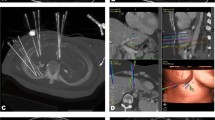
Abstract
Objective
To evaluate prognostic factors associated with local control and disease-free-survival (DFS) of oligometastatic breast cancer patients treated by percutaneous thermal ablation (PTA).
Materials and Methods
Seventy-nine consecutive patients (54.5 ± 11.2 years old) with 114 breast cancer metastases (28.9 ± 16.1 mm in diameter), involving the lungs, the liver, and/or the bone, were treated using PTA with a curative intent. The goal was to achieve a complete remission in association with systemic chemotherapy and hormonal therapy. We retrospectively evaluated the prognostic factors associated with 1- and 2-year local control and the 1- and 2-year DFS rates.
Results
The 1- and 2-year local control rates were 83.0 and 76.1 %, respectively. Tumor burden was associated with a poorer outcome for local control after PTA (HR 1.027 by additional millimeter, p = 0.026; >4 cm HR 3.90). The 1- and 2-year DFS rates were 54.2 and 30.4 %, respectively. In multivariate analysis, triple-negative histological subtype and increased size of treated metastases were associated with a poorer DFS (HR 2.22; 95 % CI [1.13–4.36]; p = 0.02 and HR 2.43; 95 % CI [1.22–4.82]; p = 0.011, respectively).
Conclusion
PTA is effective for local control of breast cancer oligometastases. Tumor burden >4 cm and triple-negative histological subtype are associated with a poorer outcome.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PTA:
-
Percutaneous thermal ablation
- DFS:
-
Disease-free survival
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- FDG-PET:
-
Fluoro-deoxy-glucose positron emission tomography
- OS:
-
Overall survival
References
Karim-Kos HE, de Vries E, Soerjomataram I, Lemmens V, Siesling S, Coebergh JW. Recent trends of cancer in Europe: a combined approach of incidence, survival and mortality for 17 cancer sites since the 1990s. Eur J Cancer. 2008;44:1345–89.
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Thun MJ. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2009;2009:225–49.
Ferlay J, Parkin DM, Steliarova-Foucher E. Estimates of cancer incidence and mortality in Europe in 2008. Eur J Cancer. 2010;46:765–81.
Cortazar P, Zhang L, Untch M, et al. Pathological complete response and long-term clinical benefit in breast cancer: the CTNeoBC pooled analysis. Lancet. 2014;12(384):164–72.
Holmes FA, Buzdar AU, Kau S-W, et al. Combined-modality approach for patients with isolated recurrences of breast cancer (IV-NED)—the M. D. Anderson experience. Breast Dis. 1994;7:7–20.
Singletary SE, Walsh G, Vauthey JN, et al. A role for curative surgery in the treatment of selected patients with metastatic breast cancer. Oncologist. 2003;8:241–51.
Bathe OF, Kaklamanos IG, Moffat FL, Boggs J, Franceschi D, Livingstone AS. Metastasectomy as a cytoreductive strategy for treatment of isolated pulmonary and hepatic metastases from breast cancer. Surg Oncol. 1999;8:35–42.
Lee MT, Kim JJ, Dinniwell R, et al. Phase I study of individualized stereotactic body radiotherapy of liver metastases. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:1585–91.
Scorsetti M, Arcangeli S, Tozzi A, et al. Is stereotactic body radiation therapy an attractive option for unresectable liver metastases? A preliminary report from a phase 2 trial. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2013;86:336–42.
Milano MT, Katz AW, Zhang H, Okunieff P. Oligometastases treated with stereotactic body radiotherapy: long-term follow-up of prospective study. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012;1(83):878–86.
Livraghi T, Goldberg SN, Solbiati L, Meloni F, Ierace T, Gazelle GS. Percutaneous radio-frequency ablation of liver metastases from breast cancer: initial experience in 24 patients. Radiology. 2001;220:145–9.
Lawes D, Chopada A, Gillams A, Lees W, Taylor I. Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) as a cytoreductive strategy for hepatic metastasis from breast cancer. Ann R Coll Surg Engl. 2006;88:639–42.
Gunabushanam G, Sharma S, Thulkar S, et al. Radiofrequency ablation of liver metastases from breast cancer: results in 14 patients. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2007;18:67–72.
Sofocleous CT, Nascimento RG, Gonen M, et al. Radiofrequency ablation in the management of liver metastases from breast cancer. Am J Roentgenol. 2007;189:883–9.
Meloni MF, Andreano A, Laeseke PF, Livraghi T, Sironi S, Lee FT. Breast cancer liver metastases: US-guided percutaneous radiofrequency ablation intermediate and long-term survival rates. Radiology. 2009;253:861–9.
