Abstract
Background
Congenital cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection can lead to severe neurological sequelae, but a defined brain magnetic resonance (MR) pattern and MR predictors of clinical outcome are still lacking.
Materials and methods
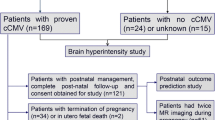
Clinical and MR findings of 14 children with symptomatic congenital CMV infection were retrospectively reviewed.
Results
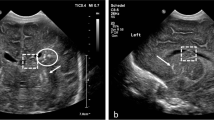
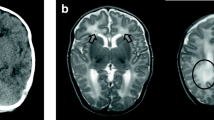
Microcephaly, cerebral palsy and epilepsy were found in eight, six and seven patients, respectively (all concomitant in 6); 12 children developed sensory-neural hearing loss (SNHL). At first MRI (mean age 21 months, range 5–54 months), white matter (WM) involvement was not assessable in two children due to incomplete myelination. WM abnormalities were common (11/12 patients); deep WM was predominantly involved in 5/11; the largest WM lesion was in the parietal lobe in 6/11. Anterior temporal lobe abnormalities were found in 13/14. Six children underwent MRI examination after 2 years of life; in this subgroup, WM abnormalities were extensive and confluent (4/6), bilateral and multifocal (1/6) or absent (1/6). Four children showed a progression of myelination. Ventriculomegaly (9/14), migration disorders (6/14 polymicrogyria and 1/14 pachygyria-lissencephaly) and hippocampal dysplasia (6/14) correlated with severe neurological sequelae (p < 0.05, Fisher exact test), while the presence of WM abnormalities (11/12), periventricular cysts (6/14) and cerebellar hypoplasia (4/14) did not predict the outcome.
Conclusions
The spectrum of brain MR abnormalities in symptomatic congenital CMV infection is extremely wide. WM involvement is variable, difficult to evaluate at a very young age and unrelated to clinical outcome, while cortical malformations, ventriculomegaly and hippocampal dysplasia seem to be strong predictors of poor outcome except for SNHL.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boppana SB, Stagno S, Pass RF et al (1992) Symptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus infection: neonatal morbidity and mortality. Pediatr Infect Dis J 11:93–99
Ivarsson S-A, Lernmark B, Svanberg L (1997) Ten-year clinical, developmental, and intellectual follow- up of children with congenital cytomegalovirus infection without neurologic symptoms at one year of age. Pediatrics 99:800–803
Pass RF, Stagno S, Myers GJ et al (1980) Outcome of symptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus infection: results of long-term longitudinal follow-up. Pediatrics 66:758–762
Stagno S (2001) Cytomegalovirus. In: Remington JS, Klein JO (eds) Infectious diseases of the fetus and newborn infant, 5th edn. Saunders, Philadelphia, pp 389–424
Fowler KB, Stagno S, Pass RF et al (1992) The outcome of congenital cytomegalovirus infection in relation to maternal antibody status. N Engl J Med 326:663–667
Crumpacker CS (2000) Cytomegalovirus. In: Mandell GM, Bennett JE, Dolin R (eds) Principles and practice of infectious diseases, 5th edn. Churchill Livingstone, Philadelphia, pp 1586–1599
Behrman RE (1997) Il feto e il neonato. In: Giovannini M (ed). Trattato di pediatria Nelson, 15th edn. Minerva Medica, Torino, pp 539–540
Barbi M, Binda S, Caroppo S et al (2003) A wider role for congenital cytomegalovirus infection in sensorineural hearing loss. Pediatr Infect Dis J 22:39–42
Williamson WD, Demmler GJ, Percy AK et al (1992) Progressive hearing loss in infants with asymptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus infection. Pediatrics 90:862–866
Boppana SB, Fowler KB, Vaid Y et al (1997) Neuroradiographic findings in the newborn period and long-term outcome in children with symptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus infection. Pediatrics 99:409–414
Noyola DE, Demmler GJ, Nelson CT et al (2001) Early predictors of neurodevelopmental outcome in symptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus infection. J Pediatr 138:325–331
Barkovich AJ, Lindan CE (1994) Congenital cytomegalovirus infection of the brain: imaging analysis and embryologic considerations. Am J Neuroradiol 15:703–715
