Abstract
Purpose
Intraoperative ultrasound (IOUS) has become a useful tool employed daily in neurosurgical procedures. In pediatric patients, IOUS offers a radiation-free and safe imaging method. This study aimed to evaluate the use of a new real-time 3-D IOUS technique (RT-3-D IOUS) in our pediatric patient cohort.
Material and methods
Over 24 months, RT-3-D IOUS was performed in 22 pediatric patients (8 girls and 14 boys) with various brain tumors. These lesions were localized by a standard navigation system followed by analyses before, intermittently during, and after neurosurgical resection using the iU22 ultrasound system (Philips, Bothell, USA) connected to the RT-3-D probe (X7-2).
Results
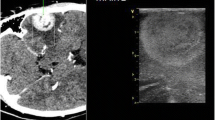
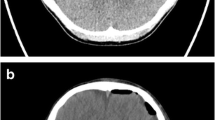
In all 22 patients, real-time 3-D ultrasound images of the lesions could be obtained during neurosurgical resection. Based on this imaging method, rapid orientation in the surgical field and the approach for the resection could be planned for all patients. In 18 patients (82%), RT-3-D IOUS revealed a gross total resection with a favorable neurological outcome.
Conclusion
RT-3-D IOUS provides the surgeon with advanced orientation at the tumor site via immediate live two-plane imaging. However, navigation systems have yet to be combined with RT-3-D IOUS. This combination would further improve intraoperative localization.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albright AL, Wisoff JH, Zeltzer PM, Boyett JM, Rorke LB, Stanley P (1996) Effects of medulloblastoma resections on outcome in children: a report from the Children's Cancer Group. Neurosurgery 38:265–271
Balmer B, Bernays RL, Kollias SS, Yonekawa Y (2002) Interventional MR-guided neuroendoscopy: a new therapeutic option for children. J Pediatr Surg 37:668–672
Berger MS, Deliganis AV, Dobbins J, Keles GE (1994) The effect of extent of resection on recurrence in patients with low grade cerebral hemisphere gliomas. Cancer 74:1784–1791
Berger MS (1996) The impact of technical adjuncts in the surgical management of cerebral hemispheric low-grade gliomas of childhood. J Neurooncol 28:129–155
Bernays RL, Kollias SS, Khan N, Brandner S, Meier S, Yonekawa Y (2002) Histological yield, complications, and technological considerations in 114 consecutive frameless stereotactic biopsy procedures aided by open intraoperative magnetic resonance imaging. J Neurosurg 97:354–362
Black PM (2000) The present and future of cerebral tumor surgery in children. Childs Nerv Syst 16:821–828
Bozinov O, Burkhardt JK, Fischer CM, Kockro RA, Bernays RL, Bertalanffy H (2011) Advantages and limitations of intraoperative 3D ultrasound in neurosurgery. Technical note. Acta Neurochir Suppl 109:191–196
Broggi G, Ferroli P, Franzini A, Dones L, Marras C, Marchetti M, Maccagnano E (2003) CT-guided neurosurgery: preliminary experience. Acta Neurochir Suppl 85:101–104
Cohen KJ, Broniscer A, Glod J (2001) Pediatric glial tumors. Curr Treat Options Oncol 2:529–536
El Beltagy MA, Aggag M, Kamal M (2010) Role of intraoperative ultrasound in resection of pediatric brain tumors. Childs Nerv Syst 26:1189–1193
Enchev Y, Bozinov O, Miller D, Tirakotai W, Heinze S, Benes L, Bertalanffy H, Sure U (2006) Image-guided ultrasonography for recurrent cystic gliomas. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 148:1053–1063, discussion 1063
Gronningsaeter A, Kleven A, Ommedal S, Aarseth TE, Lie T, Lindseth F, Lango T, Unsgard G (2000) SonoWand, an ultrasound-based neuronavigation system. Neurosurgery 47:1373–1379, discussion 1379–1380
