Abstract
BACKGROUND AND PURPOSE: Radiation-induced changes can occur after stereotactic radiosurgery for brain AVMs, potentially causing symptomatic complications. We evaluated the incidence of such changes and the efficacy of repeat gamma knife radiosurgery for incompletely obliterated AVMs.
MATERIALS AND METHODS: We retrospectively evaluated 150 patients who underwent gamma knife radiosurgery for AVMs between 2002 and 2020; twenty-five underwent further radiosurgical procedures for incompletely obliterated AVMs. We recorded the median margin doses at the first (median, 20 Gy; range, 12–23 Gy; AVM volume, 0.026–31.3 mL) and subsequent procedures (median, 18 Gy; range, 12–23 Gy; AVM volume, 0.048–9.2 mL).
RESULTS: After the first treatment, radiologic radiation-induced changes developed in 48 (32%) patients, eight of whom had symptomatic changes. After repeat gamma knife radiosurgery, 16 of 25 patients achieved complete AVM obliteration (64%). The development of radiation-induced changes after the first treatment was significantly associated with successful obliteration by subsequent radiosurgery (OR = 24.0, 95% CI 1.20–483, P = .007). Radiation-induced changes occurred in only 5 (20%) patients who underwent a second gamma knife radiosurgery, one of whom experienced transient neurologic deficits. Between the first and repeat gamma knife radiosurgery procedures, there was no significant difference in radiologic and symptomatic radiation-induced changes (P = .35 and P = 1.0, respectively).
CONCLUSIONS: Radiation-induced changes after the first gamma knife radiosurgery were associated with AVM obliteration after a repeat procedure. The risk of symptomatic radiation-induced changes did not increase with retreatment. When the first procedure fails to achieve complete AVM obliteration, a favorable outcome can be achieved by a repeat gamma knife radiosurgery, even if radiation-induced changes occur after the first treatment.
ABBREVIATIONS:
- GKRS
- gamma knife radiosurgery
- RICs
- radiation-induced changes
Gamma knife radiosurgery (GKRS) is a standard treatment for patients with intracranial AVMs. Total obliteration rates vary from 60% to 80% during the 3- to 5-year period after the first GKRS procedure.1,2 If the first procedure fails to achieve complete obliteration, the hemorrhage risk will persist.3 Additional treatments may include repeat GKRS, resection, endovascular embolization, or any combination thereof.
The most frequent complications after GKRS for AVMs are radiation-induced changes (RICs), which typically occur 6–18 months after treatment and before AVM occlusion.4 These manifest on follow-up MR imaging as perinidal T2WI radiographic changes.5 Although most RICs are asymptomatic, some are accompanied by focal neurologic deficits.4,6 We do not know if the risk of symptomatic RICs is greater after repeat GKRS than after the first treatment.7 The relationship between RICs and AVM obliteration is also unclear. We addressed these questions through a retrospective review of repeat GKRS outcomes in patients with AVM and histories of RICs after the first treatment. We evaluated RIC incidence, factors associated with total obliteration, and hemorrhage risk.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Patient Population
The National Cerebral and Cardiovascular Center’s ethics committee approved this study (M30-013). We retrospectively reviewed consecutive patients with AVMs treated with GKRS at our institution between January 2002 and December 2020. This study excluded patients who had been treated by volume-staged GKRS or who had <1 year of follow-up.
We additionally included patients who died of cerebral hemorrhage during follow-up without an MRA because they presumably had patent AVMs.
Radiosurgical Technique
All GKRS procedures were performed using a Leksell Gamma Knife model B (2002–2009), model 4C (2009–2019), or Icon (2020) (Elekta). Patients underwent biplane stereotactic angiography, 1.5T MR T2WI, TOF, and CT for dose planning. This plan was designed to minimize the risk of radiation-induced complications as predicted by the nidus volume and the radiosensitivity of the brain location.
The marginal dose was planned as 50% of the maximum prescription dose and included the entire AVM nidus volume. The median prescription dose delivered to the nidus margin was 20 Gy (range, 12–23 Gy); the median AVM volume was 3.51 mL (range, 0.026–31.3 mL) for the first GKRS. For repeat procedures, the median prescription dose was 18 Gy (range, 12–23 Gy) and the median AVM volume was 0.77 mL (range, 0.048–9.2 mL).
