Abstract
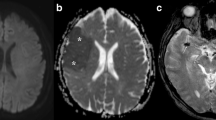
Diffusion-weighted images (DWI) of a patient with Wernicke encephalopathy were obtained during routine MR examination. Mammillary bodies were hyperintense on T2-weighted and enhanced on T1-weighted images; on DWI, a mild hyperintensity was noticed. Calculation of the apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) demonstrated an increased diffusion on the affected regions; the hyperintensity on DWI was probably due to a "T2-shine-through" effect. These findings are consistent with the presence of extracellular oedema, without significant neuronal damage. The patient recovered promptly after thiamine administration, and MR alterations disappeared. The favourable evolution indicates that no relevant neuronal death occurred. This is consistent with DWI findings. DWI are more sensitive than ordinary T1- and T2-weighted images to neuronal irreversible damage, and may differentiate between neuronal necrosis and extracellular oedema in various brain pathologies. The demonstration of a limited neuronal damage may represent a favourable prognostic factor in patients with WE.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bergui, M., Bradac, G., Zhong, J. et al. Diffusion-weighted MR in reversible Wernicke encephalopathy. Neuroradiology 43, 969–972 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002340100645
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002340100645