Abstract
Introduction
Stroke-like migraine attacks after radiation therapy (SMART) syndrome has a characteristic clinical presentation and postcontrast T1WI MRI appearance. Susceptibility-weighted imaging (SWI) may help distinguish SMART from other disorders that may have a similar postcontrast MRI appearance.
Methods
The MRI examinations of four patients with SMART syndrome are described herein, each of which included SWI, FLAIR, DWI, and postcontrast T1WI on the presenting and follow-up MRI examinations.
Results
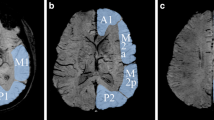
In each, the initial SWI MRI demonstrated numerous susceptibility hypointensities <5 mm in size throughout the cerebrum, particularly within the periventricular white matter (PVWM), presumably related to radiation-induced cavernous hemangiomas (RICHs). By follow-up MRI, each postcontrast examination had demonstrated resolution of the gyriform enhancement on T1WI, without susceptibility hypointensities on SWI within those previously enhancing regions.
Conclusion
These preliminary findings suggest that SWI may help identify SMART syndrome or at least help discriminate it from other disorders, by the findings of numerous susceptibility hypointensities on SWI likely representing RICHs, gyriform enhancement on T1WI, and postsurgical findings or appropriate clinical history.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PVWM:
-
Periventricular white matter
- RICH:
-
Radiation-induced cavernous hemangiomas
- SMART:
-
Stroke-like migraine attacks after radiation therapy
- SWI:
-
Susceptibility-weighted imaging
- T1WI:
-
T1-weighted imaging
- T2*WI:
-
T2*-weighted (gradient echo) imaging
References
Shuper A, Packe RJ, Vezina LG, Nicholson HS, Lafond D (1995) “Complicated migraine-like episodes” in children following cranial irradiation and chemotherapy. Neurology 45:1837–1840. doi:10.1212/WNL.45.10.1837
Bartleson JD, Krecke KN, O’Neill BP, Brown PD (2003) Reversible, strokelike migraine attacks in patients with previous radiation therapy. Neuro-Oncology 5:121–127. doi:10.1215/S1522-8517-02-00040-6
Black DF, Bartleson JD, Bell ML, Lachance DH (2006) SMART: stroke-like migraine attacks after radiation therapy. Cephalalgia 26:1137–1142. doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2006.01184.x
Pruitt A, Dalmau J, Detre J, Alavi A, Rosenfeld MR (2006) Episodic neurologic dysfunction with migraine and reversible imaging findings after radiation RHH. Neurology 67:676–678. doi:10.1212/01.wnl.0000228862.76269.62
Black DF, Morris JM, Lindell EP, Krecke KN, Worrell GA, Bartleson JD, Lachance DH (2013) Stroke-like migraine attacks after radiation therapy (SMART) syndrome is not always completely reversible: a case series. AJNR 34:2298–2303. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A3602
Armstrong AE, Gillan E, Dimario FJ (2014) SMART syndrome (stroke-like migraine attacks after radiation therapy) in adult and pediatric patients. J Child Neurol 29:336–341. doi:10.1177/0883073812474843
Bian W, Hess CP, Chang SM, Nelson SJ, Lupo JM (2014) Susceptibility-weighted MR imaging of radiation therapy-induced cerebral microbleeds in patients with glioma: a comparison between 3T and 7T. Neuroradiology 56:91–96. doi:10.1007/s00234-013-1297-8
Baumgartner JE, Ater JL, Ha CS, Kuttesch JF, Leeds NE, Fuller GN, Wilson RJ (2003) Pathologically proven cavernous angiomas of the brain following radiation therapy for pediatric brain tumors. Pediatr Neurosurg 39:201–207. doi:10.1159/000072472)
Goos JD, van der Flier WM, Knol DL, Pouwels PJW, Scheltens P, Barkhof F, Wattjes MP (2011) Clinical relevance of improved microbleed detection by susceptibility-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Stroke 42:1894–1900. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.599837
