Abstract
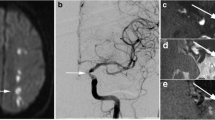
Intracranial atherosclerotic disease is increasingly recognized as a major stroke subtype worldwide. Current diagnostic evaluation of atherosclerotic disease of the middle cerebral artery (MCA) relies on detection of stenoses with luminographic imaging studies that do not directly visualize plaque unlike high-resolution MRI. This retrospective study seeks to evaluate the accuracy of high-resolution MRI vessel wall imaging, computed tomographic angiography (CTA) and digital subtraction angiography (DSA) in measuring the degree of stenosis within the MCA. 28 recently symptomatic patients with MCA territory symptoms underwent preliminary imaging with CTA followed by high-resolution MRI at 3-Tesla and definitive imaging with DSA for detection of M1 territory steno-occlusive lesions. Measurements of MCA segments on MRI and CTA were compared with reference to DSA values. Sensitivity and specificity of high-resolution MRI vessel wall imaging, CTA using maximum intensity projection (MIP) and CTA using volume rendering (VR) for the detection of stenosis > 50 % and occlusion were 80.0 and 53.6 %, 72.2 and 72.7 %, and 77.8 and 18.2 %, respectively. MRI-derived values correlated better with DSA (Spearman R = 0.68, p < 0.01) than CTA MIP and VR (Spearman R = 0.45, 0.22; p = 0.02, 0.24, respectively). High-resolution MRI of the MCA is capable of accurately measuring the degree of stenosis and is more sensitive than CTA in a sample of high-risk, symptomatic patients. This study, combined with previous reports, supports the potential of morphological MRI to measure intracranial atherosclerotic plaque non-invasively.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
WHO (2004) Causes of death. World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland
Feigin VL, Lawes CM, Bennett DA, Anderson CS (2003) Stroke epidemiology: a review of population-based studies of incidence, prevalence, and case-fatality in the late 20th century. Lancet Neurol 2:43–53
Feigin VL (2005) Stroke epidemiology in the developing world. Lancet 365:2160–2161
Gorelick PB, Wong KS, Bae HJ, Pandey DK (2008) Large artery intracranial occlusive disease: a large worldwide burden but a relatively neglected frontier. Stroke 39:2396–2399
De Silva DA, Woon FP, Lee MP, Chen CP, Chang HM, Wong MC (2007) South Asian patients with ischemic stroke: intracranial large arteries are the predominant site of disease. Stroke 38:2592–2594
Wong LK (2006) Global burden of intracranial atherosclerosis. Int J Stroke 1:158–159
Arenillas JF (2011) Intracranial atherosclerosis: current concepts. Stroke 42:S20–S23
Sacco RL, Kargman DE, Gu Q, Zamanillo MC (1995) Race-ethnicity and determinants of intracranial atherosclerotic cerebral infarction. The Northern Manhattan Stroke Study. Stroke 26:14–20
Feldmann E, Wilterdink JL, Kosinski A, Lynn M, Chimowitz MI, Sarafin J et al (2007) The stroke outcomes and neuroimaging of intracranial atherosclerosis (SONIA) trial. Neurology 68:2099–2106
Itoh T, Matsumoto M, Handa N, Maeda H, Hougaku H, Hashimoto H et al (1993) Rate of successful recording of blood flow signals in the middle cerebral artery using transcranial Doppler sonography. Stroke 24:1192–1195
Seidel G, Kaps M, Gerriets T (1995) Potential and limitations of transcranial color-coded sonography in stroke patients. Stroke 26:2061–2066
Heiserman JE, Dean BL, Hodak JA, Flom RA, Bird CR, Drayer BP, et al (1994) Neurologic complications of cerebral angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 15:1401–1407; discussion 1408–1411
Willinsky RA, Taylor SM, TerBrugge K, Farb RI, Tomlinson G, Montanera W (2003) Neurologic complications of cerebral angiography: prospective analysis of 2,899 procedures and review of the literature. Radiology 227:522–528
Shrier DA, Tanaka H, Numaguchi Y, Konno S, Patel U, Shibata D (1997) CT angiography in the evaluation of acute stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 18:1011–1020
Wong KS, Liang EY, Lam WW, Huang YN, Kay R (1995) Spiral computed tomography angiography in the assessment of middle cerebral artery occlusive disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 59:537–539
Skutta B, Furst G, Eilers J, Ferbert A, Kuhn FP (1999) Intracranial stenoocclusive disease: double-detector helical CT angiography versus digital subtraction angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 20:791–799
Nguyen-Huynh MN, Wintermark M, English J, Lam J, Vittinghoff E, Smith WS et al (2008) How accurate is CT angiography in evaluating intracranial atherosclerotic disease? Stroke 39:1184–1188
Bendib K, Poirier C, Croisille P, Roux JP, Revel D (1999) Amiel M [Characterization of arterial stenosis using 3D imaging. Comparison of 3 imaging techniques (MRI, spiral CT and 3D DSA) and 4 display methods (MIP, SR, MPVR, VA) by using physical phantoms)]. J Radiol 80:1561–1567
Willinek WA, Born M, Simon B, Tschampa HJ, Krautmacher C, Gieseke J et al (2003) Time-of-flight MR angiography: comparison of 3.0-T imaging and 1.5-T imaging–initial experience. Radiology 229:913–920
