Abstract
SUMMARY: Autoimmune encephalitis is a heterogeneous group of newly identified disorders that are being diagnosed with increasing frequency. Early recognition and treatment of autoimmune encephalitis are crucial for patients, but diagnosis remains challenging and time-consuming. In this retrospective case series, we describe the findings of conventional MR imaging and 3D pseudocontinuous arterial spin-labeling in patients with autoimmune encephalitis confirmed by antibody testing. All patients with autoimmune encephalitis showed increased CBF in the affected area, even when some of them presented with normal or slightly abnormal findings on conventional MR imaging. Additionally, serial 3D pseudocontinuous arterial spin-labeling showed perfusion reduction in 1 patient after therapy. For patients with highly suspected autoimmune encephalitis, 3D pseudocontinuous arterial spin-labeling may be added to the clinical work-up. Further studies and longitudinal data are needed to corroborate whether and to what extent 3D pseudocontinuous arterial spin-labeling improves the diagnostic work-up in patients with autoimmune encephalitis compared with conventional MR imaging.
ABBREVIATIONS:
- AE
- autoimmune encephalitis
- ASL
- arterial spin-labeling
- 3D pCASL
- 3D pseudocontinuous arterial spin-labeling
- MELAS
- mitochondrial encephalopathy with lactic acidosis and strokelike episodes
- rCBF
- relative CBF
Autoimmune encephalitis (AE) is a blanket term for a group of diseases characterized by brain inflammation and circulating autoantibodies.1 Its complicated and variable clinical manifestations present a diagnostic challenge for clinicians, probably leading to late diagnosis and interventions. It has been shown that early initiation of effective therapy for patients with AE may lead to improved clinical outcomes.2,3
Currently, the diagnostic approach includes clinical manifestations, CSF analysis, electroencephalography, antibody testing, and MR imaging used together for AE (possible, probable, or definite).4 According to the 2016 diagnostic approach for AE from Lancet Neurology, brain MR imaging, as a standard imaging technique, plays a vital role in evaluating patients with AE, especially the T2 FLAIR sequence.4 However, in some cases, AE shows normal, mild, or transient abnormal findings on MR imaging, despite the severe and persistent neurologic deficits of patients.5⇓-7
Perfusion and metabolism abnormalities derived from CTP, SPECT, and PET/CT have been previously described in some patients with AE.8⇓⇓-11 Arterial spin-labeling (ASL) perfusion imaging has broad clinical applications in routine neuroradiology practice in stroke, tumors, mitochondrial encephalopathy with lactic acidosis and strokelike episodes (MELAS), herpes simplex encephalitis, and so forth. However, the application of ASL for the assessment of AE in the clinic has seldom been described previously.6,12 Here, we conducted a retrospective study on a case series of 9 patients with AE to summarize the findings on conventional MR imaging and to investigate brain perfusion alterations.
CASE SERIES
Case Selection
From June 2015 to January 2020, a total of 21 consecutive patients with AE were enrolled. Twelve patients were excluded because 3D pseudocontinuous arterial spin-labeling (3D pCASL) was not performed. Nine patients with AE who underwent both conventional MR imaging and 3D pCASL were finally included. This retrospective study was approved by the institutional review board of the First Medical Center of PLA General Hospital, and informed consent was waived due to the retrospective nature of the study. Patient information including clinical data, conventional MR imaging, and ASL findings was reviewed. There were 6 men and 3 women with ages ranging from 29 to 68 years (mean, 51.6 years). Meanwhile, 3D pCASL was acquired in 12 healthy individuals (6 men and 6 women; age range, 30–65 years; mean, 51.2 years) at the same time, considered as the control group.
The antibody panels were performed from serum and CSF in all patients by commercial laboratories. Autoantibodies were identified through a cell-based assay using an indirect immunofluorescence test (Euroimmun).