When the AVM volume exceeded 10 mL, planned volume-staged GKRS was considered. The total AVM nidus volume was outlined on MR imaging and divided into approximately equal volumes based on anatomic landmarks such as major feeding arteries. The second procedure was scheduled 3–6 months after the first treatment.
In principle, repeat GKRS was considered if the AVM was patent 3–4 years after the first procedure and if there were no AVM composition changes evident on MR imaging. If the MR imaging follow-up showed an ongoing obliteration process, there should be a 5-year waiting period for additional treatment after the initial GKRS. In the present study, there were no AVM shrinkage cases >5 years after the initial GKRS. Direct surgery, with or without embolization, was considered in cases with persistent dural feeders or bleeding after the first GKRS.
Patient Outcomes and Data Collection
We recorded each patient’s age, sex, follow-up period, rupture history, Spetzler-Martin grade, previous embolization, AVM score, venous drainage, AVM location, AVM volume, and radiation dose.8 The modified Pollock-Flickinger AVM grading score was calculated as follows: Score = (0.1) (Volume in mL) + (0.02)(Age in Years) + (0.5) (Location: Basal Ganglia, Thalamus, or Brainstem = 1, Others = 0).9 The statistical end points were complete AVM nidus obliteration, RIC development, delayed cyst formation, and hemorrhage. The volume change ratio was calculated as follows: Target Volume at the First GKRS/Target Volume at Repeat GKRS.10
After GKRS, MRAs and MRIs were reviewed every 3–4 months. T2WI and FLAIR hyperintensity images were assessed on brain MR imaging. RICs were defined as new lesions with increased T2WI or as FLAIR imaging changes surrounding the treated nidus. Radiologic RICs included any MR imaging evidence of perinidal T2-weighted hyperintensities post-GKRS. Symptomatic RICs were considered radiologic RICs associated with new or worsening neurologic symptoms. In this study, unless otherwise specified, RICs refers to radiologic RICs.
If MR imaging/MRA findings in patients with at least a 1-year follow-up were consistent with obliteration, then cerebral angiography was requested to confirm the obliteration. A few study patients refused to undergo follow-up conventional angiography. For those patients, obliteration was evaluated on the basis of the most recent MR imaging results. On the MR imaging/MRA study, total AVM obliteration after radiosurgery was defined as the complete absence of the former nidus based on T2-weighted imaging and 3D-TOF MRA.
Statistical Analysis
All statistical analyses were performed using EZR software (https://www.jichi.ac.jp/saitama-sct/SaitamaHP.files/windowsEN.html).11 Kaplan-Meier survival analysis was performed to calculate obliteration and hemorrhage rates. The log-rank test was used to assess survival curve differences. Univariate analysis was used to evaluate patient characteristics at the first and repeat GKRS and relevant factors affecting total AVM obliteration. In detail, the Fisher exact test was performed to assess the following: 1) the male/female ratio, 2) the relationship between obliteration and AVM characteristics (rupture, deep drainage, location, eloquent cortex within adjacent brain tissue, prior embolization, >50% reduction in volume after the first GKRS, and RICs), and 3) incidences of RIC or cyst formation after the first and repeat GKRS. The Mann-Whitney U test was used to evaluate the relationship between obliteration and continuous data describing AVM characteristics (AVM score, AVM volume, and margin dose) and the AVM volume change ratio after the first and repeat GKRS. Continuous data are expressed as the mean (SD). P values < .05 were considered statistically significant. We performed the calculations for diagnosis-to-first GKRS, first GKRS-to-obliteration or repeat treatment, and post-repeat-GKRS periods. The annual hemorrhage rate was calculated as the hemorrhagic events number during the predefined period divided by the sum of the duration of individual observation periods.
