Abstract
Background
Idiopathic inflammatory demyelinating lesions (IIDL) of the brain usually present with a morphologic pattern characteristic of multiple sclerosis (MS). Atypical appearances of IIDLs also exist, however, and can pose significant diagnostic problems and uncertainty regarding prognosis and adequate therapy. We attempted to improve upon this situation by reviewing the literature.
Methods
We performed a PubMed search from January 1984 through December 2004 for articles in English reporting on IIDLs which had been considered as morphologically atypical (66 articles; 270 cases reported). From these publications 69 individual patient reports allowed the extraction of adequate information on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and associated disease characteristics.
Results
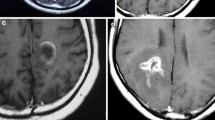
Reported atypical IIDLs most frequently manifested as large ring-like lesions (n = 27) which are now considered quite suggestive of an antibodymediated form of MS. Truly atypical IIDLs were less common and exhibited appearances which we termed megacystic (n = 8), Balolike (n = 11) and diffusely infiltrating (n = 11). Despite limitations imposed by the absence of original data the inter-rater agreement in defining these subtypes of atypical IIDLs was moderate to substantial (kappa 0.48–0.68) and we noted trends for their association with certain demographic, clinical and paraclinical variables.
Interpretation
We suggest that IIDLs reported as atypical in the literature can be segregated into several distinct subtypes based on their MRI appearance. The recognition of these patterns may be useful for the differential diagnosis and for a future classification. Because of the limitations inherent in our review this will have to be confirmed by a prospective registry.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weinshenker B, Miller D (1999) Multiple sclerosis: one disease or many? Martin Dunitz, London
Poser C, Brinar V (2004) The nature of multiple sclerosis. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 106:159–171
Fazekas F, Barkhof F, Filippi M, Grossman R, Li D, McDonald W, McFarland H, Paty DS, Simon JH, Wolinsky J, Miller D (1999) The contribution of magnetic resonance imaging to the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis. Neurology 53:448–456
Filippi M, Rocca M, Arnold D, Bakshi R, Barkhof F, De Stefano N, Fazekas F, Frohman E, Wolinsky J (2006) EFNS guidelines on the use of neuroimaging in the management of multiple sclerosis. Eur J Neurol 13:313–325
Tenembaum S, Chamoles N, Fejerman N (2002) Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis. A long-term follow-up study of 84 pediatric patients. Neurology 59:1224–1231
Wingerchuk D, Hogancamp W, O'Brien P, Weinshenker B (1999) The clinical course of neuromyelitis optica (Devic's syndrome). Neurology 53:1107–1114
Balo J (1928) Encephalitis periaxialis concentrica. Arch Neurol 19:242–263
Kepes J (1993) Large focal tumor-like demyelinating lesions of the brain: intermediate entity between multiple sclerosis and acute disseminated encephalomyelitis? A study of 31 patients. Ann Neurol 33:18–27
Gütling E, Landis T (1989) CT ring sign imitating tumour, disclosed as multiple sclerosis by MRI: a case report. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 52:903–906
Paley R, Persing J, Doctor A, Westwater J, Roberson J, Edlich R (1989) Multiple sclerosis and brain tumor: a diagnostic challenge. J Emerg Med 7:241–244
Johnson M, Lavin P, Whetsell W (1990) Fulminant monophasic multiple sclerosis, Marburg's type. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 53:918–921
Nesbit G, Forbes G, Scheithauer B, Okazaki H, Rodriguez M (1991) Multiple sclerosis: histopathologic and MR and/or CT correlation in 37 cases at biopsy and three cases at autopsy. Radiology 180:467–474
Giang D, Poduri K, Eskin T, Ketonen L, Friedman P, Wang D, Herndon R (1992) Multiple sclerosis masquerading as a mass lesion. Neuroradiology 34:150–154
Niebler G, Harris T, Davis T, Roos K (1992) Fulminant multiple sclerosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 13:1547–1551
Poser S, Luer W, Bruhn H, Frahm J, Bruck Y, Felgenhauer K (1992) Acute demyelinating disease. Classification and non-invasive diagnosis. Acta Neurol Scand 86:579–585
Von Einig M, Higer H, Mauz M, Ernst J (1992) Intrakranielle tumorähnliche Läsionen bei Kindern und jungen Erwachsenen mit multipler Sklerose. Fortschr Röntgenstr 157:384–389