Imaging Acquisition
All MR imaging was performed on a 3T MR imaging system (Discovery 750; GE Healthcare). Conventional MR images included axial T2WI, axial T1WI, and axial and/or coronal T2 FLAIR with a section thickness/gap of 5.0/1.5 mm for the axial and coronal planes. Postcontrast T1WI was performed in 8 patients, including the axial, coronal, and sagittal planes (0.1 mmol/kg, Magnevist, Gd-DTPA; Bayer Schering Pharma).
The 3D pCASL sequence was a background-suppressed 3D spiral fast spin-echo technique with the following parameters: TR/TE = 4844/10.5 ms, postlabeling delay = 2025 ms, FOV = 24 × 24 cm, section thickness = 4.0 mm, number of sections = 36, and number of excitations = 3. In addition, a 3D T1-weighted fast-spoiled gradient recalled sequence, matched with 3D pCASL, was also performed after contrast injection. Follow-up 3D pCASL examinations were performed in 1 case.
Image Analysis
All MR images were visually assessed in a blinded manner. Two neuroradiologists with >5 years’ experience reviewed the MR images. By empiric visual assessment, signal abnormalities in brain regions were reviewed on T2WI, T1WI, and T2 FLAIR, compared with the relatively normal brain. Similarly, by visual observations, the brain regions with hyperintense signal (compared with the relatively normal brain) were regarded as hyperperfusion regions, and the regions with hypointense signal (compared with the relatively normal brain) were regarded as hypoperfusion regions on 3D pCASL.
In addition to visual assessment, quantitative evaluation was also performed for each patient and healthy control. CBF values in healthy controls and lesions with AE were measured and compared. Three to 5 round ROIs (28–32 mm2) were manually and carefully drawn in the lesion areas. The postcontrast 3D T1-fast-spoiled gradient recalled sequence, for accurate anatomic reference, was used for image matching with 3D pCASL. Then 3D T1 fast-spoiled gradient recalled and T2 FLAIR images were cross-referenced to determine the location of the lesion.13 For each patient, the mean CBF value was acquired and calculated from various brain areas. The mean, maximal CBF value within different lesions of the same brain regions was regarded as the final CBF value. To minimize interindividual differences in baseline CBF, we used relative CBF (rCBF), defined as the value of mean CBF for the ROI in the lesion or healthy controls divided by the mean CBF value for the ROI in the cerebellum.
Statistical Analysis
All CBF and rCBF values of lesions in patients with AE and 12 control subjects were presented as mean (SD). The Student t test was used for continuous variables with normal distribution; otherwise the Mann-Whitney U test was performed. A P value < .05 was considered statistically significant.
RESULTS
Clinical Data
Nine patients with AE were included in this study. Summary information is detailed in the Online Supplemental Data. The time from the onset of symptoms to admission in our hospital ranged from 18 to 90 days (mean, 49.33 days). All autoantibodies were detected in serum and CSF, including tests with positive findings for anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (NMDAR) (2 patients), anti-G-protein coupled receptors for gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABAbR) (2 patients), and anti-leucine-rich, glioma inactivated 1 (LGI 1) (5 patients). Only 1 individual had a history of malignant tumor and pulmonary carcinoma–related anti-GABAbR antibodies (case 6).
Empiric treatment was started when the diagnosis of possible AE was established, after excluding an infectious etiology while awaiting antibody test results. Treatment details are shown in the Online Supplemental Data.
Conventional MR Imaging and 3D pCASL Characteristics
The neuroimaging findings of the patients are summarized in the Online Supplemental Data. One patient had a lesion that was right-sided; 3, left-sided; and 5, bilateral, showing hypointensity or isointensity on T1WI (Figs 1B and 2B) and hyperintensity or isointensity on T2WI and T2 FLAIR (Figs 1C and 2C). Cases 3 and 5 were bilaterally involved, but abnormal signals were shown on only 1 side on T1WI, T2WI, and T2 FLAIR (Figs 2 and 3). All lesions showed no enhancement on postcontrast T1WI, except for mild patchy enhancement in case 6 (Online Supplemental Data).