RESULTS
Patient Demographics
During the study period, 175 patients with 178 AVMs underwent GKRS in our department. Of these, 4 patients had been treated by volume-staged GKRS and were excluded from this study. Moreover, 21 patients with 24 AVMs were excluded due to follow-up durations of <1 year (n = 9) and incomplete clinical data (n = 12). This exclusion left 150 patients with 150 AVMs in the first GKRS group. Complete obliteration following the first GKRS was achieved in 104 (67.5%) patients. Of the 46 patients with incomplete obliteration, 25 underwent repeat GKRS (repeat GKRS group). Four patients underwent surgery after the first GKRS, 3 for nidus removal due to rupture of the residual nidus and 1 for an AVF. Eight patients refused additional treatment, and 7 patients were lost to follow-up (Online Supplemental Data). Two patients died due to hemorrhage.
The median ages of the first and repeat GKRS groups were 37 (range, 9–79) and 39 (range, 14–69) years, respectively (Table 1). The median follow-up durations after the first and repeat GKRS were 102 (range, 15–221 months) and 79 months (range, 22–209 months), respectively. On average, repeat GKRS was performed 58 months (range, 36–94 months) after the first procedure.
The demographics of patients with AVMs of the brain at initial and repeat GKRS
AVM Characteristics
Before diagnosis, 53 AVMs (35.3%) presented with hemorrhage (Table 2). The Spetzler-Martin grades were grade I/II in 80 (53.3%) and grades III/IV/V in 70 (46.7%). The median AVM score was 1.19 (range, 0.289–3.92). The AVMs were located in cerebral lobar (n = 112; 74.7%), thalamus/basal ganglia/brainstem (n = 22; 14.7%), and cerebellar (n = 16; 10.7%) regions; notably, 82 (54.6%) were present in eloquent areas.8 The median AVM volume was 3.51 mL (range, 0.026–31.3 mL).
AVM characteristics and factors associated with obliteration at initial GKRS
At the time of repeat GKRS, 18 AVMs (72%) had hemorrhage histories (Table 3). Among these patients, one had a hemorrhage before and after the first treatment and one had a hemorrhage after the first procedure with no previous bleeding history. The Spetzler-Martin grades were grade I/II in 5 (20%) and grade III/IV/V in 20 (80%). The median AVM score was 1.17 (range, 0.320–2.20). The AVMs requiring repeat GKRS were located in cerebral lobar (n = 13; 52%), thalamus/basal ganglia/brainstem (n = 10; 40%), and cerebellar regions (n = 2; 8%); 17 (68%) were present in eloquent areas. The median AVM volume was 0.77 mL (range, 0.048–9.2).
AVM characteristics and factors associated with obliteration after repeat GKRS
Outcomes of the First GKRS
Of the 150 patients, 104 achieved complete obliteration (69.3%) after the first GKRS. Of these, 64 were confirmed by catheter DSA. The overall obliteration rates 4, 5, 7, and 10 years after the first GKRS were 49.7%, 65.8%, 80.1%, and 97.0% (Online Supplemental Data). Univariate analysis demonstrated that complete obliteration was associated with Spetzler-Martin grade (P <.001), deep drainage (P = .04), lesions within eloquent areas of adjacent brain cortex (P = .02), AVM volume (P = .007), and prescribed margin dose (P <.001) (Table 2). Location was also significantly related to AVM obliteration (P = .016) because a Bonferroni correction found P < .017 to be statistically significant.
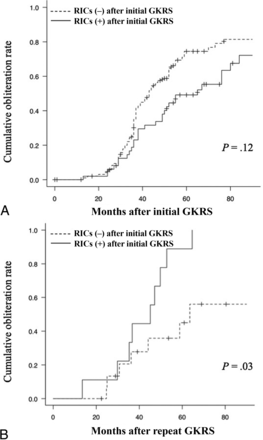
After the first GKRS, RICs occurred in 50 patients (33.3%). Table 4 shows the relationship between RIC and AVM obliteration. Of the 104 patients who achieved AVM obliteration after the first GKRS, 34 (32.7%) developed RICs. Of the 46 with incomplete obliteration, 16 (34.8%) developed RICs. Thus, RIC development after the first GKRS appeared not to be related to AVM obliteration (OR = 0.91; 95% CI, 0.44–1.89; P = .85). Kaplan-Meier analysis also revealed that RICs were not significantly related to obliteration after the first GKRS (P = .12) (Fig 1A). In 50 patients with incomplete obliteration after the first treatment, 25 patients with 25 AVMs underwent repeat GKRS.
