Abstract
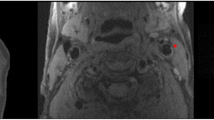
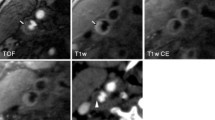
The purpose of this study was to determine if carotid artery wall thickness (CAWT) studied by using multi-detector-row CT angiography (MDCTA) can be considered an effective parameter predictive of increased risk of stroke. A total of 217 patients were retrospectively studied by using MDCTA. In all patients CAWT was measured with an internal digital caliper. Continuous data were described as the mean value ± standard deviation (SD), and they were compared with Student’s t-test. Scatter plots to determine interobserver agreement were performed, and correlation coefficient was calculated with Pearson statistics. A P value <0.05 was considered to mean statistical significance. Measurements of the distal common CAWT ranged from 0.5 to 1.6 mm. In the patient group without stroke, average CAWT was 0.82 mm (0.22 SD), whereas in patient group with stroke it was 1.096 mm (0.21 SD). CAWT in patients without stroke showed statistical difference (P < 0.0001) when compared to patients with stroke. By using a threshold of 1 mm, an important statistical association between thick CAWT and stroke was found (P < 0.0001). In fact, patients with ≥1 mm CAWT had stroke with an odds ratio of 8.16 when compared with patients with <1 mm CAWT. Resulting data suggested that an increased CAWT is an indicator for risk of stroke. This parameter should be considered in addition to other well-known risk factors such as diabetes, hypertension, smoking, and dyslipidemia.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Thom T, Haase N, Rosamond W, Rosamond W, Howard VJ, Rumsfeld J, Manolio T, Zheng ZJ, Flegal K, O’Donnel C, Kittner S, Lloyd-Jones D, Goff DC Jr, Hong Y, Adams R, Friday G, Furie K, Gorelick P, Kissela B, Marler J, Meigs J, Roger V, Sidney S, Sorlie P, Steinberger J, Wasserthiel-Smoller S, Wilson M, Wolf P, American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommitee (2006) Heart disease and stroke statistics - 2006 update. A report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation 113:85–151
Saba L, Sanfilippo R, Pirisi R, Pascalis L, Montisci R, Mallarini G (2007) Multi-detector row CT angiography in the study of atherosclerotic carotid artery. Neuroradiology 49:623–637
North American Symptomatic Carotid Endarterectomy Trial Collaborators (1991) Beneficial effect of carotid endarterectomy in symptomatic patients high with grade stenosis. N Engl J Med 325:445–453
European Carotid Surgery Trialists’ Collaborative Group (1998) Randomised trial of endarterectomy for recently symptomatic carotid stenosis: final results of the MRC European Carotid Surgery Trial (ECST). Lancet 351:1379–1387
Nandalur KR, Baskurt E, Hagspiel K, Douglas Philips C, Kramer CM (2005) Calcified carotid atherosclerotic plaque is associated less with ischemic symptoms than is non calcified plaque on MDTC. Am J Roentgenol 184:295–298
Saba L, Caddeo G, Sanfilippo R, Montisci R, Mallarini G (2007) CT and US in the study of ulcerated carotid plaque compared with surgical results. Advantages of multi-detector-row CT angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28:1061–1066
Naghavi M, Libby P, Falk E, Casscells SW, Litovsky S, Rumberger J, Badimon JJ, Stefanadis C, Moreno P, Pasterkamp G, Fayad Z, Stone PH, Waxman S, Raggi P, Madjid M, Zarrabi A, Burke A, Yuan C, Fitzgerald PJ, Siscovick DS, de Korte CL, Aikawa M, Airaksinen KE, Assmann G, Becker CR, Chesebro JH, Farb A, Galis ZS, Jackson C, Jang IK, Koenig W, Lodder RA, March K, Demirovic J, Navab M, Priori SG, Rekhter MD, Bahr R, Grundy SM, Mehran R, Colombo A, Boerwinkle E, Ballantyne C, Insull W Jr, Schwartz RS, Vogel R, Serruys PW, Hansson GK, Faxon DP, Kaul S, Drexler H, Greenland P, Muller JE, Virmani R, Ridker PM, Zipes DP, Shah PK, Willerson JT (2003) From vulnerable plaque to vulnerable patient: a call for new definitions and risk assessment strategies. Part I. Circulation 108:1664–1672
Rothwell PM, Gibson R, Warlow CP (2000) Interrelation between plaque surface morphology and degree of stenosis on carotid angiograms and the risk of ischemic stroke in patients with symptomatic carotid stenosis. Stroke 31:615–621
Takaya N, Yuan C, Chu B, Saam T, Polissar NL, Jarvik GP, Isaac C, McDonough J, Natiello C, Small R, Ferguson MS, Hatsukami TS (2005) Presence of intraplaque hemorrhage stimulates progression of carotid atherosclerotic plaques: a high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging study. Circulation 111:2768–2775
