Abstract
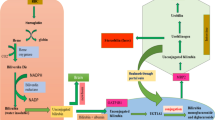
1. The pathogenesis of bilirubin encephalopathy is multifactorial, involving the transport of bilirubin or albumin/bilirubin across the blood–brain barrier and delivering bilirubin to target neurons.
2. The relative importance of the blood–brain barrier, unconjugated bilirubin levels, serum binding, and tissue susceptibility in this process is only partially understood. Even at dangerously high serum levels, bilirubin traverses the intact blood–brain barrier slowly, requiring time for encephalopathy to occur, although deposition of bilirubin can be rapid if a surge in plasma unbound bilirubin is produced by administering a drug which competes with bilirubin for binding to albumin.
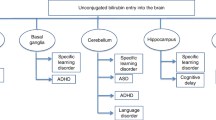
3. There may be maturational changes in permeability both in the fetus and postnatally which protect the brain from bilirubin.
4. Disruption or partial disruption of the blood–brain barrier by disease or hypoxic ischemic injury will facilitate transport of bilirubin/albumin into brain, but the relative affinities of albumin and target neurons will determine whether the tissue bilirubin load is sufficient for toxicity to occur.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Ahdab-Barmada, M., and Moossy, J. (1984). The neuropathology of kernicterus in the premature neonate: diagnostic problems. J. Neuropath. Exp. Neurol. 43:45–56.
Ahlfors, C. E., (1981). Effect of serum dilution on apparent unbound bilirubin concentration as measured by the peroxidase method. Clin. Chem. 27:692–696.
Ahlfors, C. E., and DiBiasio-Erwin, D. (1986). Rate Constants for dissociation of bilirubin from its binding sites in neonatal (cord) and adult sera. J. Pediatr 108:295–298.
Ahlfors, C. E., Bennett, S. H., Shoemaker, C. T., Ellis, W. G., Davis, S. L., Wennberg, R. P., and Goetzman, B. W. (1986). Changes in the auditory brainstem response associated with intravenous infusion of unconjugated bilirubin into infant rhesus monkeys. Pediatr. Res. 20:511–515.
Bonnett, R., Davies, J. E., and Hursthouse, M. B. (1976). Structure of bilirubin. Nature 262:326–328.
Brann, B. S., IV, Stonestreet, B. S., Oh, W., and Cashore, W. J. (1987). The in vivo effect of bilirubin and sulfisoxazole on cerebral oxygen, glucose, and lactate metabolism in newborn piglets. Pediatr. Res. 22:135–140.
Bratlid, D. (1972). The effect of pH on bilirubin binding by human erythrocytes. Scand. J. Clin. Lab. Invest. 29:453–459.
Bratlid, D., Cashore, W. J., and Oh, W. (1983). Effect of serum hyperosomality on opening of the bloodbrain barrier for bilirubin in rat brain. Pediatrics 71:909–912.
Bratlid, D., Cashore, W. J., and Oh, W. (1984). Effect of acidosis on bilirubin deposition in rat brain. Pediatrics 73:431–434.
Brodersen, R. (1974). Competitive binding of bilirubin and drugs to human serum albumin studied by enzymatic oxidation. J. Clin. Invest. 54:1353–1364.
Brodersen, R. (1979). Binding of bilirubin to albumin. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 11:305–399.
Brodersen, R., and Stern, L. (1990). Deposition of bilirubin acid in the central nervous system-A hypothesis for the development of kernicterus. Acta Paediatr. Scand. 79:12–19.
Burgess, G. H., Stonestreet, B. S., Cashore, W. J., and Oh, W. (1985a). Brain bilirubin deposition and brain blow during acute urea-induced hyperosmolality of newborn piglets. Pediatr. Res. 19:537–542.
Burgess, G. H., Oh, W., Bratlid, D., Brubakk A.-M., Cashore, W. J., and Stonestreet, B. S. (1985b). The effects of brain blood flow on brain bilirubin deposition in newborn piglets. Pediatr. Res. 19:691–696.
Cashore, W. J., Gartner, L. M., Oh, W., and Stern, L. (1978). Clinical application of neonatal bilirubin-binding determinations: Current status. J. Pediatr. 93:827–833.
