Abstract
Purpose
Our aim is to investigate whether rs-fMRI can be used as an effective technique to study language lateralization. We aim to find out the most appropriate language network among different networks identified using ICA.
Methods
Fifteen healthy right-handed subjects, sixteen left, and sixteen right temporal lobe epilepsy patients prospectively underwent MR scanning in 3T MRI (GE Discovery™ MR750w), using optimized imaging protocol. We obtained task-fMRI data using a visual-verb generation paradigm. Rs-fMRI and language-fMRI analysis were conducted using FSL software. Independent component analysis (ICA) was used to estimate rs-fMRI networks. Dice coefficient was calculated to examine the similarity in activated voxels of a common language template and the rs-fMRI language networks. Laterality index (LI) was calculated from the task-based language activation and rs-fMRI language network, for a range of LI thresholds at different z scores.
Results
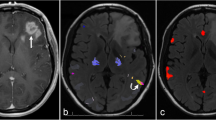
Measurement of hemispheric language dominance with rs-fMRI was highly concordant with task-fMRI results. Among the evaluated z scores for a range of LI thresholds, rs-fMRI yielded a maximum accuracy of 95%, a sensitivity of 83%, and specificity of 92.8% for z = 2 at 0.05 LI threshold.
Conclusion
The present study suggests that rs-fMRI networks obtained using ICA technique can be used as an alternative for task-fMRI language laterality. The novel aspect of the work is suggestive of optimal thresholds while applying rs-fMRI, is an important endeavor given that many patients with epilepsy have co-morbid cognitive deficits. Thus, an accurate method to determine language laterality without requiring a patient to complete the language task would be advantageous.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- RS-fMRI:
-
resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging
- TLE:
-
temporal lobe epilepsy
- ICA:
-
independent component analysis
- LI:
-
laterality index
- IAP:
-
intracarotid amobarbital procedure
- HCs:
-
healthy controls
- LTLE:
-
left temporal lobe epilepsy
- RTLE:
-
right temporal lobe epilepsy
References
Wada J, Rasmussen T (1960) Intracarotid injection of sodium amytal for the lateralization of cerebral speech dominance. J Neurosurg 17:266–282. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1960.17.2.0266
Meador KJ, Loring DW (1999) The Wada test: controversies, concerns, and insights. Neurology 52:1535–1536
Malmgren K, Bilting M, Hagberg I, Hedström A, Silfvenius H, Starmark IE (1992) A compound score for estimating the influence of inattention and somnolence during the intracarotid amobarbital test. Epilepsy Res 12:253–259
Binder JR (2011) FMRI is a valid noninvasive alternative to Wada testing. Epilepsy Behav 20:214–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2010.08.004
Dym RJ, Burns J, Freeman K, Lipton ML (2011) Is functional MR imaging assessment of hemispheric language dominance as good as the Wada test?: a meta-analysis. Radiology. 261:446–455. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.11101344
Medina LS, Aguirre E, Bernal B, Altman NR (2004) Functional MR imaging versus Wada test for evaluation of language lateralization: cost Analysis1. Radiology 230:49–54
Wagner K, Hader C, Metternich B, Buschmann F, Schwarzwald R, Schulze-Bonhage A (2012) Who needs a Wada test? Present clinical indications for amobarbital procedures. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 83:503–509. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2011-300417
Arora J, Pugh K, Westerveld M, Spencer S, Spencer DD, Todd Constable R (2009) Language lateralization in epilepsy patients: fMRI validated with the Wada procedure. Epilepsia 50:2225–2241. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1167.2009.02136.x
Janecek JK, Swanson SJ, Sabsevitz DS, Hammeke TA, Raghavan M, E. Rozman M, Binder JR (2013) Language lateralization by fMRI and Wada testing in 229 epilepsy patients: rates and predictors of discordance. Epilepsia 54:314–322. https://doi.org/10.1111/epi.12068
Bauer PR, Reitsma JB, Houweling BM, Ferrier CH, Ramsey NF (2014) Can fMRI safely replace the Wada test for preoperative assessment of language lateralisation? A meta-analysis and systematic review. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 85:581–588. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2013-305659
Binder JR, Swanson SJ, Hammeke TA, Sabsevitz DS (2008) A comparison of five fMRI protocols for mapping speech comprehension systems. Epilepsia 49:1980–1997. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1167.2008.01683.x
Rosazza C, Ghielmetti F, Minati L, Vitali P, Giovagnoli AR, Deleo F, Didato G, Parente A, Marras C, Bruzzone MG, D'Incerti L, Spreafico R, Villani F (2013) Preoperative language lateralization in temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE) predicts peri-ictal, pre- and post-operative language performance: An fMRI study. NeuroImage: Clinical 3:73–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2013.07.001
Bradshaw AR, Thompson PA, Wilson AC, Bishop DVM, Woodhead ZVJ (2017) Measuring language lateralisation with different language tasks: a systematic review. PeerJ 5:e3929. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.3929
Wilson SM, Bautista A, Yen M, Lauderdale S, Eriksson DK (2017) Validity and reliability of four language mapping paradigms. NeuroImage: Clinical 16:399–408. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nicl.2016.03.015
Biswal BB (2012) Resting state fMRI: a personal history. NeuroImage 62:938–944. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.01.090
Lee MH, Smyser CD, Shimony JS (2013) Resting state fMRI: a review of methods and clinical applications. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 34:1866–1872. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A3263
Smitha KA, Akhil Raja K, Arun KM, Rajesh PG, Thomas B, Kapilamoorthy TR, Kesavadas C (2017) Resting state fMRI: a review on methods in resting state connectivity analysis and resting state networks. Neuroradiol J 30:305–317. https://doi.org/10.1177/1971400917697342
Barkhof F, Haller S, Rombouts SARB (2014) Resting-state functional MR imaging: a new window to the brain. Radiology 272:29–49. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.14132388