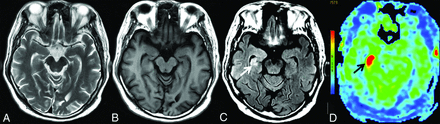
MR imaging of case 1. Findings on axial T2WI (A) and axial T1WI (B) are unremarkable. C, Axial T2 FLAIR reveals hyperintensity in the right hippocampus (white arrow). D, 3D pCASL demonstrates marked hyperperfusion in the corresponding region (black arrow).
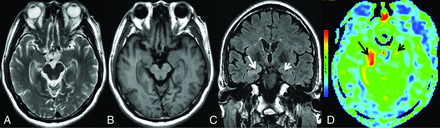
MR imaging of case 3. Findings on axial T2WI (A) and axial T1WI (B) are unremarkable. C, Coronal T2 FLAIR demonstrates hyperintensity in the right hippocampus (white arrow), whereas there are normal findings in the left hippocampus (white arrowhead). D, 3D pCASL depicts hyperperfusion in the corresponding regions on the FLAIR image, more obvious on the right side (black arrows).
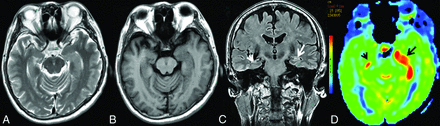
MR imaging of case 5. Findings on axial T2WI (A) and axial T1WI (B) are unremarkable. C, Coronal T2 FLAIR shows subtle hyperintensity with mild swelling in the left hippocampus (white arrow), whereas it shows normal findings in the right hippocampus (white arrowhead). D, Increased CBF in the bilateral hippocampi could be detected on 3D pCASL, the left (black arrow) greater than the right (black arrowhead).
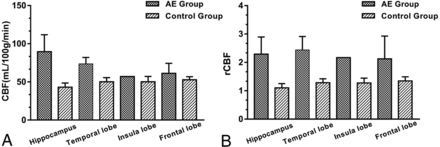
On 3D pCASL, all patients were identified as having perfusion abnormalities, showing hyperperfusion patterns on visual inspection (Figs 1D and 2D). The CBF and rCBF values of the lesions with AE and control subjects are shown in the Online Supplemental Data. In 2 of these cases, hyperperfusion could be noted in the affected areas on 3D pCASL (Figs 2D and 3D), despite initial unremarkable or normal findings on T2 FLAIR (Figs 2C and 3C). Serial MR imaging and 3D pCASL scans were performed in a 47-year-old man, which revealed dynamic alterations in perfusion features in the involved area (Fig 4). The CBF and rCBF values in AE lesions were markedly higher than those in the control group (Fig 5).
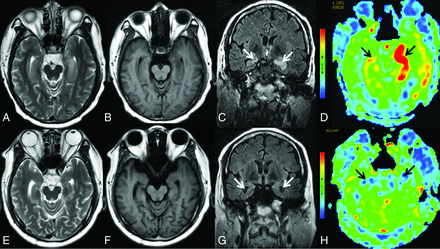
Serial MR imaging of case 7. On hospital day 3, the first conventional MR imaging examination findings were normal (not shown). On the second MR imaging check (26 days after admission), MR imaging shows swelling and hyperintensities on axial T2WI (A) and hypointensities on axial T1WI (B) in the bilateral hippocampi. C, Coronal T2 FLAIR shows hyperintensities in the bilateral hippocampi (white arrows). D, 3D pCASL reveals marked hyperperfusion in the bilateral medial temporal lobes (black arrows), the left greater than the right. On the third MR imaging check (96 days after admission), including axial T2WI (E), axial T1WI (F), and coronal T2 FLAIR (G), complete resolution of the inflammation in the bilateral medial temporal areas is seen, with enlargement of the bilateral temporal horns (white arrows), and 3D pCASL (H) shows decreased perfusion in the bilateral hippocampi (black arrows). The patient’s condition markedly improved with the administration of high-dose glucocorticoids, intravenous immunoglobulin, and plasma exchange (3 times).