Revel M, Valiente E, Gray F, Beges C, Degos J, Brugières P, Gaston A (1993) Aspects concentriques IRM des lésions de sclérose en plaque: A propos de 2 observations. Concentric MR patterns in multiple sclerosis: Report of two cases. J Neuroradiol (Paris) 20:252–257
Guadagnino M, Palma V, Tessitore A (1994) Correlation between neuroradiological and electrophysiological investigations in multiple sclerosis with features of a cerebral tumour. Acta Neurol (Napoli) 16:19–28
Korte J, Bom E, Vos L, Breuer T, Wondergem J (1994) Balo concentric sclerosis: MR diagnosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 15:1284–1285
Morioka C, Komatsu Y, Tsujio TA, Araki Y, Kondo H (1994) The evolution of the concentric lesions of atypical multiple sclerosis on MRI. Radiat Med 12:129–133
Maranhao-Filho P, Moraes Filho LC, Camara LS, Salema C (1995) Fulminant form of multiple sclerosis simulating brain tumor: a case with parkinsonian features and pathologic study. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 53:503–508
Bolay H, Karabudak R, Tacal T, Önol B, Selekler K, Saribas O (1996) Balo's concentric sclerosis: Report of two patients with magnetic resonance imaging follow-up. J Neuroimag 6:98–103
Chen C, Ro L, Wang L, Wong Y (1996) Balo's concentric sclerosis: MRI. Neuroradiology 38:322–324
Dagher A, Smirniotopoulos J (1996) Tumefactive demyelinating lesions. Neuroradiology 38:560–565
Morioka C, Nameta K, Komatsu Y, Tsujio T, Kondo H (1996) Higher cerebral dysfunction in a case with atypical multiple sclerosis with concentric lesions. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 50:41–44
Wood D, Bilbao J, O'Connors P, Moscarello M (1996) Acute multiple sclerosis (Marburg type) is associated with developmentally immature myelin basic protein. Ann Neurol 40:18–24
Kim M, Lee S, Choi C, Huh J, Lee MC (1997) Balo's concentric sclerosis: a clinical case study of brain MRI, biopsy, and proton magnetic resonance spectroscopic findings. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 62:655–658
Sekijima Y, Tokuda T, Hashimoto T, Koh C, Shoji S, Yanagisawa N (1997) Serial magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) study of a patient with Balo's concentric sclerosis treated with immunoadsorption plasmapheresis. Mult Scler 2:291–294
Ernst T, Chang L, Walot I, Huff K (1998) Physiologic MRI of a tumefactive multiple sclerosis lesion. Neurology 51:1486–1488
Bitsch A, Wegener C, da Costa C, Bunkowski S, Reimers C, Prange H, Brück W (1999) Lesion development in Marburg's type of acute multiple sclerosis: from inflammation to demyelination. Mult Scler 5:138–146
Ng S, Ko S, Cheung Y, Wong H, Wan Y (1999) MRI features of Balo's concentric sclerosis. Br J Radiol 72:400–403
Singh S, Kuruvilla A, Alexander M, Korah I (1999) Balo's concentric sclerosis: value of magnetic resonance imaging in diagnosis. Australas Radiol 43:400–404
Al-Bunyan M (2000) Tumor-like presentation of multiple sclerosis. Saudi Med J 21:393–395
Annesley-Williams D, Farrell M, Staunton H, Brett F (2000) Acute demyelination, neuropathological diagnosis, and clinical evolution. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 59:477–489
Friedman D (2000) Multiple sclerosis simulating a mass lesion. J Neuro- Ophthalmol 20:147–153
Iñiguez C, Pascual L, Ramón y Cajal S, Fayed N, Morales-Asín F (2000) Transitional multiple sclerosis (Schilder's disease): a case report. J Neurol 247:974–976
Capello E, Roccatagliata L, Pagano F, Mancardi G (2001) Tumor-like multiple sclerosis (MS) lesions: neuropathological clues. J Neurosci 22:S113–S116
Caracciolo J, Murtagh R, Rojiani A, Murtagh F (2001) Pathognomonic MR imaging findings in Balo concentric sclerosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:292–293
Censori B, Agostinis C, Partziguian T, Gazzaniga G, Biroli F, Mamoli A (2001) Large demyelinating brain lesion mimicking a herniating tumor. J Neurosci 22:325–329
Erdem H, Stalberg E, Caglar I (2001) Aphasia in multiple sclerosis. Upsala J Med Sci 106:205–210
Karaarslan E, Altintas A, Senol U, Yeni N, Dincer A, Bayindir C, Karaagac N, Siva A (2001) Balo's concentric sclerosis: clinical and radiologic features of five cases. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1362–1367
Moore G, Berry K, Oger J, Prout A, Graeb D, Nugent R (2001) Balo's concentric sclerosis: surviving normal myelin in a patient with a relapsingremitting clinical course. Mult Scler 7:375–382