He W, Jiang XQ, Wang S, Zhang MZ, Zhao JZ, Liu HZ, Ma J, Xiang DY, Wang LS (2008) Intraoperative contrast-enhanced ultrasound for brain tumors. Clin Imaging 32:419–424
Jolesz FA (2003) Future perspectives in intraoperative imaging. Acta Neurochir Suppl 85:7–13
Kremer P, Tronnier V, Steiner HH, Metzner R, Ebinger F, Rating D, Hartmann M, Seitz A, Unterberg A, Wirtz CR (2006) Intraoperative MRI for interventional neurosurgical procedures and tumor resection control in children. Childs Nerv Syst 22:674–678
Letteboer MM, Willems PW, Viergever MA, Niessen WJ (2005) Brain shift estimation in image-guided neurosurgery using 3-D ultrasound. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 52:268–276
Lindner D, Trantakis C, Renner C, Arnold S, Schmitgen A, Schneider J, Meixensberger J (2006) Application of intraoperative 3D ultrasound during navigated tumor resection. Minim Invasive Neurosurg 49:197–202
Nimsky C, Ganslandt O, Hastreiter P, Fahlbusch R (2001) Intraoperative compensation for brain shift. Surg Neurol 56:357–364, discussion 364–355
Roth J, Beni-Adani L, Biyani N, Constantini S (2006) Classical and real-time neuronavigation in pediatric neurosurgery. Childs Nerv Syst 22:1065–1071
Rubin JM, Mirfakhraee M, Duda EE, Dohrmann GJ, Brown F (1980) Intraoperative ultrasound examination of the brain. Radiology 137:831–832
Rubin JM, Quint DJ (2000) Intraoperative US versus intraoperative MR imaging for guidance during intracranial neurosurgery. Radiology 215:917–918
Samdani AF, Schulder M, Catrambone JE, Carmel PW (2005) Use of a compact intraoperative low-field magnetic imager in pediatric neurosurgery. Childs Nerv Syst 21:108–113, discussion 114
Sanai N, Polley MY, McDermott MW, Parsa AT, Berger MS (2011) An extent of resection threshold for newly diagnosed glioblastomas. J Neurosurg 115:3–8
Tronnier VM, Bonsanto MM, Staubert A, Knauth M, Kunze S, Wirtz CR (2001) Comparison of intraoperative MR imaging and 3D-navigated ultrasonography in the detection and resection control of lesions. Neurosurg Focus 10:E3
Unsgaard G, Gronningsaeter A, Ommedal S, Nagelhus Hernes TA (2002) Brain operations guided by real-time two-dimensional ultrasound: new possibilities as a result of improved image quality. Neurosurgery 51:402–411, discussion 411–402
Unsgaard G, Ommedal S, Muller T, Gronningsaeter A, Nagelhus Hernes TA (2002) Neuronavigation by intraoperative three-dimensional ultrasound: initial experience during brain tumor resection. Neurosurgery 50:804–812, discussion 812
Unsgaard G, Selbekk T, Brostrup Muller T, Ommedal S, Torp SH, Myhr G, Bang J, Nagelhus Hernes TA (2005) Ability of navigated 3D ultrasound to delineate gliomas and metastases—comparison of image interpretations with histopathology. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 147:1259–1269, discussion 1269
Unsgaard G, Rygh OM, Selbekk T, Muller TB, Kolstad F, Lindseth F, Hernes TA (2006) Intra-operative 3D ultrasound in neurosurgery. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 148:235–253, discussion 253
Disclosure
The real-time 3-D US transducer has been provided by the company Philips for research purposes. This is not the case for the US system IU22, which was bought by the department. No further financial collaborations, consulting contracts, or conflicts of interest exist.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ulrich, N.H., Burkhardt, JK., Serra, C. et al. Resection of pediatric intracerebral tumors with the aid of intraoperative real-time 3-D ultrasound. Childs Nerv Syst 28, 101–109 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-011-1571-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-011-1571-1