Bar chart with the SD for the CBF (A) and rCBF (B) values of the lesions in the AE and control groups. The unit of CBF was mL/100 g/min.
DISCUSSION
This case series describes the signal changes on conventional MR imaging and perfusion alterations on 3D pCASL in a cohort of patients with AE. Our principal findings can be summarized as follows: 1) By visual assessment, patients with AE demonstrated elevated CBF in the affected area on 3D pCASL, though the affected area could be normal or present with slightly abnormal signals on conventional MR imaging. 2) Quantitative analysis also indicated that the CBF and rCBF values of the lesions were significantly higher than those of control group. 3) 3D pCASL may potentially be applied in the evaluation of the therapeutic response in AE.
Encephalitis is a life-threatening disease associated with high morbidity and mortality throughout the world.2,14 In the past few years, increased awareness has been generated in relation to AE, and currently, the prevalence and incidence of AE are comparable with those of infectious encephalitis, and the detection of AE has been increasing with time.15 Early diagnosis is paramount for patients with encephalitis, thereby enabling clinicians to adopt earlier and more aggressive therapy and improve patients’ outcomes. The diagnostic criteria vary depending on the types of encephalitis. For patients with AE, the initial diagnosis is based on the clinical presentation as well as antibody profiles and MR imaging. In addition, several clinical tools are now available and could be used by most clinicians. For example, a scoring system based on clinical features and the initial neurologic assessment of patients with epilepsy enables an earlier clinical diagnosis before the results of antibody tests are confirmed.16 Currently, the approach for a definite diagnosis of AE depends heavily on autoantibody detection.4,17 As a drawback, it is not readily available due to local conditions in many institutions, and it takes longer to obtain the results,4,18 thus leading to a delayed diagnosis and initiation of effective therapy.19
Conventional MR imaging plays a major role in the early diagnosis of AE and might be mandatorily performed when CT findings are negative in patients with serious neurologic disorders. However, the brain MR imaging has been reported to have normal findings in approximately 50%–60% of patients with anti-NMDAR encephalitis, 30%–40% with anti-LGI 1 encephalitis, and 30%–40% with anti-GABAb receptor encephalitis.20⇓-22 In addition, different forms of AE could present with different patterns of MR imaging abnormalities. In our study, all patients had elevated CBF on 3D pCASL, even when some of them presented with mild abnormal findings on conventional MR imaging. Among them, unilateral abnormal signals were revealed on conventional MR imaging, but bilateral involvement could be detected on 3D pCASL in 2 patients, suggesting that 3D pCASL is more sensitive than conventional MR imaging in the early detection of AE. Additionally, 3D pCASL in 1 case revealed dynamic alterations in perfusion features (CBF reduction with time), indicating its potential role in the assessment of therapeutic effects in AE.
Perfusion imaging studies in patients with AE in the literature are summarized in the Online Supplemental Data, with only a few cases using the ASL technique (2D imaging). 3D pCASL, which potentially combines the advantages of both pulsed arterial spin-labeling and continuous arterial spin-labeling, was performed in this study, allowing 3D fast acquisitions and reduction of magnetic susceptibility artifacts, especially in those brain areas (eg, medial temporal lobes) near the skull base.23,24
The exact pathophysiologic mechanism leading to perfusion alteration on 3D pCASL remains to be elucidated, and the candidate mechanisms will need to be evaluated in future studies. We speculated that 1 possible reason for increased regional CBF is an inflammatory process due to an antigen-antibody–mediated immune response, causing the blood vessels to expand.25 Another reason could be the loss of vascular autoregulatory mechanisms due to autonomic instability.6 In addition, some patients with AE may experience central hypoventilation that could lead to hypercarbia accounting for increased CBF, which usually presented with global cerebral hyperperfusion.26 It is unclear whether the elevated CBF is related solely to the autoimmune processes or whether all the factors account for the increased CBF. Further study is needed to test this hypothesis.
