Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of the study was to compare the performance of second-generation embolic devices with that of platinum coils in experimental aneurysms.
Methods
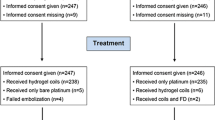
Microsurgically constructed bifurcation aneurysms in rabbits were embolized with platinum coils (n = 7), HydroCoils 10 (n = 10), HydroSoft (n = 14) or Cerecyte (n = 6) devices. After 1 month, angiographic occlusion was scored and the aneurysms were histologically evaluated by light microscopy. Continuous and ordinal results were compared using ANOVA/Tukey–Kramer HSD and χ2 tests respectively.
Results
Angiographic occlusion at follow-up was increased in the HydroCoil and HydroSoft groups and decreased in the platinum coil and Cerecyte groups. Fibrovascular tissue was observed in the sac of the Cerecyte group, while mixtures of fibrovascular tissue and fibrinous thrombus were observed in the other three groups. The inflammatory response and endothelialization of the neck were similar in all groups.
Conclusions
Expansile hydrogel devices have led to increased progressive occlusion, while degradable polymer devices led to an increased rate of thrombus organization compared with platinum coils.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bavinzski G, Richling B, Binder BR, Gruber A, Talazoglu V, Dietrich W, Schwendtenwein I, Plenk H Jr (1999) Histopathological findings in experimental aneurysms embolized with conventional and thrombogenic/antithrombolytic Guglielmi coils. Minim Invasive Neurosurg 42:167–174 doi:10.1055/s-2008–1053392
Bavinzski G, Talazoglu V, Killer M, Richling B, Gruber A, Gross CE, Plenk H Jr (1999) Gross and microscopic histopathological findings in aneurysms of the human brain treated with Guglielmi detachable coils. J Neurosurg 91:284–293
Bendszus M, Bartsch AJ, Solymosi L (2007) Endovascular occlusion of aneurysms using a new bioactive coil: a matched pair analysis with bare platinum coils. Stroke 38:2855–2857 doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.107.489088
Dai D, Ding YH, Lewis DA, Kallmes DF (2006) A proposed ordinal scale for grading histology in elastase-induced, saccular aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:132–138
Deshaies EM, Adamo MA, Boulos AS (2007) A prospective single-center analysis of the safety and efficacy of the hydrocoil embolization system for the treatment of intracranial aneurysms. J Neurosurg 106:226–233 doi:10.3171/jns.2007.106.2.226
Ding YH, Dai D, Kadirvel R, Lewis DA, Cloft HJ, Kallmes DF (2008) Relationship between aneurysm volume and histologic healing after coil embolization in elastase-induced aneurysms: a retrospective study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29:98–101 doi:10.3174/ajnr.A0752
Ding YH, Dai D, Lewis DA, Cloft HJ, Kallmes DF (2005) Angiographic and histologic analysis of experimental aneurysms embolized with platinum coils, Matrix, and HydroCoil. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 26:1757–1763
Forrest MD, O’Reilly GV (1989) Production of experimental aneurysms at a surgically created arterial bifurcation. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 10:400–402
Fujiwara NH, Kallmes DF (2002) Healing response in elastase-induced rabbit aneurysms after embolization with a new platinum coil system. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 23:1137–1144
Gaba RC, Ansari SA, Roy SS, Marden FA, Viana MAG, Malisch TW (2006) Embolization of intracranial aneurysms with hydrogel-coated coils versus inert platinum coils: effects on packing density, coil length and quantity, procedure performance, cost, length of hospital stay, and durability of therapy. Stroke 37:1443–1450 doi:10.1161/01.STR.0000221314.55144.0b
Linfante I, Akkawi NM, Perlow A, Andreone V, Wakhloo AK (2005) Polyglycolide/polylactide-coated platinum coils for patients with ruptured and unruptured cerebral aneurysms: a single-center experience. Stroke 36:1948–1953 doi:10.1161/01.STR.0000177532.94736.85