Chen, H.-C., Lien, I.-N., and Lu, T.-C. (1965). Kernicterus in newborn rabbits. Am. J. Pathol. 46:331–343.
Chen, H.-C., Tsai, D.-J., Wang, Y.-C., and Chen, Y.-C. (1969). An electron microscopic and radioautographic study on experimental kernicterus. I. Bilirubin transport via astroglia. Am. J. Pathol. 56:31–58.
Chen, H.-C., Wang, C.-H., Tsan, K.-W., and Chen, Y.-C. (1971). An electron microscopic and radioautographic study on experimental kernicterus. II. Bilirubin movement with neurons and release of waste products via astroglia. Am. J. Pathol. 64:45–66.
Chiueh, C. C., Sun, C. L., Kopin, I. J., Fredericks, W. R., and Rapoport, S. I. (1978). Entry of 3H-epinephrine, 125I-albumin and Evans blue from blood into the brain following unilateral osmotic opening of the blood-brain barrier. Brain Res. 145:291–301.
Cowger, M. L. (1971). Mechanism of bilirubin toxicity on tissue culture cells: factors that affect toxicity, reversibility by albumin, and comparisons with other respiratory poisons and surfactants. Biochem. Med. 5:1–16.
Cowger, M. L., Igo, R. P., and Labbe, R. F. (1965) The mechanism of bilirubin toxicity studies with purified respiratory enzyme and tissue culture systems. Biochemistry 4:2763–2770
Day, R. L. (1954). Inhibition of brain respiration in vitro by bilirubin: Reversal of inhibition by various means. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 85:261–264.
Diamond, I., and Schmid, R. (1966). Experimental bilirubin encephalopathy: The mode of entry of bilirubin-14C into the central nervous system. J. Clin. Invest. 45:678–689.
Ebbesen, F., and Brodersen, R. (1982). Risk of bilirubin acid precipitation in preterm infants with respiratory distress syndrome: Considerations of blood/brain bilirubin transfer equilibrium. Early Hum. Dev. 6:341–355.
Faerch, T., and Jacobsen, J. (1997). Kinetics of the binding of bilirubin to human serum albumin studied by stopped-flow technique. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 184:282–289.
Funato, M., Tamai, H., Shimada, S., and Nakamura, H. (1994). Vigintiphobia, unbound bilirubin, and auditory brainstem responses. Pediatrics 93:50–53.
Gartner, L. M., Snyder, R. N., Chabon, R. S., and Berstein, J. (1970). Kernicterus: High incidence in premature infants with low serum bilirubin concentrations. Pediatrics 45:906–917.
Habgood, M. D., Sedgwick, J. E., Dziegielewska, K. M., and Saunders, N. R. (1992). A developmentally regulated blood-cerebrospinal fluid transfer mechanism for albumin in immature rats. J. Physiol. 456:181–192.
Hahm, J. S., Ostrow, J. D., Mukerjee, P., and Celic, L. (1992). Ionization and self-association of unconjugated bilirubin, determined by rapid solvent partition from chloroform, with further studies of bilirubin solubility. J. Lipid Res. 33:1123–1137.
Hansen, P. E., Thiessen, H., and Brodersen, R. (1979). Bilirubin acidity. Titrimetric and 13C NMR studies. Acta Chem. Scand. B33:281.
Hansen, T. W. R., Øyasæter, S., Stiris, T., and Bratlid, D. (1989). Effects of sulfisoxazole, hypercarbia, and hyperosmolality on entry of bilirubin and albumin into brain regions of young rats. Biol. Neonate 56:22–30.
Haymaker, W., Margoles, C., Pentschew, A., Jacob, H., Lindenberg, R., and Arroyo, L. S. (1961). Pathology of kernicterus and posticteric encephalopathy. In Swinyard, C. A. (ed.), Kernicterus and Its Importance in Cerebral Palsy, Charles C Thomas, Springfield, IL, pp. 21–228.
Hsia, D. Y.-Y., Allen, F. H., Gellis, S. S., and Diamond, L. K. (1952). Erythroblastosis fetalis. VIII. Studies of serum bilirubin in relation to kernicterus. N. Engl. J. Med. 247:668–681.