Sugita Y, Terasaki M, Shigemori M, Sakata K, Morimatsu M (2001) Acute focal demyelinating disease simulating brain tumors: histopathologic guidelines for an accurate diagnosis. Neuropathology 21:25–31
Kastrup O, Stude P, Limmroth V (2002) Balo's concentric sclerosis: Evolution of active demyelination demonstrated by serial contrast-enhanced MRI. J Neurol 249:811–814
Khoshyomn S, Braff S, Penar P (2002) Tumefactive multiple sclerosis plaque. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 73:85
Kotil K, Kalayci M, Koseoglu T, Tugrul A (2002) Myelinoclastic diffuse sclerosis (Schilder's disease): report of a case and review of the literature. Br J Neurosurg 16:516–519
Di Patre P, Castillo V, Delavelle J, Vuillemoz S, Picard F, Landis T (2003) “Tumor-mimicking”multiple sclerosis. Clin Neuropathol 22:235–239
Dousset V (2003) Case no 2. Balo concentric sclerosis. J Radiol 84:80–81
Hayashi T, Kumabe T, Jokura H, Fujihara K, Shiga Y, Watanabe M, Higano S, Shirane R (2003) Inflammatory demyelinating disease mimicking malignant glioma. J Nucl Med 44:565–569
Iwamoto K, Oka H, Utsuki S, Ozawa T, Fujii K (2004) Late-onset multiple sclerosis mimicking brain tumor: a case report. Brain Tumor Pathol 21:83–86
Wurm G, Parsaei B, Silye R, Fellner F (2004) Distinct supratentorial lesions mimicking cerebral gliomas. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 146:19–26
Nagi S, Megdiche H, Mrabet H, Sebai R, Chaabane S, Belghith L, Touibi S (2005) Sclérose concentrique de Balò chez un patient nord-africaine. Balo's concentric sclerosis in a North-African patient. Rev Neurol (Paris) 161:78–80
Enzinger C, Strasser-Fuchs S, Ropele S, Kapeller P, Kleinert R, Fazekas F (2005) Tumefactive demyelinating lesions: conventional and advanced magnetic resonance imaging. Mult Scler 11:135–139
Fleiss J (2003) Statistical Method for Rates and Proportions. John Wiley and Sons, New York
Charil A, Yousry T, Rovaris M, Barkhof F, de Stefano N, Fazekas F, Miller D, Montalban X, Simon J, Polman C, Filippi M (2006) MRI and the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis: expanding the concept of “no better explanation”. Lancet Neurol 5:841–852
He J, Grossman R, Ge Y, Manon L (2001) Enhancing patterns in multiple sclerosis: evolution and persistence. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:64–669
Lucchinetti C, Brück W, Parisi J, Scheithauer B, Rodriguez M, Lassmann H (2000) Heterogeneity of Multiple Sclerosis Lesions: Implications for the Pathogenesis of Demyelination. Ann Neurol 47:707–717
Bruck W, Neubert K, Berger T, Weber JR (2001) Clinical, radiological, immunological and pathological findings in inflammatory CNS demyelination – possible markers for an antibodymediated process. Mult Scler 7:173–177
Masdeu J, Quinto C, Olivera C, Tenner M, Leslie D, Visintainer P (2000) Openring imaging sign: highly specific for atypical brain demyelination. Neurology 54:1427–1433
Omuro A, Leite C, Mokhtari K, Delattre J (2006) Pitfalls in the diagnosis of brain tumours. Lancet Neurol 5:937–948
Guzman RB, A, Lovblad K, El-Koussy M, Weis J, Schroth G, Seiler R (2002) Use of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in differentiating purulent brain processes from cystic brain tumors. J Neurosurg 97:1101–1107
Schwartz K, Erickson B, Lucchinetti C (2006) Pattern of T2 hypointensity associated with ring-enhancing brain lesions can help to differentiate pathology. Neuroradiology 48:143–149
Stadelmann C, Ludwin S, Tabira T, Guseo A, Lucchinetti C, Leel-Össy L, Ordinario A, Brück W, Lassmann H (2005) Tissue preconditioning may explain concentric lesions in Balo's type of multiple sclerosis. Brain 128:979–987
Yousry T, Major E, Ryschkewitsch C, Fahle G, Fischer S, Hou J, Curfman B, Miszkiel K, Mueller-Lenke N, Sanchez E, Barkhof F, Radue E, Jager H, Clifford D (2006) Evaluation of patients treated with natalizumab for progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. N Engl J Med 354:924–933
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Consortia
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seewann, A., Enzinger, C., Filippi, M. et al. MRI characteristics of atypical idiopathic inflammatory demyelinating lesions of the brain. J Neurol 255, 1–10 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-007-0754-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-007-0754-x