Abstract
Background
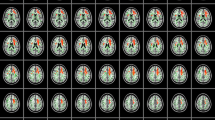
In tuberous sclerosis (TS), tubers usually involve the white matter. Diffusion tensor (DT) images are used to demonstrate white-matter tracts.
Objective
To determine the changes in DT indices in supratentorial tubers and associated changes in the white-matter tracts adjacent to tubers in patients with TS.
Materials and methods
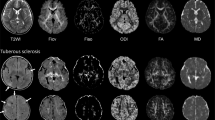
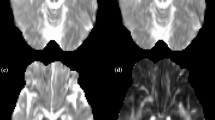
The DT imaging indices, including first, second and third eigenvalues (EVs), apparent diffusion coefficients (ADCs), and fractional anisotropy (FA) in the white-matter lesions of tubers, were assessed in seven patients with TS exhibiting developmental delay and compared with controls.
Results
EV1, EV2, EV3, ADC and FA of the white-matter lesions of tubers were significantly different from contralateral unremarkable regions of the brain and from controls (P<0.05). The number of frontal and parietal tubers was significantly negatively correlated with EV1 of the superior longitudinal fasciculi of TS patients (r=−0.60, P =0.04). In addition, TS patients had significantly larger ADCs in the corona radiata and sagittal stratum than the control subjects. EV3s of the inferior longitudinal fasciculus and sagittal stratum were significantly more increased in the TS patients than in the control subjects.
Conclusions
EV1, EV2, EV3, ADC and FA maps are potential tools for demonstrating cerebral white-matter changes owing to TS.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Seidenwurm DJ, Barkovich AJ (1992) Understanding tuberous sclerosis. Radiology 183:23–24
Joinson C, Callaghan FJ, Osborne JP, et al (2003) Learning disability and epilepsy in an epidemiological sample of individuals with tuberous sclerosis complex. Psychol Med 33:335–344
Curatolo P, Verdecchia M, Bombardieri R (2002) Tuberous sclerosis complex: a review of neurological aspects. Eur J Paediatr Neurol 6:15–23
Curatolo P, Cusmai R, Cortesi F, et al (1991) Neurologic and psychiatric aspects of tuberous sclerosis. Ann NY Acad Sci 615: 8–16
Hosoya M, Naito H, Nihei K (1999) Neurological prognosis correlated with variations over time in the number of subependymal nodules in tuberous sclerosis. Brain Dev 21:544–547
Chien JC, Peng SS, Liu HM, et al (1999) Application of fluid-attenuated inversion recovery pulse sequence in children with tuberous sclerosis. Acta Pediatr Taiwan 40:393–399
Shepherd CW, Houser OW, Gomez MR (1995) MR findings in tuberous sclerosis complex and correlation with seizure development and mental impairment. AJNR 16:149-155
Bolton PF, Griffiths PD (1997) Association of tuberous sclerosis of temporal lobes with autism and atypical autism. Lancet 349:392-395
Jambaque I, Cusmai R, Curatolo P, et al (1991) Neuropsychological aspects of tuberous sclerosis in relation to MRI findings. Dev Med Child Neurol 33: 698-705
Ridler K, Bullmore ET, DeVaries PJ, et al (2001) Widespread anatomical abnormalities of gray and white matter structure in tuberous sclerosis. Psychol Med 31:1437–1446
Braffman BH, Bilaniuk LT, Naidich TP, et al (1982) MR imaging of tuberous sclerosis: pathogenesis of this phakomatosis, use of gadopentetate dimeglumine, and literature review. Radiology 183: 227–238
Marti-Bonmati L, Menor F, Dosda R (2000) Tuberous sclerosis: differences between cerebral and cerebellar cortical tubers in a pediatric population. AJNR 21:557–560
Pierpaoli C, Jezzard P, Basser PJ, et al (1996) Diffusion tensor imaging of the human brain. Radiology 201:637–648
Roach E, Smith M, Huttenlocher P, et al (1992) Diagnostic criteria: tuberous sclerosis complex. Report of the Diagnostic Criteria Committee of the National Tuberous Sclerosis Association. J Child Neurol 7:221–224
