Abstract
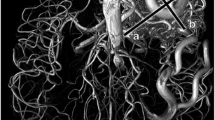
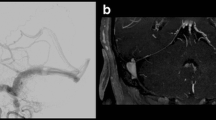
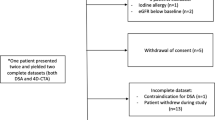
We assessed the value of three-dimensional (3D) dynamic magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) for the follow-up of patients with radiosurgically treated cerebral arteriovenous malformations (AVMs). Fifty-four patients with cerebral AVMs treated by radiosurgery (RS) were monitored using conventional catheter angiography (CCA) and 3D dynamic MRA with sensitivity encoding based on the parallel imaging. Cerebral AVM was qualitatively classified by two radiologists into one of five categories in terms of residual nidus size and persistence of early draining vein (I, >6 cm; II, 3–6 cm; III, <3 cm; IV, isolated early draining vein; V, complete obliteration). 3D MRA findings showed a good agreement with CCA in 40 cases (κ=0.62). Of 23 nidus detected on CCA, 3D dynamic MRA showed 14 residual nidus. Of 28 occluded nidus on 3D dynamic MRA, 22 nidus were occluded on CCA. The sensitivity and specificity of 3D dynamic MRA for the detection of residual AVM were 81% and 100%. 3D dynamic MRA after RS may therefore be useful in association with MRI and can be repeated as long as opacification of the nidus or early venous drainage persists, one CCA remaining indispensable to affirm the complete occlusion at the end of follow-up.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Byrne JV (2005) Cerebrovascular malformations. Eur Radiol 15:448–452
Korosec FR, Turski PA, Carroll TJ, Mistretta CA, Grist TM (1999) Contrast-enhanced MR angiography of the carotid bifurcation. J Magn Reson Imaging 10:317–325
Remonda L, Heid O, Schroth G (1998) Carotid artery stenosis, occlusion, and pseudo-occlusion: first-pass, gadolinium-enhanced, three-dimensional MR angiography-preliminary study. Radiology 209:95–102
Remonda L, Senn P, Barth A, Arnold M, Lovblad KO, Schroth G (2002) Contrast-enhanced 3D MR angiography of the carotid artery: comparison with conventional digital subtraction angiography. Am J Neuroradiol 23:213–219
Sanelli PC, Mifsud MJ, Stieg PE (2004) Role of CT angiography in guiding management decisions of newly diagnosed and residual arteriovenous malformations. Am J Roentgenol 183:1123–1126
Duran M, Schoenberg SO, Yuh WT, Knopp MV, van Kaick G, Essig M (2002) Cerebral arteriovenous malformations: morphologic evaluation by ultrashort 3D gadolinium-enhanced MR angiography. Eur Radiol 12:2957–2964
Farb RI, McGregor C, Kim JK, Laliberte M, Derbyshire JA, Willinsky RA, Cooper PW, Westman DG, Cheung G, Schwartz ML, Stainsby JA, Wright GA (2001) Intracranial arteriovenous malformations: real-time auto-triggered elliptic centric-ordered 3D gadolinium-enhanced MR angiography-initial assessment. Radiology 220:244–251
Griffiths PD, Hoggard N, Warren DJ, Wilkinson ID, Anderson B, Romanowski CA (2000) Brain arteriovenous malformations: assessment with dynamic MR digital subtraction angiography. Am J Neuroradiol 1892–1899
Klisch J, Strecker R, Hennig J, Schumacher M (2000) Time-resolved projection MRA: clinical application in intracranial vascular malformations. NeuroRadiology 42:104–107
Aoki S, Yoshikawa T, Hori M, Ishigame K, Nambu A, Kumagai H, Araki T (2000) Two-dimensional thick-slice MR digital subtraction angiography for assessment of cerebrovascular occlusive diseases. Eur Radiol 10:1858–1864
Tsuchiya K, Katase S, Yoshino A, Hachiya J (2000) MR digital subtraction angiography of cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Am J Neuroradiol 21:707–711
Mori H, Aoki S, Okubo T, Hayashi N, Masumoto T, Yoshikawa T, Tago M, Shin M, Kurita H, Abe O, Ohtomo K (2003) Two-dimensional thick-slice MR digital subtraction angiography in the assessment of small to medium-size intracranial arteriovenous malformations. NeuroRadiology 45:27–33
