Abstract
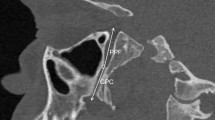
The anatomy of the pterygopalatine fossa keeps a traditional level and is viewed as constant, even though a series of structures neighboring the fossa are known to present individual variations. We aimed to evaluate on 3D volume renderizations the anatomical variables of the pterygopalatine fossa, as related to the variable pneumatization patterns of the bones surrounding the fossa. The study was performed retrospectively on cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) scans of 100 patients. The pterygopalatine fossa was divided into an upper (orbital) and a lower (pterygomaxillary) floor; the medial compartment of the orbital floor lodges the pterygopalatine ganglion. The pneumatization patterns of the pterygopalatine fossa orbital floor walls were variable: (a) the posterior wall pneumatization pattern was determined in 89.5 % by recesses of the sphenoidal sinus related to the maxillary nerve and pterygoid canals; (b) the upper continuation of the pterygopalatine fossa with the orbital apex was narrowed in 79.5 % by ethmoid air cells and/or a maxillary recess of the sphenoidal sinus; (c) according to its pneumatization pattern, the anterior wall of the pterygopalatine fossa was a maxillary (40.5 %), maxillo-ethmoidal (46.5 %), or maxillo-sphenoidal (13 %) wall. The logistic regression models showed that the maxillo-ethmoidal type of pterygopalatine fossa anterior wall was significantly associated with a sphenoidal sinus only expanded above the pterygoid canal and a spheno-ethmoidal upper wall. The pterygopalatine fossa viewed as an intersinus space is related to variable pneumatization patterns which can be accurately identified by CBCT and 3DVR studies, for anatomic and preoperatory purposes.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvernia JE, Spomar DG, Olivero WC (2007) A computed tomography scan and anatomical cadaveric study of the pterygopalatine ganglion for use in Gamma Knife treatment of cluster headache. J Neurosurg 107(4):805–808. doi:10.3171/JNS-07/10/0805
Angelopoulos C, Thomas SL, Hechler S, Parissis N, Hlavacek M (2008) Comparison between digital panoramic radiography and cone-beam computed tomography for the identification of the mandibular canal as part of presurgical dental implant assessment. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 66(10):2130–2135. doi:10.1016/j.joms.2008.06.021
Arslan H, Aydinlioglu A, Bozkurt M, Egeli E (1999) Anatomic variations of the paranasal sinuses: CT examination for endoscopic sinus surgery. Auris Nasus Larynx 26(1):39–48
Awwad RJ, Goyal P, Emko P (2006) Endoscopic transnasal approach for retrieval of foreign bodies from the pterygomaxillary fossa. Am J Otolaryngol 27(6):440–442. doi:10.1016/j.amjoto.2006.03.009
Batra PS, Citardi MJ, Gallivan RP, Roh HJ, Lanza DC (2004) Software-enabled computed tomography analysis of the carotid artery and sphenoid sinus pneumatization patterns. Am J Rhinol 18(4):203–208
Bolger WE, Butzin CA, Parsons DS (1991) Paranasal sinus bony anatomic variations and mucosal abnormalities: CT analysis for endoscopic sinus surgery. Laryngoscope 101(1 Pt 1):56–64. doi:10.1288/00005537-199101000-00010
Cappabianca P, Cavallo LM, Esposito F, De Divitiis O, Messina A, De Divitiis E (2008) Extended endoscopic endonasal approach to the midline skull base: the evolving role of transsphenoidal surgery. Adv Tech Stand Neurosurg 33:151–199
Carter LC, Pfaffenbach A, Donley M (1999) Hyperaeration of the sphenoid sinus: cause for concern? Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 88(4):506–510
Cavallo LM, Messina A, Gardner P, Esposito F, Kassam AB, Cappabianca P, de Divitiis E, Tschabitscher M (2005) Extended endoscopic endonasal approach to the pterygopalatine fossa: anatomical study and clinical considerations. Neurosurg Focus 19(1):E5
Ciobanu IC, Motoc A, Jianu AM, Cergan R, Banu MA, Rusu MC (2009) The maxillary recess of the sphenoid sinus. Rom J Morphol Embryol 50(3):487–489