A, Kaplan-Meier curve for the obliteration of AVMs after the first GKRS. Cumulative complete obliteration of AVMs after the first GKRS with or without the development of RICs. RIC development was not significantly associated with AVM obliteration (P = .12). The dotted line represents AVMs without RICs (−), and the solid line, those with RICs (+). B, Cumulative obliteration of AVMs after repeat GKRS with or without the development of RICs after the first GKRS. The development of RICs was significantly associated with AVM obliteration (P = .03).
The relationship between the development of RICs and AVM obliteration after each GKRS
Outcome and Obliteration Predictors of Repeat GKRS
After repeat GKRS, 16 (64%) of the 25 patients with 25 AVMs achieved complete obliteration. Among these 16 patients, 3 were confirmed by DSA and 13 were diagnosed on the basis of MR imaging/MRA. The median interval between the first and repeat GKRS was 58 months (range, 36–94 months), and the median follow-up after repeat radiosurgery was 79 months (range, 22–209 months) (Table 1). Of the 18 (72%) patients with ruptured AVMs at the repeat GKRS, 1 had hemorrhaged after the first GKRS with no bleeding history before the first procedure. Overall obliteration 4, 5, and 7 years after repeat GKRS was achieved in 50.5%, 65.4%, and 76.9% (Online Supplemental Data). There was no significant difference in the latency period before obliteration between the first and repeat GKRS procedures (P = .77).
Among 16 patients without RIC histories after the first GKRS, 7 (43.8%) achieved complete obliteration after the repeat procedure. On the other hand, 9 patients who underwent repeat GKRS had histories of RIC after the first treatment; all these patients achieved complete obliteration (OR = 24.0; 95% CI, 1.2–489; P = .007) (Table 4). Five patients showed RICs after repeat GKRS. Three of these 5 patients achieved complete obliteration. RIC development after repeat GKRS had no significant relationship with obliteration (P = 1.0).
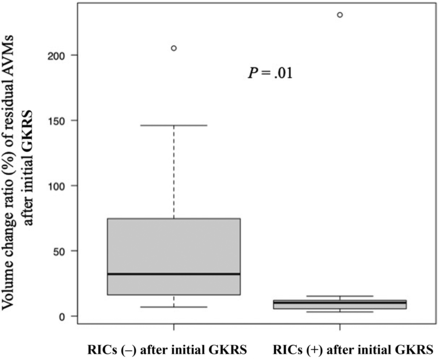
Kaplan-Meier analysis found that patients with AVMs who developed RICs after the first GKRS had a significantly higher obliteration rate after a repeat procedure (P = .03) (Fig 1B). After repeat GKRS, the complete obliteration rates at 4, 5, and 7 years were 36.8%, 45.8%, and 56.7% for patients without RICs after the first GKRS and 66.7%, 88.9%, and 100% for those with RICs after the first GKRS. Factors associated with AVM obliteration after the first treatment (ie, Spetzler-Martin grade, deep drainage, location, eloquent cortex of the adjacent brain, AVM volume, and margin dose) were not significantly related to obliteration after repeat GKRS (Table 3). Among patients with repeat GKRS, the median AVM volume change rate after the first treatment was 21.1% (range, 3.18%–231%) (Fig 2). The median AVM volume change rates were 32.2% (range, 6.9%–205%) for patients without RICs (n = 16) and 10.2% (range, 3.18%–231%) for those with RICs (n = 9) (P = .01) (Fig 2).
Radiation-induced changes and the volume change ratio of residual AVMs after the first GKRS. The association between RIC development and AVM volume reduction after the first GKRS. Among patients who underwent repeat GKRS, the median rate of AVM volume change after the first treatment was 32.2% (range, 6.9%–205%) for patients without RICs (−) and 10.2% (range, 3.18%–231%) for those with RICs (+), respectively (P = .01).
Postradiosurgery Complications
After the first GKRS, 48 RICs (32%) were noted (Table 5). Among these, 8 patients presented with neurologic deficits (including 6 with transient and 2 with permanent symptoms). The transient neurologic deficits after the first GKRS included seizures (n = 2), upper-extremity weakness (n = 2), sensory dysfunction (n = 1), scintillating scotoma (n = 1), and visual field deficits (n = 2). Permanent symptoms after the first GKRS included impaired consciousness due to deep drainage congestion (n = 1) and visual field deficits (n = 1).