Warren DJ, Hoggard N, Walton L, Radatz MW, Kemeny AA, Forster DM, Wilkinson ID, Griffiths PD (2001) Cerebral arteriovenous malformations: comparison of novel magnetic resonance angiographic techniques and conventional catheter angiography. Neurosurgery 48:973–982
Pruessmann KP, Weiger M, Scheidegger MB, Boesiger P (1999) SENSE: sensitivity encoding for fast MRI. Magn Reson Med 42:952–962
Weiger M, Pruessmann KP, Kassner A, Roditi G, Lawton T, Reid A, Boesiger P (2000) Contrast-enhanced 3D MRA using SENSE. J Magn Reson Imaging 12:671–677
Sodickson DK, Manning WJ (1997) Simultaneous acquisition of spatial harmonics (SMASH): fast imaging with radiofrequency coil arrays. Magn Reson Med 38:591–603
Chen Q, Quijano CV, Mai VM, Krishnamoorthy SK, Li W, Storey P, Edelman RR (2004) On improving temporal and spatial resolution of 3D contrast-enhanced body MR angiography with parallel imaging. Radiology 231:893–899
Tsuchiya K, Aoki C, Fujikawa A, Hachiya J (2004) Three-dimensional MR digital subtraction angiography using parallel imaging and keyhole data sampling in cerebrovascular diseases: initial experience. Eur Radiol 14:1494–1497
Betti OO (1987) Treatment of arteriovenous malformations with the linear accelerator. Appl Neurophysiol 50:262
Schlienger M, Lefkopoulos D, Nataf F, Mammar H, Missir O, Meder JF, Huart J, Platoni P, Deniaud-Alexandre E, Merienne L (2003) Repeat linear accelerator radiosurgery for cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 56:529–536
Flickinger JC, Kondziolka D, Maitz AH, Lunsford LD (2002) An analysis of the dose-response for arteriovenous malformation radiosurgery and other factors affecting obliteration. Radiother Oncol 63:347–354
Anzalone N, Scomazzoni F, Strada L, Patay Z, Scotti G (1998) Intracranial vascular malformations. Eur Radiol 8:685–690
Ehricke HH, Schad LR, Gademann G, Wowra B, Engenhart R, Lorenz WJ (1992) Use of MR angiography for stereotactic planning. J Comput Assist Tomogr 16:35–40
Parker DL, Tsuruda JS, Goodrich KC, Alexander AL, Buswell HR (1998) Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography of cerebral arteries. A review. Invest Radiol 33:560–572
Du YP, Parker DL, Davis WL, Cao G, Buswell HR, Goodrich KC (1996) Experimental and theoretical studies of vessel contrast-to-noise ratio in intracranial time-of-flight MR angiography. J Magn Reson Imaging 6:99–108
Marchal G, Michiels J, Bosmans H, Van Hecke P (1992) Contrast-enhanced MRA of the brain. J Comput Assist Tomogr 16:25–29
Runge VM, Kirsch JE, Lee C (1993) Contrast-enhanced MR angiography. J Magn Reson Imaging 3:233–239
Jung HW, Chang KH, Choi DS, Han MH, Han MC (1995) Contrast-enhanced MR angiography for the diagnosis of intracranial vascular disease: optimal dose of gadopentetate dimeglumine. Am J Roentgenol 165:1251–1255
Sanelli PC, Mifsud MJ, Zelenko N, Heier LA (2005) CT angiography in the evaluation of cerebrovascular diseases. Am J Roentgenol 184:305–312
Stancanello J, Cavedon C, Francescon P, Cerveri P, Ferrigno G, Colombo F, Perini S (2004) Development and validation of a CT-3D rotational angiography registration method for AVM radiosurgery. Med Phys 31:1363–1371
Wu J, Chen X, Shi Y, Chen S (2000) Noninvasive three-dimensional computed tomographic angiography in preoperative detection of intracranial arteriovenous malformations. Chin Med J (Engl) 113:915–920
Tanaka H, Numaguchi Y, Konno S, Shrier DA, Shibata DK, Patel U (1997) Initial experience with helical CT and 3D reconstruction in therapeutic planning of cerebral AVMs: comparison with 3D time-of-flight MRA and digital subtraction angiography. J Comput Assist Tomogr 21:811–817
