Abstract
Purpose
Spontaneous vertebrobasilar dissecting aneurysm (VBD) is a very challenging disease with an unpredictable clinical course and controversies on treatment strategy. The present study reports radiological and clinical outcomes of stent-alone treatment (SAT) for VBD.
Methods
Twenty-four VBDs treated with SAT are included in the present study. Clinical and angiographic data were reviewed retrospectively.
Results
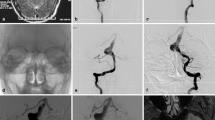
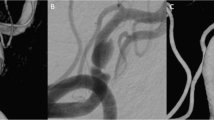
A total of 24 lesions in 22 patients with a mean follow-up period of 16.21 months were included. Of the 24 individual lesions, 23 were intracranial vertebral artery lesions and 1 lesion was located in the basilar artery. There were six cases of ruptured dissections with the other cases having various symptoms. The immediate post-SAT angiographic outcomes included 5 lesions with good remodeling over 90% recovery and 19 poorly remodeled lesions. The latest angiographic outcomes included 17 cases of good remodeling (remodeling rate over 90%), 6 cases of poor remodeling (remodeling rate below 70%), and 1 case with morphological aggravation. The overlapping stent technique was used in seven cases and it was significantly associated with good angiographic results. None of the rupture cases underwent re-rupture post SAT. There was one case of a symptomatic complication of a femoral arteriovenous fistula.
Conclusions
The SAT could be a feasible alternative for the treatment of VBD. The overlapping technique was significantly associated with good angiographic outcome. We expect that technological development of the intracranial stent will allow better procedural outcomes of SAT.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn JY, Chung SS, Lee BH, Kim SH, Yoon PH, Joo JY, Kim JK (2005) Treatment of spontaneous arterial dissections with stent placement for preservation of the parent artery. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 147:265–273, discussion 273
Ahn JY, Han IB, Kim TG, Yoon PH, Lee YJ, Lee BH, Seo SH, Kim DI, Hong CK, Joo JY (2006) Endovascular treatment of intracranial vertebral artery dissections with stent placement or stent-assisted coiling. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:1514–1520
Ansari SA, Lassig JP, Nicol E, Thompson BG, Gemmete JJ, Gandhi D (2007) Thrombosis of a fusiform intracranial aneurysm induced by overlapping neuroform stents: case report. Neurosurgery 60:E950–E951, discussion E950–951
Ansari SA, Thompson BG, Gemmete JJ, Gandhi D (2008) Endovascular treatment of distal cervical and intracranial dissections with the neuroform stent. Neurosurgery 62:636–646, discussion 636–646
Anxionnat R, de Melo Neto JF, Bracard S, Lacour JC, Pinelli C, Civit T, Picard L (2003) Treatment of hemorrhagic intracranial dissections. Neurosurgery 53:289–300, discussion 300–281
Aziz-Sultan A, Heros RC (2008) Sole stenting. J Neurosurg 108:1101–1102
Benndorf G, Claus B, Strother CM, Chang L, Klucznik RP (2006) Increased cell opening and prolapse of struts of a neuroform stent in curved vasculature: value of angiographic computed tomography: technical case report. Neurosurgery 58:ONS–E380, discussion ONS-E380
Benndorf G, Herbon U, Sollmann WP, Campi A (2001) Treatment of a ruptured dissecting vertebral artery aneurysm with double stent placement: case report. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:1844–1848
Biondi A, Janardhan V, Katz JM, Salvaggio K, Riina HA, Gobin YP (2007) Neuroform stent-assisted coil embolization of wide-neck intracranial aneurysms: strategies in stent deployment and midterm follow-up. Neurosurgery 61:460–468, discussion 468–469
Chandra A, Suliman A, Angle N (2007) Spontaneous dissection of the carotid and vertebral arteries: the 10-year UCSD experience. Ann Vasc Surg 21:178–185
Chen M, Caplan L (2005) Intracranial dissections. Front Neurol Neurosci 20:160–173
Cohen JE, Gomori JM, Umansky F (2003) Endovascular management of symptomatic vertebral artery dissection achieved using stent angioplasty and emboli protection device. Neurol Res 25:418–422
Doerfler A, Wanke I, Egelhof T, Stolke D, Forsting M (2004) Double-stent method: therapeutic alternative for small wide-necked aneurysms. Technical note. J Neurosurg 100:150–154