Hyperperfusion on 3D pCASL can be seen in various conditions, including tumors, inflammation or infection, MELAS, seizure activity, and so forth.26 MELAS, herpes simplex encephalitis, as well as high-grade glioma masquerading as AE27 present with hyperperfusion on 3D pCASL, but differentiation can be made by combining the clinical manifestation, history, lesion location, and so forth. Seizure is a common clinical manifestation in AE, and seizure activity can also cause hyperperfusion, but its perfusion alterations were linked to the timing of ASL data acquisition, with patients usually presenting with hyperperfusion during the ictal and postictal periods and hypoperfusion in the interictal phase.24,28,29 Unfortunately, we were unable to verify this finding as previously reported30 because the patients who had clinical seizures were imaged during the interictal phase in this study. Because no patients had epileptic seizures within 24 hours before the examination, we can, therefore, infer that increased ASL perfusion is caused by the underlying inflammatory process rather than being secondary to seizure activity. Furthermore, 3D pCASL can help exclude some AE-mimicking diagnoses with hypoperfusion, such as acute ischemic stroke and diffuse low-grade gliomas. In addition, AE-mimicking sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease has been reported,31,32 but Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease showed hypoperfusion on 3D pCASL.33 As stated above, we think that 3D pCASL has clinical utility in differentiating AE from its mimics.
ASL and PET/CT, as 2 different imaging modalities (perfusion and metabolism), are closely linked in neurologic disorders due to the close coupling of perfusion and metabolism in the brain.34 Dinoto et al12 reported that ASL and PET/CT findings are strongly concordant in limbic encephalitis. This concordance is particularly intriguing because ASL, without contrast medium and radiation, may be used to evaluate perfusion status and subsequent therapeutic effects in patients with AE. Two main metabolic patterns of abnormalities (mixed hyper-/hypometabolic and neurodegenerative-like) on PET/CT have been reported,35 and different “paradigms” of encephalitis (mainly limbic versus NMDAR) may have different PET/CT findings.12 Additionally, studies have shown that metabolic patterns on PET/CT, to a certain extent, are associated with different autoantibody subtypes, implying that different pathophysiologic mechanisms may exist.25 In this study, we found that all cases of AE showed patterns of hyperperfusion in the affected area. Further studies are needed to investigate the correlation between perfusion and metabolism in AE subtypes.
In clinical practice, the use of 3D pCASL seems to be feasible and reasonable in improving the sensitivity of lesion detection, especially in patients with suspected AE with normal conventional MR imaging findings. 3D pCASL could reveal abnormalities earlier than conventional MR imaging in some patients with AE and provide new insight into exploring the pathophysiologic mechanism of AE.6,36,37 Therefore, we suggest that 3D pCASL be added to the clinical work-up for patients with suspected AE, and its efficacy should be further tested in clinical practice.
Several limitations are noteworthy. First, this was a retrospective, cross-sectional study, and the sample size was relatively small. Second, 3D pCASL was performed for imaging diagnosis and follow-up in only 1 patient. Larger cohort and longitudinal data are needed to validate the results. Third, many subtypes of AE are frequently accompanied by seizures that can affect CBF, and this effect cannot be completely excluded theoretically.
CONCLUSIONS
Conventional MR imaging remains the best option, while 3D pCASL may have added value in the early diagnosis of AE, and 3D pCASL may also be used in the assessment of therapeutic effects. Clinically, 3D pCASL may be recommended in patients with highly suspected AE, especially in those with normal or unremarkable findings on conventional MR imaging. Further studies and longitudinal data are needed to corroborate whether and to what extent 3D pCASL can improve the diagnostic work-up in AE compared with conventional MR imaging.
Footnotes
Disclosure forms provided by the authors are available with the full text and PDF of this article at www.ajnr.org.
References
- Received July 27, 2021.
- Accepted after revision February 8, 2022.
- © 2022 by American Journal of Neuroradiology