Choi CG, Lee DH, Lee JH, Pyun HW, Kang DW, Kwon SU et al (2007) Detection of intracranial atherosclerotic steno-occlusive disease with 3D time-of-flight magnetic resonance angiography with sensitivity encoding at 3T. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 28:439–446
Muhlenbruch G, Das M, Mommertz G, Schaaf M, Langer S, Mahnken AH et al (2010) Comparison of dual-source CT angiography and MR angiography in preoperative evaluation of intra- and extracranial vessels: a pilot study. Eur Radiol 20:469–476
Wong KS, Lam WW, Liang E, Huang YN, Chan YL, Kay R (1996) Variability of magnetic resonance angiography and computed tomography angiography in grading middle cerebral artery stenosis. Stroke 27:1084–1087
Swartz RH, Bhuta SS, Farb RI, Agid R, Willinsky RA, Terbrugge KG et al (2009) Intracranial arterial wall imaging using high-resolution 3-tesla contrast-enhanced MRI. Neurology 72:627–634
Xu WH, Li ML, Gao S, Ni J, Zhou LX, Yao M et al (2010) In vivo high-resolution MR imaging of symptomatic and asymptomatic middle cerebral artery atherosclerotic stenosis. Atherosclerosis 212:507–511
Li ML, Xu WH, Song L, Feng F, You H, Ni J et al (2009) Atherosclerosis of middle cerebral artery: evaluation with high-resolution MR imaging at 3T. Atherosclerosis 204:447–452
Niizuma K, Shimizu H, Takada S, Tominaga T (2008) Middle cerebral artery plaque imaging using 3-Tesla high-resolution MRI. J Clin Neurosci 15:1137–1141
Klein IF, Lavallee PC, Touboul PJ, Schouman-Claeys E, Amarenco P (2006) In vivo middle cerebral artery plaque imaging by high-resolution MRI. Neurology 67:327–329
Weimar C, Goertler M, Harms L, Diener HC (2006) Distribution and outcome of symptomatic stenoses and occlusions in patients with acute cerebral ischemia. Arch Neurol 63:1287–1291
Kern R, Steinke W, Daffertshofer M, Prager R, Hennerici M (2005) Stroke recurrences in patients with symptomatic vs asymptomatic middle cerebral artery disease. Neurology 65:859–864
Tang CW, Chang FC, Chern CM, Lee YC, Hu HH, Lee IH (2011) Stenting versus medical treatment for severe symptomatic intracranial stenosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 32:911–916
Ni J, Yao M, Gao S, Cui LY (2011) Stroke risk and prognostic factors of asymptomatic middle cerebral artery atherosclerotic stenosis. J Neurol Sci 301:63–65
Wong KS, Ng PW, Tang A, Liu R, Yeung V, Tomlinson B (2007) Prevalence of asymptomatic intracranial atherosclerosis in high-risk patients. Neurology 68:2035–2038
Saba L, Sanfilippo R, Montisci R, Mallarini G (2010) Assessment of intracranial arterial stenosis with multidetector row CT angiography: a postprocessing techniques comparison. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31:874–879
Samuels OB, Joseph GJ, Lynn MJ, Smith HA, Chimowitz MI (2000) A standardized method for measuring intracranial arterial stenosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 21:643–646
Mohammad Y, Qattan M, Prabhakaran S (2010) Epidemiology and pathophysiology of intracranial large artery stenosis. Open Atherosclerosis Thromb J 3:3–7
Buerke B, Wittkamp G, Seifarth H, Heindel W, Kloska SP (2009) Dual-energy CTA with bone removal for transcranial arteries: intraindividual comparison with standard CTA without bone removal and TOF-MRA. Acad Radiol 16:1348–1355
Bash S, Villablanca JP, Jahan R, Duckwiler G, Tillis M, Kidwell C et al (2005) Intracranial vascular stenosis and occlusive disease: evaluation with CT angiography, MR angiography, and digital subtraction angiography. Am J Neuroradiol 26:1012–1021
Villablanca JP, Rodriguez FJ, Stockman T, Dahliwal S, Omura M, Hazany S et al (2007) MDCT angiography for detection and quantification of small intracranial arteries: comparison with conventional catheter angiography. AJR Am J Roentgenol 188:593–602
Prokop M, Shin HO, Schanz A, SchaeferProkop CM (1997) Use of maximum intensity projections in CT angiography: a basic review. Radiographics 17:433–451
Kuszyk BS, Heath DG, Johnson PT, Eng J, Fishman EK (1999) CT angiography with volume rendering for quantifying vascular stenoses: in vitro validation of accuracy. Am J Roentgenol 173:449–455
Lopez-Cancio E, Dorado L, Millan M, Reverte S, Sunol A, Massuet A et al (2011) The population-based Barcelona-Asymptomatic Intracranial Atherosclerosis Study (ASIA): rationale and design. BMC Neurol 11:22
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by National Key Project of Scientific and Technical Supporting Programs funded by Ministry of Science & Technology of China during the 11th 5-year Plan (No. 2007BAI05B07), BHF PG/11/74/29100 and the NIHR Cambridge Biomedical Research Centre.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Q., Huang, J., Degnan, A.J. et al. Comparison of high-resolution MRI with CT angiography and digital subtraction angiography for the evaluation of middle cerebral artery atherosclerotic steno-occlusive disease. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging 29, 1491–1498 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-013-0237-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10554-013-0237-3