Daniels DL, Mark LP, Ulmer JL, Mafee MF, McDaniel J, Shah NC, Erickson S, Sether LA, Jaradeh SS (1998) Osseous anatomy of the pterygopalatine fossa. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 19(8):1423–1432
Earwaker J (1993) Anatomic variants in sinonasal CT. Radiographics 13(2):381–415
Erdogan N, Unur E, Baykara M (2003) CT anatomy of pterygopalatine fossa and its communications: a pictorial review. Comput Med Imaging Graph 27(6):481–487
Fortes FS, Sennes LU, Carrau RL, Brito R, Ribas GC, Yasuda A, Rodrigues AJ Jr, Snyderman CH, Kassam AB (2008) Endoscopic anatomy of the pterygopalatine fossa and the transpterygoid approach: development of a surgical instruction model. Laryngoscope 118(1):44–49. doi:10.1097/MLG.0b013e318155a492
Georgescu CE, Rusu MC, Sandulescu M, Enache AM, Didilescu AC (2012) Quantitative and qualitative bone analysis in the maxillary lateral region. Surg Radiol Anat. doi:10.1007/s00276-012-0955-6
Gunkel AR, Freysinger W, Thumfart WF (1997) 3D anatomo-radiological basis of endoscopic surgery of the paranasal sinuses. Surg Radiol Anat 19(1):7–10
Hamid O, El Fiky L, Hassan O, Kotb A, El Fiky S (2008) Anatomic variations of the sphenoid sinus and their impact on trans-sphenoid pituitary surgery. Skull Base 18(1):9–15. doi:10.1055/s-2007-992764
Hewaidi G, Omami G (2008) Anatomic variation of sphenoid sinus and related structures in Libyan population: CT scan study. Libyan J Med 3(3):128–133. doi:10.4176/080307
Hofstetter CP, Singh A, Anand VK, Kacker A, Schwartz TH (2010) The endoscopic, endonasal, transmaxillary transpterygoid approach to the pterygopalatine fossa, infratemporal fossa, petrous apex, and the Meckel cave. J Neurosurg 113(5):967–974. doi:10.3171/2009.10.JNS09157
Holbrook Curtis H (1904) The sphenoidal sinus and its surgical relationship. Laryngoscope 11:856–867
Hwang SH, Seo JH, Joo YH, Kim BG, Cho JH, Kang JM (2011) An anatomic study using three-dimensional reconstruction for pterygopalatine fossa infiltration via the greater palatine canal. Clin Anat 24(5):576–582. doi:10.1002/ca.21134
Idowu OE, Balogun BO, Okoli CA (2009) Dimensions, septation, and pattern of pneumatization of the sphenoidal sinus. Folia Morphol 68(4):228–232
Kassam AB, Gardner P, Snyderman C, Mintz A, Carrau R (2005) Expanded endonasal approach: fully endoscopic, completely transnasal approach to the middle third of the clivus, petrous bone, middle cranial fossa, and infratemporal fossa. Neurosurg Focus 19(1):E6
Lewin JS, Curtin HD, Eelkema E, Obuchowski N (1999) Benign expansile lesions of the sphenoid sinus: differentiation from normal asymmetry of the lateral recesses. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20(3):461–466
Meloni F, Mini R, Rovasio S, Stomeo F, Teatini GP (1992) Anatomic variations of surgical importance in ethmoid labyrinth and sphenoid sinus. A study of radiological anatomy. Surg Radiol Anat 14(1):65–70
Methathrathip D, Apinhasmit W, Chompoopong S, Lertsirithong A, Ariyawatkul T, Sangvichien S (2005) Anatomy of greater palatine foramen and canal and pterygopalatine fossa in Thais: considerations for maxillary nerve block. Surg Radiol Anat 27(6):511–516. doi:10.1007/s00276-005-0016-5
Meyers RM, Valvassori G (1998) Interpretation of anatomic variations of computed tomography scans of the sinuses: a surgeon’s perspective. Laryngoscope 108(3):422–425
Miracle AC, Mukherji SK (2009) Conebeam CT of the head and neck, part 2: clinical applications. AJNR. Am J Neuroradiol 30(7):1285–1292. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A1654
Mosher HP (1903) The anatomy of the sphenoidal sinus and the method of approaching it from the antrum. Laryngoscope XII:177–214
Omami G, Hewaidi G, Mathew R (2011) The neglected anatomical and clinical aspects of pterygoid canal: CT scan study. Surg Radiol Anat 33(8):697–702. doi:10.1007/s00276-011-0808-8
Osawa S, Rhoton AL Jr, Seker A, Shimizu S, Fujii K, Kassam AB (2009) Microsurgical and endoscopic anatomy of the vidian canal. Neurosurgery 64(5 Suppl 2):385–411; discussion 411–382. doi:10.1227/01.NEU.0000338945.54863.D9