Lv H, Wang Z, Tong E, Williams LM, Zaharchuk G, Zeineh M, Goldstein-Piekarski AN, Ball TM, Liao C, Wintermark M (2018) Resting-state functional MRI: everything that nonexperts have always wanted to know. Am J Neuroradiol. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A5527
Sbardella E, Petsas N, Tona F, Pantano P (2015) Resting-state fMRI in MS: general concepts and brief overview of its application. Biomed Res Int 2015:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/212693
Su L, An J, Ma Q, Qiu S, Hu D (2015) Influence of resting-state network on lateralization of functional connectivity in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Am J Neuroradiol 36:1479–1487. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A4346
Tie Y, Rigolo L, Norton IH, Huang RY, Wu W, Orringer D, Mukundan S Jr, Golby AJ (2014) Defining language networks from resting-state fMRI for surgical planning—a feasibility study. Hum Brain Mapp 35:1018–1030. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.22231
Branco P, Seixas D, Deprez S, Kovacs S, Peeters R, Castro SL, Sunaert S (2016) Resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging for language preoperative planning. Front Hum Neurosci 10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2016.00011
Wang L, Chen D, Yang X, Olson JJ, Gopinath K, Fan T, Mao H (2013) Group independent component analysis and functional MRI examination of changes in language areas associated with brain tumors at different locations. PLoS One 8:e59657. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0059657
DeSalvo MN, Tanaka N, Douw L et al (2016) Resting-state functional MR imaging for determining language laterality in intractable epilepsy. Radiology 281:264–269. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2016141010
Doucet GE, Pustina D, Skidmore C, Sharan A, Sperling MR, Tracy JI (2015) Resting-state functional connectivity predicts the strength of hemispheric lateralization for language processing in temporal lobe epilepsy and normals. Hum Brain Mapp 36:288–303. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.22628
Suarez RO, Whalen S, Nelson AP, Tie Y, Meadows ME, Radmanesh A, Golby AJ (2009) Threshold-independent fMRI determination of language dominance: a validation study against clinical gold-standards. Epilepsy Behav 16:288–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2009.07.034
Fisher RS, Cross JH, French JA, Higurashi N, Hirsch E, Jansen FE, Lagae L, Moshé SL, Peltola J, Roulet Perez E, Scheffer IE, Zuberi SM (2017) Operational classification of seizure types by the international league against epilepsy: position paper of the ILAE Commission for Classification and Terminology. Epilepsia 58:522–530. https://doi.org/10.1111/epi.13670
Rosazza C, Aquino D, D’Incerti L, Cordella R, Andronache A, Zacà D, Bruzzone MG, Tringali G, Minati L (2014) Preoperative mapping of the sensorimotor cortex: comparative assessment of task-based and resting-state fMRI. PLoS One 9:e98860. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0098860
Smitha KA, Arun KM, Rajesh PG, Thomas B, Kesavadas C (2017) Resting-state seed-based analysis: an alternative to task-based language fMRI and its laterality index. Am J Neuroradiol 38:1187–1192. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A5169
James JS, Kumari SR, Sreedharan RM et al (2015) Analyzing functional, structural, and anatomical correlation of hemispheric language lateralization in healthy subjects using functional MRI, diffusion tensor imaging, and voxel-based morphometry. Neurol India 63:49. https://doi.org/10.4103/0028-3886.152634
Smith SM (2002) Fast robust automated brain extraction. Hum Brain Mapp 17:143–155. https://doi.org/10.1002/hbm.10062
Jenkinson M, Bannister P, Brady M, Smith S (2002) Improved optimization for the robust and accurate linear registration and motion correction of brain images. Neuroimage 17:825–841
Beckmann CF, Smith SM (2005) Tensorial extensions of independent component analysis for multisubject FMRI analysis. Neuroimage 25:294–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.10.043
Smith SM, Jenkinson M, Woolrich MW, Beckmann CF, Behrens TEJ, Johansen-Berg H, Bannister PR, de Luca M, Drobnjak I, Flitney DE, Niazy RK, Saunders J, Vickers J, Zhang Y, de Stefano N, Brady JM, Matthews PM (2004) Advances in functional and structural MR image analysis and implementation as FSL. Neuroimage 23(Suppl 1):S208–S219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2004.07.051
Beckmann CF, Smith SM (2004) Probabilistic independent component analysis for functional magnetic resonance imaging. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 23:137–152. https://doi.org/10.1109/TMI.2003.822821
Seghier ML (2008) Laterality index in functional MRI: methodological issues. Magn Reson Imaging 26:594–601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mri.2007.10.010
Harrington GS, Buonocore MH, Farias ST (2006) Intrasubject reproducibility of functional MR imaging activation in language tasks. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:938–944
Adcock JE, Wise RG, Oxbury JM, Oxbury SM, Matthews PM (2003) Quantitative fMRI assessment of the differences in lateralization of language-related brain activation in patients with temporal lobe epilepsy. Neuroimage 18:423–438
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the DBT Research Associateship Program of the Department of Biotechnology, Govt of India, for financial support to first author. We acknowledge help from Dr. Matthew N. DeSalvo, Diagnostic Radiology Specialist, in Boston, Massachusetts.
Funding
No funding was received for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in the studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 29 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smitha, K.A., Arun, K.M., Rajesh, P.G. et al. Resting fMRI as an alternative for task-based fMRI for language lateralization in temporal lobe epilepsy patients: a study using independent component analysis. Neuroradiology 61, 803–810 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-019-02209-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00234-019-02209-w