Zureik M, Ducimetiere P, Touboul PJ, Courbon D, Bonithon-Kopp C, Berr C, Magne C (2000) Common carotid intima-media thickness predicts occurrence of carotid atherosclerotic plaques: longitudinal results from the aging vascular study (EVA). Aterioscler Thromb Vasc Bio 20(6):1622–1629
Inoue K, Matsumoto M, Shono T, Toyokawa S, Moriki A (2007) Increased intima-media thickness and atherosclerotic plaque in the carotid artery as risk factors for silent brain infarcts. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 16:14–20
Pruissen DM, Gerristen SA, Prinsen TJ, Dijk JM, Kappelle LJ, Algra A (2007) SMART Study Group. Carotid intima media thickness is different in large and small-vessel ischemic stroke: the SMART study. Stroke 38:1371–1373
Salonen JR, Salonen R (1993) Ultrasound B-mode imaging in observational studies of atherosclerotic progression. Circulation 87 (suppl II):56–65
Baldassarre D, Amato M, Bondioli A, Sirtori CR, Tremoli E (2000) Carotid artery intima-media thickness measured by ultrasonography in normal clinical practice correlates well with atherosclerotic risk factors. Stroke 31:2426–2430
Frauchiger B, Schmid HP, Roedel C, Moosmann P, Staub D (2001) Comparison of carotid arterial resistive indices with intima-media thickness as sonographic markers of atherosclerosis. Stroke 32:836–841
Bozzao A, Floris R, Pocek M, Fasoli F, Garaci FG, Simonetti G (2001) Non-invasive assessment of epiaortic vessels. Comparison of magnetic resonance angiography with gadolinium, spiral computerized tomography angiography, and digital angiography. Radiol Med 101:48–53
Bartlett ES, Walters TD, Symons SP, Fox AJ (2006) Diagnosing carotid stenosis near-occlusions by using CT angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:632–637
Saba L, Caddeo G, Sanfilippo R, Montisci R, Mallarini G (2007) CT and US in the study of ulcerated carotid plaque compared with surgical results. Advantages of multi-detector-row CT angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28:716–723
Hardie AD, Kramer CM, Raghavan P, Baskurt E, Nandalur K (2007) The impact of expansive arterial remodeling on clinical presentation in carotid artery disease: a multidetector CT angiography study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28:1067–1070
Saba L, Mallarini G (2008) MDCTA in the study of carotid plaque stenosis degree: evaluation of inter-observer agreement. AJR Am J Roentgenol 190:W41–W46
Ebrahim S, Papacosta O, Whincup P, Wannamethee G, Walker M, Nicolaides AN, Dhanjil S, Griffin M, Belcaro G, Rumley A, Rowe GD (1999) Carotid plaque, intima media thickness, cardiovascular risk factors, and prevalent cardiovascular disease in men and women: the British Regional Heart Study. Stroke 30:841–850
Tahmasebpour HR, Buckley AR, Cooperberg PL, Fix CH (2005) Sonographic examination of the carotid arteries. RadioGraphics 25:1561–1575
Davis PH, Dawson JD, Riley WA, Lauer RM (2001) Carotid intimal-medial thickness is related to cardiovascular risk factors measured from childhood through middle age: the Muscatine study. Circulation 104:2815–2819
Simon A, Gariepy J, Chironi G, Megnien JL, Levenson J (2002) Intima-media thickness: a new tool for diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular risk. J Hypertens 20:159–169
Bots ML, Hoes AW, Koudstaal PJ, Hofman A, Grobbee DE (1997) Common carotid intima-media thickness and risk of stroke and myocardial infarction: the Rotterdam study. Circulation 96:1432–1437
O’Leary DH, Polak JF, Kronmal RA, Manolio TA, Burke GL, Wolfson SK Jr (1999) Carotid-artery intima and media thickness as a risk factor for myocardial infarction and stroke in older adults. Cardiovascular Health Study Collaborative Research Group. N Engl J Med 340:14–22
Hollander M, Hak AE, Koudstaal PJ, Bots ML, Grobbee DE, Hofman A, Witteman JC, Breteler MM (2003) Comparison between measures of atherosclerosis and risk of stroke: the Rotterdam study. Stroke 34:2367–2372
Chambless LE, Folsom AR, Clegg LX, Sharrett AR, Shahar E, Nieto FJ, Rosamond WD, Evans G (2000) Carotid wall thickness is predictive of incident clinical stroke: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study. Am J Epidemiol 151:478–487
