: International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine
Frydrychowicz A, Russe MF, Bock J, Stalder AF, Bley TA, Harloff A, Markl M (2010) Comparison of gadofosveset trisodium and gadobenate dimeglumine during time-resolved thoracic MR angiography at 3 T. Acad Radiol 17(11):1394–1400. doi:10.1016/j.acra.2010.05.022
Borden JA, Wu JK, Shucart WA (1995) A proposed classification for spinal and cranial dural arteriovenous fistulous malformations and implications for treatment. J Neurosurg 82(2):166–179. doi:10.3171/jns.1995.82.2.0166
Li D, Lin J, Yan F, Wu Q, Lv W, San Y, Yun H (2011) Unenhanced calf MR angiography at 3.0 T using electrocardiography-gated partial-fourier fast spin echo imaging with variable flip angle. Eur Radiol 21(6):1311–1322. doi:10.1007/s00330-010-2028-8
Hélène Raoult EB, Benjamin Robert, Peter Schmitt, and Jean-Yves Gauvrit (2013) Non-contrast-enhanced high-temporal-resolution 4D MRA with an acquisition window covering two cardiac cycles: assessment of arteriovenous malformations in the brain. [abstr]. In: Proceedings of the Twenty First Meeting of the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. Berkeley, Calif: International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine
Ganter C (2004) Off-resonance effects in the transient response of SSFP sequences. Magn Reson Med 52(2):368–375. doi:10.1002/mrm.20173
Schmitt P, Griswold MA, Gulani V, Haase A, Flentje M, Jakob PM (2006) A simple geometrical description of the TrueFISP ideal transient and steady-state signal. Magn Reson Med 55(1):177–186. doi:10.1002/mrm.20738
Malik GM, Pearce JE, Ausman JI, Mehta B (1984) Dural arteriovenous malformations and intracranial hemorrhage. Neurosurgery 15(3):332–339
Lanzino G, Jensen ME, Kongable GL, Kassell NF (1994) Angiographic characteristics of dural arteriovenous malformations that present with intracranial hemorrhage. Acta Neurochir 129(3–4):140–145
Zaharchuk G (2011) Arterial spin label imaging of acute ischemic stroke and transient ischemic attack. Neuroimaging Clin N Am 21(2):285–301. doi:10.1016/j.nic.2011.01.003, x
Yan L, Salamon N, Wang DJ (2013) Time-resolved noncontrast enhanced 4-D dynamic magnetic resonance angiography using multibolus TrueFISP-based spin tagging with alternating radiofrequency (TrueSTAR). Magn Reson Med. doi:10.1002/mrm.24689
Hori M, Aoki S, Oishi H, Nakanishi A, Shimoji K, Kamagata K, Houshito H, Kuwatsuru R, Arai H (2011) Utility of time-resolved three-dimensional magnetic resonance digital subtraction angiography without contrast material for assessment of intracranial dural arterio-venous fistula. Acta Radiol 52(7):808–812. doi:10.1258/ar.2011.110128
Farb RI, Agid R, Willinsky RA, Johnstone DM, Terbrugge KG (2009) Cranial dural arteriovenous fistula: diagnosis and classification with time-resolved MR angiography at 3 T. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30(8):1546–1551. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A1646
Nishimura S, Hirai T, Sasao A, Kitajima M, Morioka M, Kai Y, Omori Y, Okuda T, Murakami R, Fukuoka H, Awai K, Kuratsu JI, Yamashita Y (2010) Evaluation of dural arteriovenous fistulas with 4D contrast-enhanced MR angiography at 3 T. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31(1):80–85. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A1898
Mossa-Basha M, Chen J, Gandhi D (2012) Imaging of cerebral arteriovenous malformations and dural arteriovenous fistulas. Neurosurg Clin N Am 23(1):27–42. doi:10.1016/j.nec.2011.09.007
Conflict of interest
PS, IK and MP are employees of Siemens Healthcare.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jang, J., Schmitt, P., Kim, By. et al. Non-contrast-enhanced 4D MR angiography with STAR spin labeling and variable flip angle sampling: a feasibility study for the assessment of Dural Arteriovenous Fistula. Neuroradiology 56, 305–314 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-014-1336-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-014-1336-0