Aoki S, Sasaki Y, Machida T, Hayashi N, Shirouzu I, Ohkubo T, Terahara A, Kawamoto S, Araki T, Maehara T (1998) 3D-CT angiography of cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Radiat Med 16:263–271
Royal College of Radiologists (1998) Making the best use of a Department of Radiology: guidelines for doctors, 4th edn. Royal College of Radiologists, London
EU Council Directive (1997) Health protection of individuals against the dangers of ionising radiation in relation to medical exposure. 1997/43, Euratom, 30 June
Korosec FR, Frayne R, Grist TM, Mistretta CA (1996) Time-resolved contrast-enhanced 3D MR angiography. Magn Reson Med 36:345–351
Prince MR, Yucel EK, Kaufman JA, Harrison DC, Geller SC (1993) Dynamic gadolinium-enhanced three-dimensional abdominal MR arteriography. J Magn Reson Imaging 3:877–881
Barger AV, Block WF, Toropov Y, Grist TM, Mistretta CA (2002) Time-resolved contrast-enhanced imaging with isotropic resolution and broad coverage using an undersampled 3D projection trajectory. Magn Reson Med 48:297–305
Carroll TJ (2002) The emergence of time-resolved contrast-enhanced MR imaging for intracranial angiography. Am J Neuroradiol 23:346–348
Shim YW, Chung TS, Kang WS, Joo JY, Strecker R, Hennig J (2002) Non-invasive follow-up evaluation of post-embolized AVM with time-resolved MRA: a case report. Korean J Radiol 3:271–275
Leclerc X, Khalil C, Silvera S, Gauvrit JY, Bracard S, Meder JF, Pruvo JP (2003) Imaging of non-traumatic intracerebral hematoma. J Neuroradiol 30:303–316
Mori H, Aoki S, Masumoto T, Yoshikawa T, Tago M, Shin M, Ohtomo K, Kabasawa H (2002) Two-dimensional magnetic resonance digital substraction angiography using array spatial sensitivity encoding techniques in the assessment of intracranial hemodynamics. Radiat Med 20:223–229
Sodickson DK, McKenzie CA, Li W, Wolff S, Manning WJ, Edelman RR (2000) Contrast-enhanced 3D MR angiography with simultaneous acquisition of spatial harmonics: a pilot study. Radiology 217:284–289
Gauvrit JY, Leclerc X, Oppenheim C, Munier T, Trystram D, Rachdi H, Nataf F, Pruvo JP, Meder JF (2005) Three-dimensional dynamic MR digital subtraction angiography using sensitivity encoding for the evaluation of intracranial arteriovenous malformations: a preliminary study. Am J Neuroradiol 26:1525–1531
Paschal CB, Morris HD (2004) K-space in the clinic. J Magn Reson Imaging 19:145–159
Frayne R, Grist TM, Swan JS, Peters DC, Korosec FR, Mistretta CA (2000) 3D MR DSA: effects of injection protocol and image masking. J Magn Reson Imaging 12:476–487
Guo WY, Lindquist C, Karlsson B, Kihlstrom L, Steiner L (1993) Gamma knife surgery of cerebral arteriovenous malformations: serial MR imaging studies after radiosurgery. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 25:315–323
Kihlstrom L, Guo WY, Karlsson B, Lindquist C, Lindqvist M (1997) Magnetic resonance imaging of obliterated arteriovenous malformations up to 23 years after radiosurgery. J Neurosurg 86:589–593
Friedman WA, Bova FJ, Mendenhall WM (1995) Linear accelerator radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations: the relationship of size to outcome. J Neurosurg 82:180–189
Lunsford LD, Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC, Bissonette DJ, Jungreis CA, Maitz AH, Horton JA, Coffey RJ (1991) Stereotactic radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations of the brain. J Neurosurg 75:512–524
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gauvrit, JY., Oppenheim, C., Nataf, F. et al. Three-dimensional dynamic magnetic resonance angiography for the evaluation of radiosurgically treated cerebral arteriovenous malformations. Eur Radiol 16, 583–591 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-005-0011-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-005-0011-6