Kitamura A, Iso H, Imano H, Ohira T, Okada T, Sato S, Kiyama M, Tanigawa T, Yamagishi K, Shimamoto T (2004) Carotid intima-media thickness and plaque characteristics as a risk factor for stroke in Japanese elderly men. Stroke 35:2788–2794
Zhang S, Cai J, Luo Y, Han C, Polissar NL, Hatsukami TS, Yuan C (2003) Measurement of carotid wall volume and maximum area with contrast-enhanced 3D MR imaging: initial observations. Radiology 228:200–205
Underhill HR, Kerwin WS, Hatsukami TS, Yuan C (2006) Automated measurement of mean wall thickness in the common carotid artery by MRI: a comparison to intima-media thickness by B-mode ultrasound. J Mafn Reson Imaging 24:379–387
Boussel L, Serusclat A, Skilton MR, Vincent F, Bernard S, Moulin P, Saloner D, Douek PC (2007) The reliability of high resolution MRI in the measurement of early stage carotid wall thickening. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 9:771–776
Rosvall M, Janzon L, Berglund G, Engstrom G, Hedblad B (2005) Incidence of stroke is related to carotid IMT even in the absence of plaque. Atherosclerosis 179:325–331
Dijk JM, van der Graaf Y, Bots ML, Grobbee DE, Algral A, on behalf of the SMART study group (2006) Carotid intima–media thickness and the risk of new vascular events in patients with manifest atherosclerotic disease: the SMART study. Eur Heart J 27:1971–1978
Manolio T, Kronmal R, Burke G et al (1994) Magnetic resonance abnormalities and cardiovascular disease in older adults. The Cardiovascular Health Study. Stroke 25:318–327
Veller MG, Fisher CM, Nicolaides AN (1993) Measurement of the ultrasonic intima-media complex thickness in normal subjects. J Vasc Surg 17:719–725
Howard G, Sharrett AR, Heiss G, Evans GW, Chambless LE, Riley WA, Burke GL, for the ARIC Investigators (1993) Carotid artery intimal-medial thickness distribution in general populations as evaluated by B-mode ultrasound. Stroke 24:1297–1304
Lemne C, Jogestrand T, de Faire U (1995) Carotid intima-media thickness and plaque in borderline hypertension. Stroke 26:34–39
Jensen-Urstad K, Rosfors S (1997) A methodological study of arterial wall function using ultrasound technique. Clin Physiol 17:557–567
Jensen-Urstad KJ, Reichard PG, Rosfors JS, Lindblad LEL, Jensen-Urstad MT (1996) Early atherosclerosis is retarded by improved long-term blood glucose control in patients with IDDM. Diabetes 45:1253–1258
Adams MR, Nakagomi A, Keech A, Robinson J, McCredie R, Bailey BP, Freedman SB, Celermayer DS (1995) Carotid intima-media thickness is only weakly correlated with the extent and severity of coronary artery disease. Circulation 92:2127–2134
Allan PL, Mowbray PI, Lee AJ, Fowkes GR (1997) Relationship between carotid intima-media thickness and symptomatic and asymptomatic peripheral arterial disease: the Edinburgh Artery Study. Stroke 28:348–353
Bonithon-Kopp C, Touboul PJ, Berr C, Magne C, Ducimetiere P (1996) Factors of carotid arterial enlargement in a population aged 59 to 71 years: the EVA study. Stroke 27:654–660
Rosfors S, Hallerstam S, Jensen-Urstad K, Zetterling M, Carlström C (1998) Relationship between intima-media thickness in the common carotid artery and atherosclerosis in the carotid bifurcation. Stroke 29:1378–1382
Mackinnon AD, Jerrard-Dunne P, Sitzer M, Buehler A, von Kegler S, Markus HS (2004) Intima-media thickness: the carotid atherosclerosis progression study rates and determinants of site-specific progression of carotid artery. Stroke 35:2150–2154
Veller MG, Fisher CM, Nicolaides AN (1993) Measurement of the ultrasonic intima-media complex thickness in normal subjects. J Vasc Surg 17:719–725
Bots ML (1993) Wall thickness of the carotid artery as an indicator of generalized atherosclerosis. PhD Thesis, Erasmus University, Rotterdam, Netherlands
Salonen JT, Salonen R (1993) Ultrasound B-mode imaging in observational studies of atherosclerotic progression. Circulation 87 (suppl II):II-56–II-65
Claves JL, Wise SW, Hopper KD et al (1997) Evaluation of contrast densities in the diagnosis of carotid stenosis by CT angiography. AJR Am J Roentgenol 169:569–573
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Saba, L., Sanfilippo, R., Pascalis, L. et al. Carotid artery wall thickness and ischemic symptoms: evaluation using multi-detector-row CT angiography. Eur Radiol 18, 1962–1971 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-008-0962-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-008-0962-5