Paturet G (1958) Traite d’anatomie humaine. Masson et C.i.e Paris
Piagkou M, Demesticha T, Troupis T, Vlasis K, Skandalakis P, Makri A, Mazarakis A, Lappas D, Piagkos G, Johnson EO (2011) The pterygopalatine ganglion and its role in various pain syndromes: from anatomy to clinical practice. Pain Pract. doi:10.1111/j.1533-2500.2011.00507.x
Roche PH, Fournier HD, Laccourreye L, Mercier P (2001) Surgical anatomy of the infratemporal fossa using the transmaxillary approach. Surg Radiol Anat 23(4):209–213
Rumboldt Z, Castillo M, Smith JK (2002) The palatovaginal canal: can it be identified on routine CT and MR imaging? AJR Am J Roentgenol 179(1):267–272
Rusu MC (2011) Doubled foramen rotundum and maxillary nerve fenestration. Surg Radiol Anat 33(8):723–726. doi:10.1007/s00276-011-0810-1
Rusu MC (2010) Microanatomy of the neural scaffold of the pterygopalatine fossa in humans: trigeminovascular projections and trigeminal-autonomic plexuses. Folia Morphol (Warsz) 69(2):84–91
Rusu MC, Leonardi R (2010) The sphenoidal spine and the sphenoidal tubercle. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 39(10):1042–1043; author reply 1043. doi: 10.1016/j.ijom.2010.06.008
Rusu MC, Pop F (2010) The anatomy of the sympathetic pathway through the pterygopalatine fossa in humans. Ann Anat 192(1):17–22. doi:10.1016/j.aanat.2009.10.003
Rusu MC, Pop F, Curca GC, Podoleanu L, Voinea LM (2009) The pterygopalatine ganglion in humans: a morphological study. Ann Anat 191(2):196–202. doi:10.1016/j.aanat.2008.09.008
Sareen D, Agarwal AK, Kaul JM, Sethi A (2005) Study of sphenoid sinus anatomy in relation to endoscopic surgery. Int J Morphol 23(3):261–266
Stojcev Stajcic L, Gacic B, Popovic N, Stajcic Z (2010) Anatomical study of the pterygopalatine fossa pertinent to the maxillary nerve block at the foramen rotundum. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 39(5):493–496. doi:10.1016/j.ijom.2009.11.002
Tan HK, Ong YK (2007) Sphenoid sinus: an anatomic and endoscopic study in Asian cadavers. Clin Anat 20(7):745–750. doi:10.1002/ca.20507
Terra ER, Guedes FR, Manzi FR, Boscolo FN (2006) Pneumatization of the sphenoid sinus. Dentomaxillofac Radiol 35(1):47–49. doi:10.1259/dmfr/55048928
Theodosopoulos PV, Guthikonda B, Brescia A, Keller JT, Zimmer LA (2010) Endoscopic approach to the infratemporal fossa: anatomic study. Neurosurgery 66(1):196–202; discussion 202–193. doi:10.1227/01.NEU.0000359224.75185.43
Uddin FJ, Sama A, Jones NS (2003) Three-dimensional computer-aided endoscopic sinus surgery. J Laryngol Otol 117(5):333–339. doi:10.1258/002221503321626348
Unal B, Bademci G, Bilgili YK, Batay F, Avci E (2006) Risky anatomic variations of sphenoid sinus for surgery. Surg Radiol Anat 28(2):195–201. doi:10.1007/s00276-005-0073-9
Vallejo R, Benyamin R, Yousuf N, Kramer J (2007) Computed tomography-enhanced sphenopalatine ganglion blockade. Pain Pract 7(1):44–46. doi:10.1111/j.1533-2500.2007.00110.x
Van Alyea OE (1941) Sphenoid sinus. Arch Otolaryngol 34:225–253
Wanamaker HH (1996) Role of Haller’s cell in headache and sinus disease: a case report. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 114(2):324–327
Williams PL, Gray H, Bannister LH (1999) Gray’s anatomy: the anatomical basis of medicine and surgery. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh
Wormald PJ (2008) Endoscopic sinus surgery. Anatomy, Three-Dimensional Reconstruction, and Surgical Technique. Thieme New York
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Sectoral Operational Programme Human Resources Development (SOP HRD), financed from the European Social Fund and by the Romanian Government under the contract number POSDRU/89/1.5/S/64153.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rusu, M.C., Didilescu, A.C., Jianu, A.M. et al. 3D CBCT anatomy of the pterygopalatine fossa. Surg Radiol Anat 35, 143–159 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-012-1009-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-012-1009-9