De Vries LS, Gunardi H, Barth PG et al (2004) The spectrum of cranial ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging abnormalities in congenital cytomegalovirus infection. Neuropediatrics 35:113–119
van der Knaap MS, Vermeulen G, Barkhof F et al (2004) Pattern of white matter abnormalities at MR imaging: use of polymerase chain reaction testing of Guthrie cards to link pattern with congenital cytomegalovirus infection. Radiology 230:529–536
Ross SA, Boppana SB (2004) Congenital cytomegalovirus infection: outcome and diagnosis. Semin Pediatr Infect Dis 16:44–49
van der Knaap MS (2005) Myelination and retarded myelination. In: Magnetic resonance of myelination and myelin disorders, 3rd edn. Springer, pp 40–41
Kenneson A, Cannon MJ (2007) Review and meta-analysis of the epidemiology of congenital cytomegalovirus infection. Rev Med Virol 17:253–276
Nelson CT, Demmler GJ, Istas AS et al (1993) Early prediction of neurodevelopmental outcome in symptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus infection. Pediatr Res 39:180A
Salmaso R, Franco R, de Santis M et al (2007) Early detection by magnetic resonance imaging of fetal cerebral damage in a fetus with hydrops and cytomegalovirus infection. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 20:559–561
Doneda C, Parazzini C, Righini A et al (2010) Early cerebral lesions in cytomegalovirus infection: prenatal MR imaging. Radiology 255:613–621
Benoist G, Salomon LJ, Mohlo M et al (2008) Cytomegalovirus-related fetal brain lesions: comparison between targeted ultrasound examination and magnetic resonance imaging. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 32:900–905
Benoist G, Salomon LJ, Jacquemard F et al (2008) The prognostic value of ultrasound abnormalities and biological parameters in blood of fetuses infected with cytomegalovirus. BJOG 115:823–829
Guerra B, Simonazzi G, Puccetti C et al (2008) Ultrasound prediction of symptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus infection. Am J Obstet Gynecol 198:380.e1–380.e7
Steinlin MI, Nadal D, Eich GF et al (1996) Late intrauterine cytomegalovirus infection: clinical and neuroimaging findings. Pediatr Neurol 15:249–253
Barkovich AJ (2005) Infections of the nervous system. In: Barkovich AJ (ed) Pediatric neuroimaging, 4th edn. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 802–806
Boesch J, Issakainen J, Kewitz G et al (1989) Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain in congenital cytomegalovirus infection. Pediatr Radiol 19:91–93
Sugita K, Ando M, Makino M et al (1991) Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain in congenital rubella virus and cytomegalovirus infection. Neuroradiology 33:239–242
Lopez-Pison J, Rubio-Rubio R, Ureña-Hornos T et al (2005) Diagnóstico retrospectivo de infección congenital por citomegalovirus en un caso clínico infantile. Rev Neurol 40:733–736
O'Rourke D, Bradley L, King MD et al (2010) Leukoencephalopathy with anterior temporal cysts due to congenital CMV infection diagnosed retrospectively. J Neuroimaging 20:292–293
Tatli B, Ozmen M, Aydinli N et al (2005) Not a new leukodystrophy but congenital cytomegalovirus infection. J Child Neurol 20:525
Suzuki Y, Toribe Y, Mogami Y et al (2008) Epilepsy in patients with congenital cytomegalovirus infection. Brain Dev 30:420–424
Guibaud L, Attia-Sobol J, Buenerd A et al (2004) Focal sonographic periventricular pattern associated with mild ventriculomegaly in foetal cytomegalic infection revealing cytomegalic encephalitis in the third trimester of pregnancy. Prenat Diagn 24:727–732
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Chiara Briani, M.D., for helpful comments in the preparation of this manuscript.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manara, R., Balao, L., Baracchini, C. et al. Brain magnetic resonance findings in symptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus infection. Pediatr Radiol 41, 962–970 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-011-2120-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-011-2120-5