The development of RICs and cyst formation after each GKRS in patients with AVMs of the brain
After repeat GKRS, 5 (20%) patients developed RICs, including one (4%) with symptomatic RICs, which led to transient scintillating scotoma. Most important, no patients developed permanent symptoms after repeat GKRS. One patient developed RICs after both the first and repeat GKRS procedures; however, both were asymptomatic. Delayed cyst formation occurred in 2 patients (1.3%) after the first GKRS; both were symptomatic. No cysts were observed after repeat GKRS. The incidences of radiologic RIC, symptomatic RIC, and cysts did not significantly differ between the first and repeat GKRS procedures (P = .35, 1.0, and 0.56, respectively).
RICs and Postradiosurgery Hemorrhages
Among patients with initial GKRS (n = 150), 1 hemorrhage event was documented between AVM diagnosis and initial GKRS (median follow-up, 1.5 months; range, 0.03–261 months); thus, the annual hemorrhage risk before initial GKRS was 0.71%/year.
During the latency interval after the first GKRS and before obliteration or additional treatment, 19 hemorrhages occurred in 15 (10%) patients (median follow-up, 43 months; range, 1–114 months). Only 2 patients died due to hemorrhage. The overall annual preobliteration hemorrhage risk was 2.5%/year for all AVMs after the initial GKRS. Among the 15 patients who experienced hemorrhage after the initial treatment, RICs developed in 6 patients (20%). In patients with RICs, Kaplan-Meier analysis identified the cumulative hemorrhage rates as 4.1% at 1 year, 10.2% at 4 years, and 12.7% at 10 years after the first GKRS, compared with 4.0%, 7.0%, and 8.3%, respectively, in patients without RIC (Online Supplemental Data). The RIC incidence after the first GKRS was not related to the postradiosurgery cumulative hemorrhage rate (P = .44).
Among the 25 patients with repeat radiosurgery, 2 events in 2 patients (8.0%) were documented after repeat GKRS. They also experienced hemorrhage during the latency period between the initial and repeat treatment (median follow-up, 45 months; range, 14–165 months). After the repeat GKRS, the annual hemorrhage risk before obliteration was 1.8%/year. The median follow-up duration after AVM obliteration diagnosis was 61.7 months (range, 0.0–178 months) for the patients with initial GKRS and 41.5 months (range, 0.0–159 months) for those with repeat treatment. After initial or repeat GKRS, no hemorrhage occurred after AVM obliteration diagnosis.
DISCUSSION
Radiation-Induced Changes and AVM Obliteration
RIC development after the first GKRS was significantly correlated with complete obliteration after repeat radiosurgery. Of the 9 patients with RICs after the first GKRS who underwent repeat GKRS, all achieved complete obliteration; in contrast, 43.8% (7/16 patients) of those without RICs after the first GKRS achieved complete obliteration (P = .007). Kaplan-Meier analysis also revealed that RIC development after the first GKRS was associated with a significantly higher rate of obliteration after repeat GKRS (P = .03).
Kano et al10 retrospectively reviewed 105 patients who underwent repeat GKRS for incompletely obliterated AVMs and found that greater volume reduction after the first procedure was significantly associated with complete obliteration after the repeat procedure (P = .035). We also found that RIC development was significantly associated with a higher volume reduction of the AVM nidus after the first GKRS. This led to complete obliteration after repeating the procedure. We speculate that RICs might represent radiologic reactivity in AVMs.
RICs could be epiphenomena of ongoing AVM obliteration.12,13 Yen et al12 reported that 62.8% of AVM cases that developed RICs achieved total obliteration versus 52.1% of those without RICs (P < .001). They also found that AVMs with extensive RICs were more likely to achieve total obliteration than those with mild RICs. We found RICs to be associated with a higher volume reduction of the AVM nidus after failed obliteration after the first radiosurgery (P = .01) (Fig 2). RICs appear to indicate AVM obliteration progress after GKRS.