Barratt MS, Moyer VA (2000) Pediatric resident and faculty knowledge of the Denver II. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med 154:411–413
Tseng WY, Reese TG, Weisskoff RM, et al (1999) Cardiac diffusion tensor MRI in vivo without strain correction. Magn Reson Med 42:393–403
Griffiths PD, Bolton P, Verity C (1998) White matter abnormalities in tuberous sclerosis complex. Acta Radiol 39:482–486
Hirose T, Scheithauer BW, Lopes MB, et al (1995) Tuber and subependymal giant cell astrocytoma associated with tuberous sclerosis: an immunohistochemical, ultrastructural, and immunoelectron and microscopic study. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 90: 387–399
Arai N, Umitsu R, Komori T, et al (2003) Peculiar form of cerebral microdysgenesis characterized by white matter neurons with perineuronal and perivascular glial satellitosis: a study using a variety of human autopsied brains. Pathol Int 53:345-352
Nixon JR, Miller GM, Okazaki H, et al (1989) Cerebral tuberous sclerosis: postmortem magnetic resonance imaging and pathologic anatomy. Mayo Clin Proc 64:305–311
Yagishita A, Arai N (1999) Cortical tubers without other stigmata of tuberous sclerosis: imaging and pathological findings. Neuroradiology 41:428–432
Kingsley DP, Kendall BE, Fitz CR (1986) Tuberous sclerosis: a clinicoradiologic evaluation of 110 cases with particular reference to atypical presentation. Neuroradiology 28:38–43
Sener RN (1998) Cerebellar involvement in tuberous sclerosis. Comput Med Imaging Graph 22:63–65
DiPaolo D, Zimmerman RA (1995) Solitary cortical tuber. AJNR 16: 1360–1364
Sener RN (2002) Tuberous sclerosis: diffusion MRI findings in the brain. Eur Radiol 12:138–143
Pierpaoli C, Barnett A, Pajevic S, et al (2001) Water diffusion changes in Wallerian degeneration and their dependence on white matter architecture. Neuroimage 13:1174–1185
Eriksson SH, Rugg-Gunn FJ, Symms MR, et al (2001) Diffusion tensor imaging in patients with epilepsy and malformations of cortical development. Brain 124:617–626
Rintahaka PJ, Chugani HT (1997) Clinical role of positron emission tomography in children with tuberous sclerosis complex. J Child Neurol 12:42–52
Roach ES (1997) Tuberous sclerosis: function follows form. J Child Neurol 12:75–76
Goodman M, Lamm SH, Engel A, et al (1996) Cortical tuber count: a biomarker indicating neurologic severity of tuberous sclerosis complex. J Child Neurol 12:85–90
Posner MI, Petersen SE (1990) The attention system of the human brain. Ann Rev Neurosci 3:25–42
Tamminga CA, Shadmehr R, Holcomb HH (2000) Images in neuroscience. Cognition: procedural memory. Am J Psychol 157:162
Eriksson SH, Symms MR, Rugg-Gunn FJ, et al (2002) Exploring white matter tracts in band heterotopia using diffusion tractography. Ann Neurol 52:327–334
Bahn MM (1999) A linear relationship exists among brain diffusion eigenvalues measured by diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging. J Magn Reson 137:33–38
Sorensen AG, Wu O, Copen WA, et al (1999) Human acute cerebral ischemia: detection of changes in water diffusion anisotropy by using MR imaging. Radiology 212:785–792
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by a grant (NSC92-2320-B-002-107) from the National Science Council of Taiwan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, S.SF., Lee, WT., Wang, Y.H. et al. Cerebral diffusion tensor images in children with tuberous sclerosis: a preliminary report. Pediatr Radiol 34, 387–392 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-004-1162-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-004-1162-3