Fiorella D, Albuquerque FC, Deshmukh VR, Woo HH, Rasmussen PA, Masaryk TJ, McDougall CG (2006) Endovascular reconstruction with the Neuroform stent as monotherapy for the treatment of uncoilable intradural pseudoaneurysms. Neurosurgery 59:291–300, discussion 291–300
Fiorella D, Albuquerque FC, Masaryk TJ, Rasmussen PA, McDougall CG (2005) Balloon-in-stent technique for the constructive endovascular treatment of "ultra-wide necked" circumferential aneurysms. Neurosurgery 57:1218–1227, discussion 1218-1227
Fiorella D, Woo HH, Albuquerque FC, Nelson PK (2008) Definitive reconstruction of circumferential, fusiform intracranial aneurysms with the pipeline embolization device. Neurosurgery 62:1115–1120, discussion 1120–1111
Flemming KD, Wiebers DO, Brown RD Jr, Link MJ, Huston J 3rd, McClelland RL, Christianson TJ (2005) The natural history of radiographically defined vertebrobasilar nonsaccular intracranial aneurysms. Cerebrovasc Dis 20:270–279
Geremia G, Brack T, Brennecke L, Haklin M, Falter R (2000) Occlusion of experimentally created fusiform aneurysms with porous metallic stents. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:739–745
Hanel RA, Boulos AS, Sauvageau EG, Levy EI, Guterman LR, Hopkins LN (2005) Stent placement for the treatment of nonsaccular aneurysms of the vertebrobasilar system. Neurosurg Focus 18:1–9
Hashimoto M, Johkura K, Ichikawa T, Kojima A, Nishimura S, Shinonaga M (2008) Conservative treatment of ruptured vertebrobasilar dissecting aneurysm. Neurol Sci 29:241–244
Joo JY, Ahn JY, Chung YS, Han IB, Chung SS, Yoon PH, Kim SH, Choi EW (2005) Treatment of intra- and extracranial arterial dissections using stents and embolization. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol 28:595–602
Kaku Y, Yoshimura S, Yamakawa H, Sakai N (2003) Failure of stent-assisted endovascular treatment for ruptured dissecting aneurysms of the basilar artery. Neuroradiology 45:22–26
Kim M, Taulbee DB, Tremmel M, Meng H (2008) Comparison of two stents in modifying cerebral aneurysm hemodynamics. Ann Biomed Eng 36:726–741
Koebbe CJ, Veznedaroglu E, Jabbour P, Rosenwasser RH (2006) Endovascular management of intracranial aneurysms: current experience and future advances. Neurosurgery 59:S93–S102, discussion S103–113
Kurata A, Ohmomo T, Miyasaka Y, Fujii K, Kan S, Kitahara T (2001) Coil embolization for the treatment of ruptured dissecting vertebral aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:11–18
Lanzino G, Wakhloo AK, Fessler RD, Mericle RA, Guterman LR, Hopkins LN (1998) Intravascular stents for intracranial internal carotid and vertebral artery aneurysms: preliminary clinical experience. Neurosurg Focus 5:E5
Liou TM, Li YC (2008) Effects of stent porosity on hemodynamics in a sidewall aneurysm model. J Biomech 41:1174–1183
Lucas C, Moulin T, Deplanque D, Tatu L, Chavot D (1998) Stroke patterns of internal carotid artery dissection in 40 patients. Stroke 29:2646–2648
Lylyk P, Cohen JE, Ceratto R, Ferrario A, Miranda C (2001) Combined endovascular treatment of dissecting vertebral artery aneurysms by using stents and coils. J Neurosurg 94:427–432
Lylyk P, Miranda C, Ceratto R, Ferrario A, Scrivano E, Luna HR, Berez AL, Tran Q, Nelson PK, Fiorella D (2009) Curative endovascular reconstruction of cerebral aneurysms with the pipeline embolization device: the Buenos Aires experience. Neurosurgery 64:632–642, discussion 642–633; quiz N636
Matsumoto Y, Nagashima H, Toriyama T, Kobayashi S, Hongo K (2008) Uncommon course for a vertebral artery dissection: rupture, occlusion and recanalization. J Clin Neurosci 15:700–703
Mehta B, Burke T, Kole M, Bydon A, Seyfried D, Malik G (2003) Stent-within-a-stent technique for the treatment of dissecting vertebral artery aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:1814–1818
Mizutani T, Miki Y, Kojima H, Suzuki H (1999) Proposed classification of nonatherosclerotic cerebral fusiform and dissecting aneurysms. Neurosurgery 45:253–259, discussion 259–260
Park SI, Kim BM, Kim DI, Shin YS, Suh SH, Chung EC, Kim SY, Kim SH, Won YS (2009) Clinical and angiographic follow-up of stent-only therapy for acute intracranial vertebrobasilar dissecting aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30:1351–1356
Peluso JP, van Rooij WJ, Sluzewski M, Beute GN, Majoie CB (2008) Endovascular treatment of symptomatic intradural vertebral dissecting aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 29:102–106