Ives, N. K., and Gardiner, R. M. (1990). Blood-brain barrier permeability to bilirubin in the rat studied using intracarotid bolus injection and in situ brain perfusion techniques. Pediatr. Res. 27:436–441.
Ives, N. K., Bolas, N. M., and Gardiner, R. M. (1989). The effects of bilirubin on brain energy metabolism during hyperosmolar opening of the blood-brain barrier: An in vivo study using 31P nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Pediatr. Res. 26:356–361.
Jacobsen, J. (1969). Binding of bilirubin to human serum albumin: determination of the dissociation constants. FEBS Lett. 5: 112–114.
Jacobsen, J., and Brodersen, R. (1976). The effect of pH on albumin-bilirubin binding. Birth Defects Orig. Art. Ser. 12:175–178.
Jacobsen, J., and Wennberg, R. P. (1974). Determination of unbound bilirubin in the serum of newborns. Clin. Chem. 20:783–789.
Jardine, D. S., and Rogers, K. (1989). Relationship of benzyl alcohol to kernicterus, intraventricular hemorrhage, and mortality in preterm infants. Pediatrics 83:153–160.
Johnson, L., Garcia, M. L., Figueroa, E., and Sarmiento, F. (1961). Kernicterus in rats lacking glucuronyl transferase. II. Factors which alter bilirubin concentration and frequency of kernicterus. Am. J. Dis. Child. 101:322–349.
Kapitulnik, J., Horner-Mibashan, R., Blondheim, S., Kaufmann, N. A., and Russell, A. (1975). Increase in bilirubin-binding affinity of serum with age of infant. J. Pediatr. 86:442–445.
Katoh-Semba, R., and Kashiwamata, S. (1980). Interactions of bilirubin with brain capillaries and its toxicity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 632:290–297.
Lee, C., Oh, W., Stonestreet, B. S., and Cashore, W. J. (1989). Permeability of the blood brain barrier for 125I-albumin-bound bilirubin in newborn piglets. Pediatr. Res. 25:452–456.
Lee, C., Stonestreet B. S., Oh, W., Outerbridge, E. W., and Cashore, W. J. (1995). Postnatal maturation of the blood-brain barrier for unbound bilirubin in newborn piglets. Brain Res. 689:233–238.
Lee, J. J., Daly, L. H., and Cowger, M. L. (1974). Bilirubin ionic equilibria: Their effects on spectra and on conformation. Res. Commun. Chem. Pathol. Pharm. 9:763–770.
Lending, M., Slobody, L. B., and Mestern, J. (1967). The relationship of hypercapnia to the production of kernicterus. Dev. Med. Child. Neurol. 9:145–151.
Lenhardt, M. L., McArtor, R., and Bryant, B. (1984). Effects of neonatal hyperbilirubinemia on the brainstem electric response. J. Pediatr. 104:281–284.
Levine, R. L., Fredericks, W. R., and Repoport, S. I. (1982). Entry of bilirubin into the brain due to opening of the blood brain barrier. Pediatrics 69:255–259.
Lucey, J. F., Hibbard, E., Behrman, R. D., Esquivel de Gallardo, F. O., and Windle, W. F. (1964). Kernicterus in asphyxiated newborn rhesus monkeys. Exp. Neurol. 9:43–58.
McCandless, D. W., and Abel, M. S. (1980). The effect of unconjugated bilirubin on regional cerebellar energy metabolism. Neurobehav. Toxicol. 2:81–84.
Matsuoka, Y., et al. (1999). J. Neurobiol. 39:383–392.
Møllgård, K., and Saunders, N. R. (1986). The development of the human blood-brain and blood-CSF barriers. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 12:337–358.
Mustafa, M. G., Cowger, M. L., and King. T. E. (1969). Effects of bilirubin on mitochondrial reactions. J. Biol. Chem. 244:6403–6414.
Nakamura, H., Takada, S., Shimabuku, R., Matsuo, M., Matsuo, T., and Negishi, H. (1985). Auditory nerve and brainstem responses in newborn infants with hyperbilirubinemia. Pediatrics 75:703–708.