Molyneux AJ, Kerr RS, Yu LM, Clarke M, Sneade M, Yarnold JA, Sandercock P (2005) International subarachnoid aneurysm trial (ISAT) of neurosurgical clipping versus endovascular coiling in 2143 patients with ruptured intracranial aneurysms: a randomised comparison of effects on survival, dependency, seizures, rebleeding, subgroups, and aneurysm occlusion. Lancet 366:809–817 doi:10.1016/S0140–6736(05)67214–5
Murayama Y, Tateshima S, Gonzalez NR, Vinuela F (2003) Matrix and bioabsorbable polymeric coils accelerate healing of intracranial aneurysms: long-term experimental study. Stroke 34:2031–2037 doi:10.1161/01.STR.0000083394.33633.C2
Pierot L, Leclerc X, Bonafe A, Bracard S (2008) Endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms with matrix detachable coils: midterm anatomic follow-up from a prospective multicenter registry. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29:57–61 doi:10.3174/ajnr.A0738
Raymond J, Guilbert F, Weill A, Georganos SA, Juravsky L, Lambert A, Lamoureux J, Chagnon M, Roy D (2003) Long-term angiographic recurrences after selective endovascular treatment of aneurysms with detachable coils. Stroke 34:1398–1403 doi:10.1161/01.STR.0000073841.88563.E9
Reul J, Weis J, Spetzger U, Konert T, Fricke C, Thron A (1997) Long-term angiographic and histopathologic findings in experimental aneurysms of the carotid bifurcation embolized with platinum and tungsten coils. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 18:35–42
Richling B, Gruber A, Bavinzski G, Killer M (1995) GDC-system embolization for brain aneurysms—location and follow-up. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 134:177–183 doi:10.1007/BF01417686
Roy D, Milot G, Raymond J (2001) Endovascular treatment of unruptured aneurysms. Stroke 32:1998–2004 doi:10.1161/hs0901.095600
Sherif C, Plenk H Jr, Grossschmidt K, Kanz F, Bavinzski G (2006) Computer-assisted quantification of occlusion and coil densities on angiographic and histological images of experimental aneurysms. Neurosurgery 58:559–566; discussion 559–566
Szikora I, Seifert P, Hanzely Z, Kulcsar Z, Berentei Z, Marosfoi M, Czirjak S, Vajda J, Nyary I (2006) Histopathologic evaluation of aneurysms treated with Guglielmi detachable coils or matrix detachable microcoils. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:283–288
Turk A, Luty C, Carr-Brendel V, Polyakov I, Consigny D, Grinde J, Mukherjee R, Strother C (2008) Angiographic and histological comparison of canine bifurcation aneurysms treated with first generation matrix and standard GDC coils. Neuroradiology 50:57–65 doi:10.1007/s00234–007–0302–5
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by MicroVention Terumo, Aliso Viejo, CA, USA. We gratefully acknowledge the surgical assistance of Drs. R. Agic, M. Kral, and L. Ritter.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Comment
The authors compare different embolic devices to fill up brain aneurysms In an experimental rat model. They demonstrated minor differences between the various devices tested, but the standard platinum coils compared with expansile hydrogels and degradable polymers surrounding platinum coils are less efficient. Thus, for neurosurgeons the hydrogel and degradable devices might become the devices of the future.
The weak point in the paper seems to be the histological analysis of the data. The authors stain two-dimensional sections only at the surface and try to deduce the histological composition of the whole tridimensional aneurysm. This is only valuable if the content in the filled aneurysm is homogeneous, which is rather doubtful.
Leo De Ridder
Ghent University, Belgium
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Killer, M., Hauser, T., Wenger, A. et al. Comparison of experimental aneurysms embolized with second-generation embolic devices and platinum coils. Acta Neurochir 151, 497–505 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-009-0237-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-009-0237-1