Rhee K, Han MH, Cha SH (2002) Changes of flow characteristics by stenting in aneurysm models: influence of aneurysm geometry and stent porosity. Ann Biomed Eng 30:894–904
Santos-Franco JA, Zenteno M, Lee A (2008) Dissecting aneurysms of the vertebrobasilar system. A comprehensive review on natural history and treatment options. Neurosurg Rev 31:131–140, discussion 140
Schievink WI (2001) Spontaneous dissection of the carotid and vertebral arteries. N Engl J Med 344:898–906
Scott NA (2006) Restenosis following implantation of bare metal coronary stents: pathophysiology and pathways involved in the vascular response to injury. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 58:358–376
Shin YS, Kim HS, Kim SY (2007) Stenting for vertebrobasilar dissection: a possible treatment option for nonhemorrhagic vertebrobasilar dissection. Neuroradiology 49:149–156
Sugiu K, Tokunaga K, Watanabe K, Sasahara W, Ono S, Tamiya T, Date I (2005) Emergent endovascular treatment of ruptured vertebral artery dissecting aneurysms. Neuroradiology 47:158–164
Suzuki S, Kurata A, Iwamoto K, Sato K, Niki J, Miyazaki T, Yamada M, Oka H, Fujii K, Kan S (2008) Endovascular surgery using stents for vertebral artery dissecting aneurysms and a review of the literature. Minim Invasive Neurosurg 51:193–198
Takagi T, Takayasu M, Suzuki Y, Yoshida J (2007) Prediction of rebleeding from angiographic features in vertebral artery dissecting aneurysms. Neurosurg Rev 30:32–38, discussion 38–39
Wakhloo AK, Mandell J, Gounis MJ, Brooks C, Linfante I, Winer J, Weaver JP (2008) Stent-assisted reconstructive endovascular repair of cranial fusiform atherosclerotic and dissecting aneurysms: long-term clinical and angiographic follow-up. Stroke 39:3288–3296
Willing SJ, Skidmore F, Donaldson J, Nobo UL, Chernukha K (2003) Treatment of acute intracranial vertebrobasilar dissection with angioplasty and stent placement: report of two cases. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 24:985–989
Yoon WK, Kim YW, Kim SD, Park IS, Baik MW, Kim SR (2008) Intravascular ultrasonography-guided stent angioplasty of an extracranial vertebral artery dissection. J Neurosurg 109:1113–1118
Zenteno MA, Santos-Franco JA, Freitas-Modenesi JM, Gomez C, Murillo-Bonilla L, Aburto-Murrieta Y, Diaz-Romero R, Nathal E, Gomez-Llata S, Lee A (2008) Use of the sole stenting technique for the management of aneurysms in the posterior circulation in a prospective series of 20 patients. J Neurosurg 108:1104–1118
Acknowledgment
We express our special thanks to Dr. Im (Su-Bin Im M.D. Assistant professor, Department of Neurosurgery, Soonchunhyang University, Bucheon Hospital, Bucheon, South Korea) who made the conceptual schematic graphics of arterial dissection and hemodynamic change after stent placement.
Notification of conflicts of interest and financial disclosure
The authors report no conflict of interest, including specific financial interests and relationships and affiliations relevant to the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Comment
As the authors discuss in this article, the use of a balloon-mounted stent to treat vertebrobasilar dissections should be performed with great caution as balloon inflation can extend or rupture the dissected segment. In addition, the navigability of these stents may be a limiting factor if the circulation is too tortuous. The authors show good results with these stents, but self-expanding stents approved for use in the intracranial circulation are considered safer and are equally amenable to an overlapping technique to improve chances of parent vessel remodeling and aneurysm stasis. We recommend as a safety measure the use of a balloon guide so that flow arrest can be instituted prior to stent deployment with aspiration prior to reestablishing flow to remove any clots that might be liberated during stent expansion.
Mandy J. Binning, MD and L. Nelson Hopkins, MD
University at Buffalo, State University of New York
Buffalo, New York, USA
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoon, W.K., Kim, Y.W., Kim, SR. et al. Angiographic and clinical outcomes of stent-alone treatment for spontaneous vertebrobasilar dissecting aneurysm. Acta Neurochir 152, 1477–1486 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-010-0693-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-010-0693-7