Nelson, T., Jacobsen, J., and Wennberg, R. P. (1974). Effect of pH on the interaction of bilirubin with albumin and tissue culture cells. Pediatr. Res. 8:963–967.
Noir, B. A., Boveris, A., Garaza Pereira, A. M., and Stoppani, A. O. M. (1972). Bilirubin: A multi-site inhibitor of mitochondrial respiration. FEBS Lett. 27:270–274.
Nwaesei, C. G., Van Aerde, J., Boyden, M., and Perlman, M. (1984). Changes in auditory brainstem responses in hyperbilirubinemia infants before and after exchange transfusion. Pediatrics 75:800–803.
Odell, G. B. (1959). Studies in kernicterus. I. The protein binding of bilirubin. J. Clin. Invest. 38:823–833.
Odell, G. B. (1965). Influence of pH on distribution of bilirubin between albumin and mitochondria. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 120:352–354.
Ohsugi, M., Sato, H., and Yamamura, H. (1992). Transfer of 125I-albumin from blood to brain in newborn rats and the effect of hyperbilirubinemia on the transfer. Biol. Neonate 62:47–54.
Øie, S., Levy, G. (1979). Effect of sulfisoxazole on pharmacokinetics of free and plasma protein-bound bilirubin in experimental unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia. J. Pharm. Sci. 68:6–9.
Oldendorf, W. H. (1970). Measurement of brain uptake of radiolabeled substances using a tritiated water internal standard. Brain Res. 24:372–376.
Perlman, M., Fainmesser, P., Sohmer, H., Tamari, H., Wax, Y., and Pevsmer, B. (1983). Auditory nerve-brainstem evoked responses in hyperbilirubinemic neonates. Pediatrics 72:658–664.
Plateel, M., Teissier, E., and Cecchelli, R. (1997) Hypoxia dramatically increases the nonspecific transport of blood-borne proteins to the brain. J. Neurochem. 68:874–877.
Rapoport, S. I., Fredericks, W. R., Ohno, K., and Pettigrew, K. D. (1980). Quantitative aspects of reversible osmotic opening of the blood-brain barrier. Am. J. Physiol. 238:R421-R431.
Ritter, D. A., Kenny, J. D., Norton, H., and Rudolph, A. J. (1982). A prospective study of free bilirubin and other risk factors in the development of kernicterus in premature infants. Pediatrics 69:260–266.
Robertson, A., Karp, W., and Brodersen, R. (1991). Bilirubin displacing effect of drugs used in neonatology. Acta Paediatr. Scand. 80:1119–1127.
Robinson, P. J., and Rapoport, S. I. (1987). Binding effect of albumin on uptake of bilirubin by brain. Pediatrics 79:553–558.
Roger, C., Koziel, V., Vort, P., and Nehlig, A. (1993). Effects of bilirubin infusion on local cerebral glucose utilization in the immature rat. Brain Res. Dev. Brain Res. 76:115–130.
Rozdilsky, B. (1966). Kittens as experimental model for study of kernicterus. Am. J. Dis. Child. 111:161–165.
Rozdilsky, B., and Olszewski, J. (1960). Permeability of cerebral vessels to albumin in hyperbilirubinemia. Neurology 10:631–638.
Rozdilsky, B., and Olszewski, J. (1961). Experimental study of the toxicity of bilirubin in newborn animals. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 20:193–205.
Sawitsky, A., Cheung, W. H., and Seifter, E. (1968). The effect of pH on the distribution of bilirubin in peripheral blood, cerebrospinal fluid, and fat tissues. J. Pediatr. 72:700–707.
Schiff, D., Chan, G., and Poznansky, M. J. (1985). Bilirubin toxicity in neural cell lines N115 and NBR10A. Pediatr. Res. 19:908–911.
Schumacher, U., and Mollgård, K. (1997). Histochem. Cell Biol. 108:179–182.
Silberberg, D. H., Johnson, L., and Ritter, L. (1970). Factors influencing toxicity of bilirubin in cerebellar tissue culture. J. Pediatr. 77:386–396.