Cheng AL, Batool S, McCreary CR, Lauzon ML, Frayne R, Goyal M, Smith EE (2013) Susceptibility-weighted imaging is more reliable than T2*-weighted gradient-recalled echo MRI for detecting microbleeds. Stroke 44:2782–2786. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.113.002267
McKinney AM, Sarikaya B, Gustafson C, Truwit CL (2012) Detection of microhemorrhage in posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome using susceptibility-weighted imaging. AJNR 33:896–903. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A2886
Fazekas F, Kleinert R, Roob G, Kleinert G, Kapeller P, Schmidt R, Hartung HP (1999) Histopathologic analysis of foci of signal loss on gradient-echo T2*-weighted MR images in patients with spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: evidence of microangiopathy-related microbleeds. AJNR 20:637–642
Bai Q, Zhao Z, Sui H, Xie X, Chen J, Yang J, Zhang L (2013) Susceptibility-weighted imaging for cerebral microbleed detection in super-acute ischemic stroke patients treated with intravenous thrombolysis. Neurol Res 35:586–593. doi:10.1179/1743132813Y.0000000179
Smirniotopoulos JG, Murphy FM, Rushing EJ, Rees JH, Schroeder JW (2007) Patterns of contrast enhancement in the brain and meninges. Radiographics 27:525–551. doi:10.1148/rg.272065155
Varon D, Simons M, Chiang F, Tedesqui G, Pacheco G, Martinez P, Castillo M (2014) Brain radiation-related black dots on susceptibility-weighted imaging. Neuroradiol J 27:445–451. doi:10.15274/NRJ-2014-10071
Haacke EM, Mittal S, Wu Z, Neelavalli J, Cheng YCN (2009) Susceptibility-weighted imaging: technical aspects and clinical applications, part 1. AJNR 30:19–30. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A1400
Mittal S, Wu Z, Neelavalli J, Haacke EM (2009) Susceptibility-weighted imaging: technical aspects and clinical applications, part 2. AJNR 30:232–252. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A1461
Tsui YK, Tsai FY, Hasso AN, Greensite F, Nguyen BV (2009) Susceptibility-weighted imaging for differential diagnosis of cerebral vascular pathology: a pictorial review. J Neurol Sci 287:7–16. doi:10.1016/j.jns.2009.08.064
Reichenbach JR, Venkatesan R, Schillinger DJ, Kido DK, Haacke EM (1997) Small vessels deoxyhemoglobin in the human MR venography as an intrinsic contrast agent. Radiology 204:272–277
Tong KA, Ashwal S, Holshouser BA, Shutter LA, Herigault G, Haacke EM, Kido DK (2003) Hemorrhagic shearing lesions in children and adolescents with posttraumatic diffuse axonal injury: improved detection and initial results. Radiology 227:332–339. doi:10.1148/radiol.2272020176
Gaensler EH, Dillon WP, Edwards MS, Larson DA, Rosenau W, Wilson CB (1994) Radiation-induced telangiectasia in the brain simulates cryptic vascular malformations at MR imaging. Radiology 193:629–636. doi:10.1148/radiology.193.3.7972799
Rimkus CDM, Andrad CS, Leite CDC, McKinney AM, Lucato LT (2014) Toxic leukoencephalopathies, including drug, medication, environmental, and radiation-induced encephalopathic syndromes. Semin Ultrasound CT MR 35:97–117. doi:10.1053/j.sult.2013.09.005
Farid K, Meissner WG, Samier-Foubert A, Barret O, Menegon P, Rouanet F (2010) Normal cerebrovascular reactivity in stroke-like migraine attacks after radiation therapy syndrome. Clin Nucl Med 35:583–585. doi:10.1097/RLU.0b013e3181e4db6f
Ethical standards and patient consent
We declare that all human and animal studies have been approved by the Institutional Internal Review Board and have therefore been performed in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments. We declare that all patients gave informed consent prior to inclusion in this study.
Conflict of interest
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Khanipour Roshan, S., Salmela, M.B. & McKinney, A.M. Susceptibility-weighted imaging in stroke-like migraine attacks after radiation therapy syndrome. Neuroradiology 57, 1103–1109 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-015-1567-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-015-1567-8