Jakobs TF, Hoffmann RT, Schrader A, et al. CT-guided radiofrequency ablation in patients with hepatic metastases from breast cancer. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol. 2009;32:38–46.
Palussière J, Dixmerias F, Buy X, et al. Interventional radiology procedures in the treatment of bone metastasis. Cancer. 2009;96:1117–26.
Gangi A, Buy X. Interventional radiology in lung cancer: from diagnosis to treatment. Rev Mal Respir. 2007;24(6):137–45.
de Baere T, Palussiere J, Auperin A, et al. Midterm local efficacy and survival after radiofrequency ablation of lung tumors with minimum follow-up of 1 year: prospective evaluation. Radiology. 2006;240:587–96.
Hellman S, Weichselbaum RR. Oligometastases. J Clin Oncol. 1995;13:8–10.
Bergenfeldt M, Jensen BV, Skjoldbye B, Nielsen D. Liver resection and local ablation of breast cancer liver metastases. A systematic review. EJSO. 2011;37:549–57.
Casiraghi M, De Pas T, Maisonneuve P, et al. A 10-year single-center experience on 708 lung metastasectomies: the evidence of the international registry of lung metastases. J Thorac Oncol. 2011;6:1373–8.
Tree AC, Khoo VS, Eeles RA, et al. Stereotactic body radiotherapy for oligometastases. Lancet Oncol. 2013;14:28–37.
Singh D, Chen Y, Hare MZ, et al. Local control rates with five-fraction stereotactic body radiotherapy for oligometastatic cancer to the lung. J Thorac Dis. 2014;6:369–74.
Rusthoven KE, Kavanagh BD, Cardenes H, et al. Multi-institutional phase I/II trial of stereotactic body radiation therapy for liver metastases. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:1572–8.
Lermite E, Marzano E, Chéreau E, Rouzier R, Pessaux P. Surgical resection of liver metastases from breast cancer. Surg Oncol. 2010;19:79–84.
Illing R, Gillams A. Radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of breast cancer liver metastases. Clin Oncol. 2010;22:781–4.
Gervais DA. Cryoablation versus radiofrequency ablation for renal tumor ablation: time to reassess? J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2013;24:1135–8.
Vogl TJ, Farshid P, Naguib NN, et al. Ablation therapy of hepatocellular carcinoma: a comparative study between radiofrequency and microwave ablation. Abdom Imaging. 2015;40(1829–1837):35.
Gazelle GS, McMahon PM, Beinfeld MT, Halpern EF, Weinstein MC. Metastatic colorectal carcinoma: cost-effectiveness of percutaneous radiofrequency ablation versus that of hepatic resection. Radiology. 2004;233:729–39.
Gillams AR, Lees WR. Five-year survival in 309 patients with colorectal liver metastases treated with radiofrequency ablation. Eur Radiol. 2009;19:1206–13.
Lencioni R, Crocetti L, Cioni R, et al. Response to radiofrequency ablation of pulmonary tumours: a prospective, intention-to-treat, multicentre clinical trial (the RAPTURE study). Lancet Oncol. 2008;9:621–8.
Palussiere J, Lagarde P, Aupérin A, Deschamps F, Chomy F, de Baere T. Percutaneous lung thermal ablation of non-surgical clinical N0 non-small cell lung cancer: results of eight years’ experience in 87 patients from two centers. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2015;38:160–6.
Iguchi T, Hiraki T, Gobara H, et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of lung cancer presenting as ground-glass opacity. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2015;38:409–15.
Wei Z, Ye X, Yang X, et al. Microwave ablation in combination with chemotherapy for the treatment of advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2015;38:135–42.
Koelblinger C, Strauss S, Gillams A. Outcome after radiofrequency ablation of sarcoma lung metastases. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2014;37:147–53.
Deschamps F, Farouil G, Ternes N, et al. Thermal ablation techniques: a curative treatment of bone metastases in selected patients? Eur Radiol. 2014;24:1971–80.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
All authors of the manuscript: Barral Matthias, Aupérin Anne, Hakimé Antoine, Cartier Victoire, Tacher Vania, Otmezguine Yves, Tselikas Lambros, de Baere Thierry, and Deschamps Frédéric have nothing to disclose.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Barral, M., Auperin, A., Hakime, A. et al. Percutaneous Thermal Ablation of Breast Cancer Metastases in Oligometastatic Patients. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 39, 885–893 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-016-1301-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-016-1301-x