The mechanisms underlying post-GKRS RICs are incompletely understood but could be related to perinidal edema resulting from tissue injury or venous congestion.4,14 Direct tissue damage, especially to endothelial or glial cells, may damage the blood-brain barrier, cause excessive production of free radicals, and induce inflammation.4,14 Venous congestion–induced imaging changes result from obstruction of venous outflow due to AVM obliteration.15
Complications of Repeat GKRS
Our results indicated that repeat GKRS did not increase the risk of symptomatic complications compared with the first procedure. The development of RICs was 32% after the first GKRS and 20% after repeat GKRS (P = .35). After repeat GKRS, 1/25 (4%) patients demonstrated symptomatic RICs with transient neurologic deficits. In contrast, 8/150 patients (5.3%) demonstrated symptomatic RICs after the first procedure. The incidence of symptomatic RICs was not higher after repeat GKRS (P = 1.0). One patient (4%) developed RICs after both the first and repeat GKRS procedures; however, in both instances the changes were asymptomatic. Delayed cyst formation occurred in 2 patients (1.3%) after the first GKRS and was not observed after the repeat procedure. Hence, repeat GKRS did not increase the risk of delayed cyst formation (P = .56) (Table 5).
In previous research, 30%–40% of AVMs developed RICs after the first GKRS; however, only 2.5%–10.8% developed symptomatic RICs, with a minimal number having permanent deficits.12,14,16 After repeat treatment for residual AVMs, Karlsson et al17 reported an overall complication rate of up to 14%, higher than that observed after the first treatment. However, many patients in their study underwent treatment in the 1970s and early 1980s, when technologies such as stereotactic 3D imaging for brain AVMs and refined dosimetric protocols were not yet available.15,18 Studies that reviewed patients who underwent repeat radiosurgery procedures during the late 1980s to 2000s found rates of symptomatic RICs ranging from 3.6% to 9.5% after repeat treatment.7,19 Therefore, we do not expect repeat GKRS to increase the risk of complications compared with the first GKRS.
Repeat Radiosurgery for Residual AVMs
The high obliteration rate on retreatment and the relatively low risk of complications indicated that repeat GKRS for residual AVMs is a safe and beneficial treatment option. Several studies have found no difference in the AVM hemorrhage risk pre-to-post-GKRS (incompletely obliterated).20 Additional treatments are recommended to eliminate residual AVMs after the first procedure.7,20
Large-scale studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of repeat GKRS for residual AVMs, with total obliteration rates ranging from 55% to 62%,7,18,19 concordant with our finding of 64%. These authors concluded that patients who had a residual nidus after the first treatment nonetheless demonstrated a substantial therapeutic effect (volume reduction) and were encouraged to undergo repeat GKRS.
Limitations
This study was limited by our relatively small patient cohort; subsequent, well-powered studies are needed. Additionally, this study was retrospective, and the external validity may be limited by patient selection bias in our treatment algorithms. Throughout our 15-year experience, our understanding of dose-volume relationships, conformality, treatment plan selectivity, and reliance on both angiographic and 3D MR imaging data have gradually changed. Patients treated in the latter years of this study likely benefited from our greater knowledge and improved technique. The incidence of GKRS-related complications and hemorrhage may be slightly inaccurate because we excluded patients who had volume-staged GKRS (n = 4) and those with a follow-up period of <1 year (n = 9) and incomplete clinical data (n = 7). Furthermore, careful longitudinal clinical follow-up studies are needed to continue monitoring long-term complications after GKRS.
CONCLUSIONS
RICs after the first GKRS are a favorable indicator of AVM obliteration after repeat GKRS. Although RICs occurred in 25%–33% of patients, most did not result in neurologic deficits and permanent sequelae were uncommon. Moreover, the risk of symptomatic RICs after repeat GKRS is comparable with that following the first procedure. When the first GKRS fails to achieve complete obliteration and results in RICs, a favorable outcome can occur by repeating the procedure.
Footnotes
Disclosure forms provided by the authors are available with the full text and PDF of this article at www.ajnr.org.
References
- Received August 26, 2022.
- Accepted after revision December 30, 2022.
- © 2023 by American Journal of Neuroradiology