Silverman, W. A., Anderson, D., Blanc, W., and Crozier, D. N. (1956). A difference in mortality rate and incidence of kernicterus among premature infants allotted to two prophylactic antibacterial regimens. Pediatrics 18:614–625.
Stonestreet, B. S., Patlak, C. S., Pettigrew, K. D., Reily, C. B., and Cserr, H. F. (1996). Ontogeny of blood-brain barrier function in ovine fetuses, lambs, and adults. Am. J. Physiol. 271:R1594-R1601.
Svenson, A. E., Holmer, and Andersson L.-O. (1974). A new method for the measurement of dissociation rates for complexes between small ligands and proteins as applied to the palmitate and bilirubin complexes with serum albumin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 342:54–59.
Takahashi, M., Sugiyama, K., Shumiya, S., and Nagase, S. (1984). Penetration of bilirubin into the brain in albumin-deficient and jaundiced rats (AJR) and Nagase analbuminemic rats (NAR). J. Biochem. 96:1705–1712.
Takasato, Y., Rapoport, H. I., and Smith Q. R. (1984). An in situ brain perfusion technique to study cerebrovascular transport in the rat. Am. J. Physiol. 247:H484-H493.
Valaes, T., Kapitulnik, J., Kaufman, N. A., and Blondheim, S. H. (1976). Experience with Sephadex gel filtration in assessing the risk of bilirubin encephalopathy in neonatal jaundice. Birth Defects Orig. Art. Ser. 12:215–228.
Van Praagh, R. (1961). Diagnosis of kernicterus in the neonatal period. Pediatrics 28:870–876.
Vohr, B. R., Lester, B., Rapisardi, G., O'Dea, C., Brown, L., Peucker, M., Cashore, W., and Oh, W. (1989). Abnormal brain-stem function (brainstem auditory evoked response) correlates with acoustic cry features in term infants with hyperbilirubinemia. J. Pediatr. 115:303–308.
Watchko, J. F., et al. (1998). Pediatr. Res. 44:763–766.
Wennberg, R. P. (1983). In Levine, R. L., and Maisels, M. J. (eds.), Hyperbilirubinemia in the newborn. Report of the 85th Ross Conference on Pediatric Research, Ross Laboratories, Columbus, OH, p. 122.
Wennberg, R. P. (1988). The importance of free bilirubin acid salt in bilirubin uptake by erythrocytes and mitochondria. Pediatr. Res. 23:443–447.
Wennberg, R. P. (1990). Bilirubin encephalopathy: Role of the blood-brain barrier. In Johansson, B. B., Owman, C., and Widner, H. (eds.), Pathophysiology of the Blood-Brain Barrier: Long Term Consequences of Barrier Dysfunction for the Brain, Fernström Foundation Series, Vol. 14, Elsevier Science, Amsterdam, pp. 269–278.
Wennberg, R. P., and Hance, A. J. (1986). Experimental encephalopathy: Importance of total bilirubin, protein binding, and blood-brain barrier. Pediatr. Res. 20:789–792.
Wennberg, R. P., Ahlfors, C. E., Bickers, R., McMurtry, C. A., and Shetter, J. L. (1982). Abnormal auditory brainstem response in a newborn infant with hyperbilirubinemia: improvement with exchange transfusion. J. Pediatr. 100:624–626.
Wennberg, R. P., Johanssen, B. B., Folbergrova, J., and Siesjo, B. K. (1991). Bilirubin-induced changes in brain energy metabolism after osmotic opening of the blood-brain barrier. Pediatr. Res. 30:473–478.
Wennberg, R., Rhine, W., Gospe, S., Seyal, M., Saeed, D., and Sosa, G. (1993). Brainstem bilirubin toxicity in the newborn primate may be promoted and reversed by modulating pCO2. Pediatr. Res. 34:6–9.
Zetterström, R., and Ernster, L. (1956). Bilirubin, an uncoupler or oxidative phosphorylation in isolated mitochondria. Nature 178:1335–1336.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wennberg, R.P. The Blood–Brain Barrier and Bilirubin Encephalopathy. Cell Mol Neurobiol 20, 97–109 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006900111744
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006900111744